 For the benefit of new visitors, text items in bold are clickable links. A complete video from this event will be posted as soon as possible.
For the benefit of new visitors, text items in bold are clickable links. A complete video from this event will be posted as soon as possible.
Good evening. My name is Phillip Dampier from Stop the Cap!, a Rochester-based all-volunteer consumer group fighting for better broadband service and against Internet usage caps.
This is a critical moment for New York. The Internet has become a necessity for most of us and the future is largely in the hands of one company capable of delivering 21st century broadband to the majority of upstate New York. That company isn’t Verizon, which has ended FiOS fiber expansion while abandoning most of its upstate customers with slow speed DSL. Indeed, as their market share will attest, our broadband future is held in the hands of Time Warner Cable.
Comcast could have become a big player in New York had it chosen to compete head to head with Time Warner. But large cable operators avoid that kind of competition, preferring comfortable fiefdoms that only change hands at the whim of the companies involved. As local officials from across New York have already discovered, no major cable operator will compete for an expiring franchise currently held by another major cable operator.
Ironically, Comcast is using that fact in its favor, noting that since neither company competes directly with the other, making Comcast larger has no impact on competition. But that should hardly be the only test.
At issue is whether this merger is in the public interest. This year, for the first time in a long time, the rules have changed in New York. In the past, the Commission had to prove the merger was not in the best interests of New Yorkers. Now the onus is on Comcast to prove it is. It has fallen far short of meeting that burden.
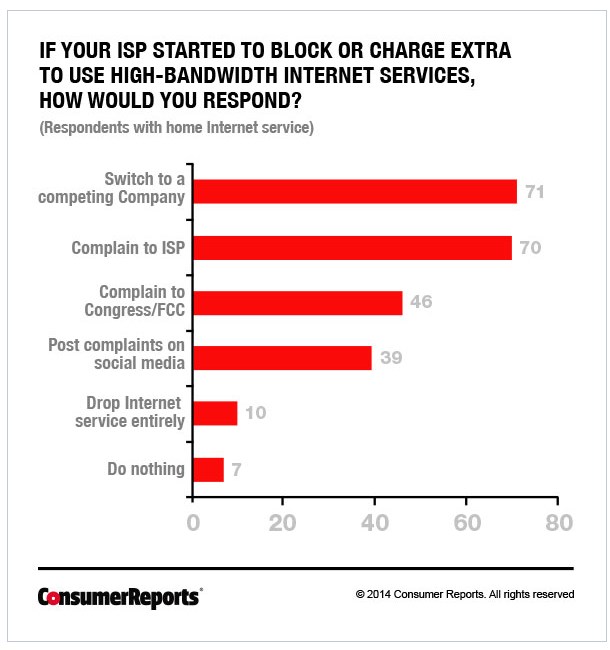
Let’s start with Comcast’s dysfunctional relationship with its customers. With more than 75 citizen comments filed with the Commission so far. Comcast’s reputation clearly precedes it. The consensus view is perhaps best represented by one exasperated Clinton-area resident who wrote, I quote, “No. No no no. HELL no.”
 That kind of reaction is unsurprising considering Consumer Reports ranked Comcast 15th out of 17 large cable companies and called their Internet service and customer relations mediocre. Every year since 2007, Comcast’s CEO acknowledges the problems with customer service and promises to do better. Seven years later, the American Customer Satisfaction Index reports absolutely no measurable improvement. In fact, ACSI has concluded Comcast had the worst customer satisfaction rating of any company or government agency in the country, including the IRS.
That kind of reaction is unsurprising considering Consumer Reports ranked Comcast 15th out of 17 large cable companies and called their Internet service and customer relations mediocre. Every year since 2007, Comcast’s CEO acknowledges the problems with customer service and promises to do better. Seven years later, the American Customer Satisfaction Index reports absolutely no measurable improvement. In fact, ACSI has concluded Comcast had the worst customer satisfaction rating of any company or government agency in the country, including the IRS.
In order to sell this $45 billion boondoggle to a skeptical public, Comcast has hired 76 lobbyists from 24 different firms and will reportedly spend millions trying to convince regulators and our elected leaders this deal is good for New York. If the deal gets done, Comcast’s biggest spending spree won’t be on behalf of its customers. Instead, Comcast has announced a $17 billion share buyback to benefit their shareholders. Imagine if this money was instead spent on improving customer service and selling a better product at a lower price.
