 Wall Street is increasingly pessimistic about Comcast and Time Warner Cable pulling off their merger deal as regulators stop the clock to take a closer look at the transaction.
Wall Street is increasingly pessimistic about Comcast and Time Warner Cable pulling off their merger deal as regulators stop the clock to take a closer look at the transaction.
The Capitol Forum, an in-depth news and analysis service dedicated to informing policymakers, investors, and industry stakeholders on how policy affects market competition, specializes in examining marketplace mergers and their potential impact on American consumers and the general economy. The group has shared a copy of their assessment — “Comcast/Time Warner Cable: A Closer Look at FCC, DOJ Decision Processes; Merits and Politics May Drive Merger Challenge, Especially as Wheeler Unlikely to Embrace Title II Regulation for Net Neutrality” — with Stop the Cap! and we’re sharing a summary of the report with our readers.
The two most important government agencies reviewing the merger proposal are the Federal Communications Commission and the Department of Justice. The FCC is responsible for overseeing telecommunications in the United States and is also tasked with reviewing telecom industry mergers to verify if they are in the public interest. The Department of Justice becomes involved in big mergers as well, concerned with compliance with antitrust and other laws.
In many instances, the two agencies work separately and independently to review merger proposals, but not so with Comcast and Time Warner Cable.
Sources tell Capitol Forum there is a high level of coordination and information sharing between DOJ and the FCC, potentially positioning the two agencies in a stronger legal position if they jointly challenge the merger. Readers may recall AT&T’s attempt to buy T-Mobile was thwarted in 2011 when the FCC followed the DOJ’s lead in jointly challenging the merger on competition and antitrust grounds. With a united front against the deal in Washington, AT&T quickly capitulated.
 Despite a blizzard of Comcast talking points claiming the cable industry is fiercely competitive, Capitol Forum’s report indicates the DOJ staff level believes the cable industry suffers dearly from a lack of competition already, and allowing further marketplace concentration would exacerbate an already difficult problem.
Despite a blizzard of Comcast talking points claiming the cable industry is fiercely competitive, Capitol Forum’s report indicates the DOJ staff level believes the cable industry suffers dearly from a lack of competition already, and allowing further marketplace concentration would exacerbate an already difficult problem.
Capitol Forum reports the DOJ’s staff is inclined to “take an aggressive posture with regards to [antitrust] enforcement.”
The DOJ would certainly not be walking the beltway plank to its political doom if it ultimately decides to oppose the merger.
Few on Capitol Hill are likely to fiercely advocate for a cable company generally despised by their constituents. The Capitol Forum report notes that Comcast faces powerful opposition and its political support is overstated. Comcast’s lobbying efforts and ties to President Obama and several high level Democrats have also been widely exposed in the media, which makes it more difficult for D.C.’s powerful to be seen carrying Comcast’s water.
In fact, the report indicates a regulatory challenge against Comcast and Time Warner Cable would face considerably less political opposition than what the FCC faces if it reclassifies broadband as a “telecommunications service,” protecting Net Neutrality and exposing the industry to stronger regulatory oversight.
The report suggests FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler, who seems intent on opposing reclassification of broadband under Title II, may appease his critics by taking a stronger stance on the Comcast/Time Warner deal instead.
Wheeler has already expressed concern about the state of competitiveness of American broadband. He considers providers capable of delivering at least 25Mbps part of broadband’s key market, which in many communities means a monopoly for the local cable operator.
Understanding “The Public Interest” and the Implications of a Combined Comcast/Time Warner Cable on Competition
 The FCC will review the transaction pursuant to Sections 214 and 310(d) of the Communications Act of 1934, in order to ensure that “public interest, convenience, and necessity will be served thereby.”
The FCC will review the transaction pursuant to Sections 214 and 310(d) of the Communications Act of 1934, in order to ensure that “public interest, convenience, and necessity will be served thereby.”
The merger proposal must also demonstrate it does not violate antitrust laws.
It is here that merger opponents have a wealth of arguments to use against Comcast and Time Warner Cable.
Despite Comcast’s insistence the deal would have no competitive implications, the Capitol Forum reports the merger’s potential anticompetitive effects are “widely recognized and evidence from the investigation could provide DOJ and FCC with a solid foundation to challenge the merger.”
Although the two cable companies don’t directly compete with each other (itself a warning sign of an already noncompetitive marketplace), the report finds “a wide array of anti-competitive effects and several antitrust theories” that would implicate the cable company in a Clayton Act violation.
Comcast is betting heavily on its surface argument that by the very fact customers will not see any change in the number of competitors delivering service to their area, the merger should easily clear any antitrust hurdles. That argument makes it more difficult for the DOJ to fall back on the usual market concentration precedents that would prevent such a colossal merger deal. To argue excessive horizontal integration — the enlarging of Comcast’s territory — the DOJ would first have to prove Comcast’s size in comparison with other cable companies is a reason for the courts to shoot down the deal. Or it could bypass Comcast’s favorite argument and move to the issue of vertical integration — one company’s ability to control not just the pipes that deliver content, but also the content itself.