 The only suitable response to this merger deal is its outright rejection. Some may recommend imposing a handful of temporary conditions in return for approval – like the kind Sen. Al Franken accused Comcast of reneging on after its earlier merger with NBCUniversal. But this is one of those cases where you just can’t fit a round peg into a square deal for consumers, no matter how hard you try.
The only suitable response to this merger deal is its outright rejection. Some may recommend imposing a handful of temporary conditions in return for approval – like the kind Sen. Al Franken accused Comcast of reneging on after its earlier merger with NBCUniversal. But this is one of those cases where you just can’t fit a round peg into a square deal for consumers, no matter how hard you try.
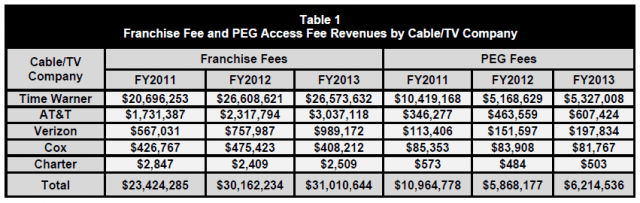
With respect to television, volume discounts have a huge impact on cable programming costs and competition. The biggest players get the best discounts, smaller ones are stunned by programming rate hikes and new competitors think twice about getting into the business.
AT&T said last week its 5.7 million customer U-verse television service was too small to get the kind of discounts its cable and satellite competitors receive. AT&T’s solution is to buy DirecTV, which might be good for AT&T but is bad for competition.
Frontier Communications has also felt the volume discount sting after adopting several Verizon FiOS franchises. When it lost Verizon’s volume discounts, Frontier began a relentless marketing effort to convince its customers to abandon FiOS TV and switch to technically inferior satellite TV.
Combining Comcast and Time Warner Cable will indeed help Comcast secure better deals from major programmers (including Comcast itself). But Comcast is already on record warning those savings won’t be shared with customers.
Comcast’s executive vice president David Cohen summed it up best: “We are certainly not promising that customer bills will go down or increase less rapidly.”
Is that in the public interest?
 Comcast suggests this merger will make its cable television market share no larger than it had in 2002 when it bought the assets of AT&T Cable. But this is 2014 and cable television is increasingly no longer the industry’s biggest breadwinner. Broadband is, and post-merger Comcast will control 40-50 percent of the Internet access market nationwide.
Comcast suggests this merger will make its cable television market share no larger than it had in 2002 when it bought the assets of AT&T Cable. But this is 2014 and cable television is increasingly no longer the industry’s biggest breadwinner. Broadband is, and post-merger Comcast will control 40-50 percent of the Internet access market nationwide.
So what do Time Warner Cable customers get if Comcast takes over? A higher bill and worse service.
Several months before Comcast sought this merger, Time Warner announced a series of major upgrades under an initiative called TWC Maxx. Over the next two years, Time Warner Cable plans to more than triple the Internet speeds customers get now at no additional charge. Those upgrades are already available in parts of New York City, Los Angeles, and Austin.
A Time Warner Cable customer in Queens used to pay $57.99 for 15 megabit broadband. As of last month, for the same price, they get 50 megabits.
In contrast, Comcast’s Internet Plus plan delivers just 25 megabits and costs $69.95 a month – nearly $12 more for half the speed. Who has the better broadband at a better price? Time Warner Cable.
New York State’s digital economy depends on Internet innovation, which means some customers need faster speeds than others. Time Warner Cable’s Maxx initiative already delivers far superior speeds than what Comcast offers, despite claims from Comcast this merger would deliver New York a broadband upgrade.
 Time Warner’s new top of the line Internet service, Ultimate 300 (formerly Ultimate 50), delivers 300 megabit service for $74.99 a month. Comcast’s top cable broadband offer listed on their website is Extreme 105, offering 105 megabit speeds at prices ranging from $99.95 to $114.95.
Time Warner’s new top of the line Internet service, Ultimate 300 (formerly Ultimate 50), delivers 300 megabit service for $74.99 a month. Comcast’s top cable broadband offer listed on their website is Extreme 105, offering 105 megabit speeds at prices ranging from $99.95 to $114.95.
Is the public interest better served with 300 megabits for $74.99 from Time Warner Cable or paying almost $40 more for one-third of that speed from Comcast? Again, Time Warner Cable has the better deal for customers.
But the charges keep coming.
At least 90 percent of cable customers lease their cable modem from the cable company, and Comcast charges one of the highest lease rates in the industry – $8 a month. Time Warner Cable charges just under $6.
So I ask again, is this merger really in the public interest when broadband customers will be expected to pay more for less service?
Then there is the issue of usage caps, a creative way to put a toll on innovation. Usage caps make high bandwidth applications of the future untenable while also protecting cable television revenue.
If the PSC approves this transaction, the vast majority of New York will live under Comcast’s returning usage cap regime. There is simply no justification for usage limits on residential broadband service, particularly from a company as profitable as Comcast. Verizon FiOS does not have caps. Neither does Cablevision. But the majority of upstate New Yorkers won’t have the option of choosing either.
In 2009, Time Warner Cable lived through a two week public relations nightmare when they attempted an experiment with compulsory usage caps on customers in Rochester. After Stop the Cap! pushed back, then CEO Glenn Britt shelved the idea. Britt would later emphasize he now believed Time Warner should always have an unlimited use tier available for customers who want it.
Whether intended or not, Time Warner actually proved that was the right idea. In early 2012, the company introduced optional usage caps in return for discounts. They quickly discovered customers have no interest in having their Internet usage measured and limited, even for a discount. Out of 11 million Time Warner Cable broadband customers, only a few thousand have been convinced to enroll.
 Comcast doesn’t give customers a choice. In 2008, a strict 250GB usage cap was imposed on all residential customers with disconnect threats for violators. Since announcing it would re-evaluate that cap in May 2012, it now appears Comcast has settled on a new residential 300GB usage allowance gradually being reintroduced in Comcast service areas starting in southern U.S. markets.
Comcast doesn’t give customers a choice. In 2008, a strict 250GB usage cap was imposed on all residential customers with disconnect threats for violators. Since announcing it would re-evaluate that cap in May 2012, it now appears Comcast has settled on a new residential 300GB usage allowance gradually being reintroduced in Comcast service areas starting in southern U.S. markets.
Comcast executive vice president David Cohen cutely calls them “usage thresholds.” At Stop the Cap! we call it Internet Overcharging.
Cohen predicts Comcast will have broadband usage thresholds imposed on every city they serve within five years. Whether you call it a cap or a threshold, it is in fact a limit on how much Internet service you can consume without risking overlimit fees of $10 for each 50GB increment over your allowance.
Unlike Time Warner Cable, Comcast isn’t offering a discount with its usage cap, so those who use less will still pay the same they always have, proving again that usage caps don’t save customers money. (See below for clarification)
At the end of May I watched CNBC interview Comcast CEO Brian Roberts who implied during a discussion about Comcast’s usage caps that usage growth was impinging on the viability of its broadband business. Moments later, Time Warner Cable ran an ad emphasizing its broadband service has no usage caps. Both companies are making plenty of money from broadband.
This merger is bad news for customers faced with Comcast’s legendary bad service, its forthcoming usage caps, or the higher prices it charges. Even promised innovations like their much touted X1 set top platform comes with a gotcha Comcast routinely forgets to mention. Customers have to pay a $99 installation fee.
Stop the Cap! will submit a more comprehensive filing with the PSC outlining all of our objections to this merger, and there are several more. We invite anyone in the audience to visit stopthecap.com for this and other matters related to cable television and broadband. We appreciate being invited to share our views with the Commission and hope to bring a consumer perspective to this important development in our shared telecommunications future. I’d be happy to answer any questions you might have.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/TWC News Hearing on Comcast 6-16-14.mp4[/flv]
Time Warner Cable News covered the Public Service Commission hearing in Buffalo, which included testimony from Stop the Cap!’s Phillip Dampier. Also appearing was a representative from the National Black Chamber of Commerce advocating that telecom companies merge as fast as possible. The Chamber has received significant support from Comcast for several years now and representatives routinely testify in favor of Comcast’s business initiatives. (2:30)
Clarification: Comcast has different trials in different cities:
Nashville, Tennessee: 300 GB per month with $10/50GB overlimit fee;
Tucson, Arizona: Economy Plus through Performance XFINITY Internet tiers: 300 GB. Blast! Internet tier: 350 GB; Extreme 50 customers: 450 GB; Extreme 105: 600 GB. $10/50GB overlimit fee;
Huntsville and Mobile, Alabama; Atlanta, Augusta and Savannah, Georgia; Central Kentucky; Maine; Jackson, Mississippi; Knoxville and Memphis, Tennessee and Charleston, South Carolina: 300 GB per month with $10/50GB; XFINITY Internet Economy Plus customers can choose to enroll in the Flexible-Data Option to receive a $5.00 credit on their monthly bill and reduce their data usage plan from 300 GB to 5 GB. If customers choose this option and use more than 5 GB of data in any given month, they will not receive the $5.00 credit and will be charged an additional $1.00 for each gigabyte of data used over the 5 GB included in the Flexible-Data Option;
Fresno, California, Economy Plus customers also have the option of enrolling in the Flexible-Data Option.
Comcast suggested customers can enroll in a cheaper usage plan in some of these markets. Yes they can, but only if they downgrade to Economy Plus service which offers speeds only up to 3Mbps. Their $5 discount is not available on any other plan.

 Powell and others made certain that Internet Service Providers would not be classified as “common carriers,” which would require them to rent their broadband pipes at a reasonable wholesale rate to competitors. The industry and their well-compensated friends in the House and Senate argued such a status would destroy investment in broadband expansion and innovation. Instead it destroyed the family budget as prices for mediocre service in uncompetitive markets soared. Today, consumers in common carrier countries including France and Britain pay a fraction of what Americans do for Internet access, and get faster speeds as well.
Powell and others made certain that Internet Service Providers would not be classified as “common carriers,” which would require them to rent their broadband pipes at a reasonable wholesale rate to competitors. The industry and their well-compensated friends in the House and Senate argued such a status would destroy investment in broadband expansion and innovation. Instead it destroyed the family budget as prices for mediocre service in uncompetitive markets soared. Today, consumers in common carrier countries including France and Britain pay a fraction of what Americans do for Internet access, and get faster speeds as well.

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 AT&T and Verizon sold the legislation to the public as a red-tape cutter to bring Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse to millions of Californians without unnecessary bureaucratic delay.
AT&T and Verizon sold the legislation to the public as a red-tape cutter to bring Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse to millions of Californians without unnecessary bureaucratic delay.


 Reed is theoretically trying to promote the Comcast merger with skeptical political and religious conservatives who have heard loud complaints from constituents about the cable company. But one of Reed’s self-proclaimed selling points is that he prefers to move in the shadows.
Reed is theoretically trying to promote the Comcast merger with skeptical political and religious conservatives who have heard loud complaints from constituents about the cable company. But one of Reed’s self-proclaimed selling points is that he prefers to move in the shadows.
 For the benefit of new visitors, text items in bold are clickable links. A complete video from this event will be posted as soon as possible.
For the benefit of new visitors, text items in bold are clickable links. A complete video from this event will be posted as soon as possible. That kind of reaction is unsurprising considering Consumer Reports
That kind of reaction is unsurprising considering Consumer Reports  The only suitable response to this merger deal is its outright rejection. Some may recommend imposing a handful of temporary conditions in return for approval – like the kind Sen. Al Franken accused Comcast of reneging on after its earlier merger with NBCUniversal. But this is one of those cases where you just can’t fit a round peg into a square deal for consumers, no matter how hard you try.
The only suitable response to this merger deal is its outright rejection. Some may recommend imposing a handful of temporary conditions in return for approval – like the kind Sen. Al Franken accused Comcast of reneging on after its earlier merger with NBCUniversal. But this is one of those cases where you just can’t fit a round peg into a square deal for consumers, no matter how hard you try. Comcast suggests this merger will make its cable television market share no larger than it had in 2002 when it bought the assets of AT&T Cable. But this is 2014 and cable television is increasingly no longer the industry’s biggest breadwinner. Broadband is, and post-merger
Comcast suggests this merger will make its cable television market share no larger than it had in 2002 when it bought the assets of AT&T Cable. But this is 2014 and cable television is increasingly no longer the industry’s biggest breadwinner. Broadband is, and post-merger  Time Warner’s new top of the line Internet service, Ultimate 300 (formerly Ultimate 50), delivers 300 megabit service for
Time Warner’s new top of the line Internet service, Ultimate 300 (formerly Ultimate 50), delivers 300 megabit service for  Comcast doesn’t give customers a choice. In 2008, a strict
Comcast doesn’t give customers a choice. In 2008, a strict 