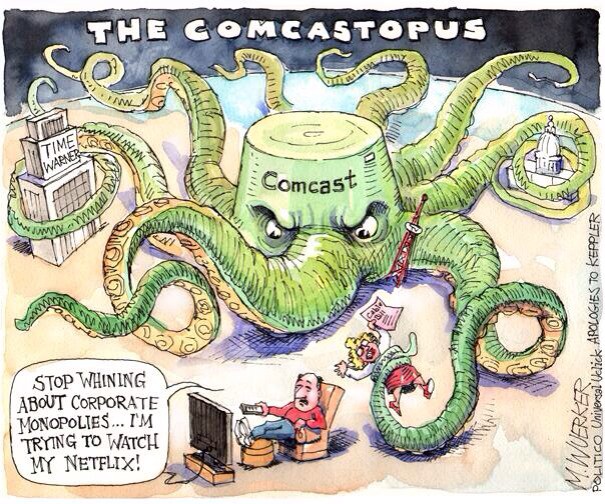 Here the examples of potential abuse are plentiful:
Here the examples of potential abuse are plentiful:
- Comcast would enjoy increased power to force cable programmers to favor Comcast in cable programming pricing and policies while allowing it to demand restrictions on competitive online video competitors or restrict access to popular cable programming;
- Comcast could impose data caps and usage-based pricing to deter online viewing while exempting its own content by delivering it over a Wi-Fi enabled gateway, game console or set top box, claiming all are unrelated to Comcast’s broadband Internet service or network;
- Force consumers to use Comcast set top boxes that would not support competing providers’ online video;
- Use interconnection agreements as a clever way to bypass the paid prioritization Net Neutrality debate. Netflix and other content producers would be forced to compensate Comcast for reliable access to its broadband customers;
- Noting AT&T has declared U-verse can not effectively succeed in the cable television business without combining its customer base with DirecTV to qualify for better volume discounts, there is clear evidence that a super-sized Comcast could command discounts new entrants like Google Fiber could never hope to get, putting them at a distinct price disadvantage.
The FCC’s scrutiny of Comcast’s merger deal has already uncovered evidence previously unavailable because of non-disclosure agreements which show Comcast’s heavy hand already at work.
The report notes Michael Mooney, a senior vice president and group general counsel at Level 3, told the Capitol Forum the dispute earlier this year between Netflix and Comcast could have been resolved in about five minutes had Comcast added a port to relieve congestion at an interconnection point. The cost? Just $5,000. Had Comcast been willing to spend the money, millions of Comcast customers would have never experienced problems using Netflix.
Whether Comcast is ultimately deemed too large to permit another consolidating merger or whether it is given conditional approval to absorb Time Warner Cable remains a close call, according to the Capitol Forum, despite the fact consumers have urged regulators for something slightly more concrete – a single sentence, total denial of its application.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Capitol Forum The Consumer Welfare Test.mp4[/flv]
The Capitol Forum broadly explores how the “consumer welfare standard” has become a part of the antitrust review process over the last 30 years. Sometimes, a strict antitrust test is not sufficient to protect “the public interest” of consumers, and allows the dominant player(s) to harm competition. In the digital economy, corporate mergers that empower companies to restrict innovation can prove far more damaging than classic monopoly abuse. (15:52)
 T-Mobile has asked the Federal Communications Commission to investigate AT&T’s “artificially high roaming rates” charged when its customers travel outside of T-Mobile’s home service area.
T-Mobile has asked the Federal Communications Commission to investigate AT&T’s “artificially high roaming rates” charged when its customers travel outside of T-Mobile’s home service area. Because of AT&T’s artificially high roaming rates, T-Mobile wireless customers roaming in South Africa have a better user experience than customers roaming on AT&T’s network in South Dakota, argues T-Mobile. Their speed is twice as fast, and their data usage is unlimited.
Because of AT&T’s artificially high roaming rates, T-Mobile wireless customers roaming in South Africa have a better user experience than customers roaming on AT&T’s network in South Dakota, argues T-Mobile. Their speed is twice as fast, and their data usage is unlimited.

 Subscribe
Subscribe New Zealanders want faster broadband and they want it without a usage cap, and Snap is ready to offer both.
New Zealanders want faster broadband and they want it without a usage cap, and Snap is ready to offer both. Snap’s new service comes as a result of New Zealand’s deployment of fiber networks and an end to usage caps, consumption billing, and/or bandwidth throttling. Snap has been well received in New Zealand because it guarantees no traffic shaping, traffic management schemes, or mandatory usage caps. This comes at a time when North American providers are trying to force customers into usage-capped broadband plans and wireless carriers insist on using traffic shaping and caps.
Snap’s new service comes as a result of New Zealand’s deployment of fiber networks and an end to usage caps, consumption billing, and/or bandwidth throttling. Snap has been well received in New Zealand because it guarantees no traffic shaping, traffic management schemes, or mandatory usage caps. This comes at a time when North American providers are trying to force customers into usage-capped broadband plans and wireless carriers insist on using traffic shaping and caps.


 Comcast: 88% of customers met or exceeded state and federal standards;
Comcast: 88% of customers met or exceeded state and federal standards; Wall Street is increasingly pessimistic about Comcast and Time Warner Cable pulling off their merger deal as regulators stop the clock to take a closer look at the transaction.
Wall Street is increasingly pessimistic about Comcast and Time Warner Cable pulling off their merger deal as regulators stop the clock to take a closer look at the transaction. Despite a blizzard of Comcast talking points claiming the cable industry is fiercely competitive, Capitol Forum’s report indicates the DOJ staff level believes the cable industry suffers dearly from a lack of competition already, and allowing further marketplace concentration would exacerbate an already difficult problem.
Despite a blizzard of Comcast talking points claiming the cable industry is fiercely competitive, Capitol Forum’s report indicates the DOJ staff level believes the cable industry suffers dearly from a lack of competition already, and allowing further marketplace concentration would exacerbate an already difficult problem. The FCC will review the transaction pursuant to Sections 214 and 310(d) of the Communications Act of 1934, in order to ensure that “public interest, convenience, and necessity will be served thereby.”
The FCC will review the transaction pursuant to Sections 214 and 310(d) of the Communications Act of 1934, in order to ensure that “public interest, convenience, and necessity will be served thereby.” Here the examples of potential abuse are plentiful:
Here the examples of potential abuse are plentiful: