 There are stark contrasts in internet subscription rates depending on where you live and how much money you make, according to newly released findings from the U.S. Census Bureau.
There are stark contrasts in internet subscription rates depending on where you live and how much money you make, according to newly released findings from the U.S. Census Bureau.
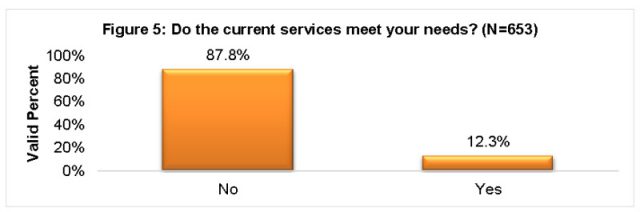
As the cost of internet access continues to rise, affordability is increasingly a problem for poor Americans. In rural areas, a lack of broadband availability is also holding down subscription rates.
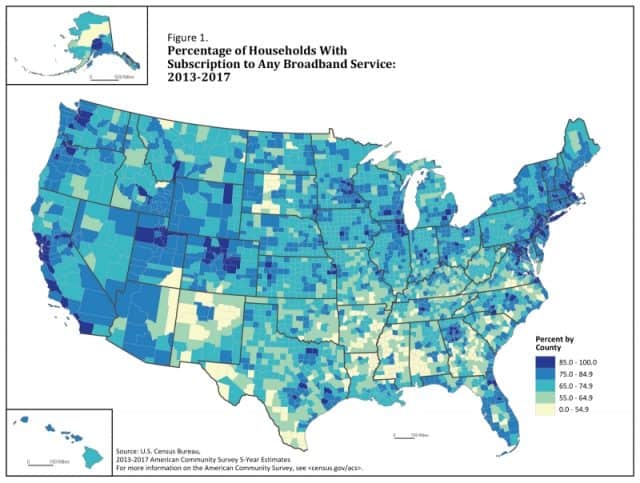
Telfair County, Ga. has the dubious distinction of being America’s worst connected county, with just 25% of households signed up for internet access. The most connected communities are found in suburban areas surrounding major cities along the Pacific Coast and northeastern U.S. More than 90% of households also have internet access in suburban areas outside of the District of Columbia, Atlanta, and Denver.
Urban Poor Americans Can’t Afford Increasingly Expensive Service Plans; Many Turn to Smartphones Instead
Although internet subscription rates are sky-high in wealthier suburban areas, poor inner city neighborhoods score poorly for internet subscriptions. In the Chicago metropolitan area, 77% of Cook County households subscribe to the internet. In downtown Los Angeles, just 80% are signed up. In D.C., only 78% subscribe.
 In Philadelphia, there were some neighborhoods with just 25% of residents getting internet service. In the Tioga-Nicetown neighborhood, only 37.1% of households had internet service. Persistent poverty, crime, unemployment, and low-income in poorer parts of the inner city have conspired to make it very difficult for residents to afford internet access at prices often over $50 a month.
In Philadelphia, there were some neighborhoods with just 25% of residents getting internet service. In the Tioga-Nicetown neighborhood, only 37.1% of households had internet service. Persistent poverty, crime, unemployment, and low-income in poorer parts of the inner city have conspired to make it very difficult for residents to afford internet access at prices often over $50 a month.
Increasingly, poor urban residents are turning to their smartphones as their sole source of internet. In the Philadelphia neighborhood of Fairhill, where internet subscriptions are below 38%, 12% of homes report smartphones are the only way they connect to the internet.
Pew Research Center senior researcher Monica Anderson told The Inquirer that 31 percent of Americans who earn less than $30,000 a year now rely only on smart phones for internet access, a percentage that has doubled since 2013.
“We are seeing smartphones help more people get online,” she told the newspaper, adding that data caps and data plan costs lead people to cancel or suspend services.
Rural and Native Americans Suffer Without Service, If They Can Afford It
 Some of the worst scoring counties where internet subscription rates were lower than average are located in rural areas across the upper Plains, the Southwest and South. The desert states of Arizona and New Mexico, south Texas, the lower Mississippi through Southern Alabama and some areas of the Piedmont of Georgia, the Carolinas and Southern Virginia were notable for containing many counties with low broadband internet subscription rates, although there were exceptions throughout.
Some of the worst scoring counties where internet subscription rates were lower than average are located in rural areas across the upper Plains, the Southwest and South. The desert states of Arizona and New Mexico, south Texas, the lower Mississippi through Southern Alabama and some areas of the Piedmont of Georgia, the Carolinas and Southern Virginia were notable for containing many counties with low broadband internet subscription rates, although there were exceptions throughout.
Only 67% of Native Americans have signed up for internet access, compared with 82 percent for non-Native Americans. Native Americans living on American Indian land had a subscription rate of 53 percent.
Thirteen percent of the counties achieving better than an 80% subscription rate were located in “mostly rural” or “completely rural” counties, often getting telecommunications services from a local co-op or municipal utility. Assuming a rural customer can buy internet access, the next impediment is often cost.
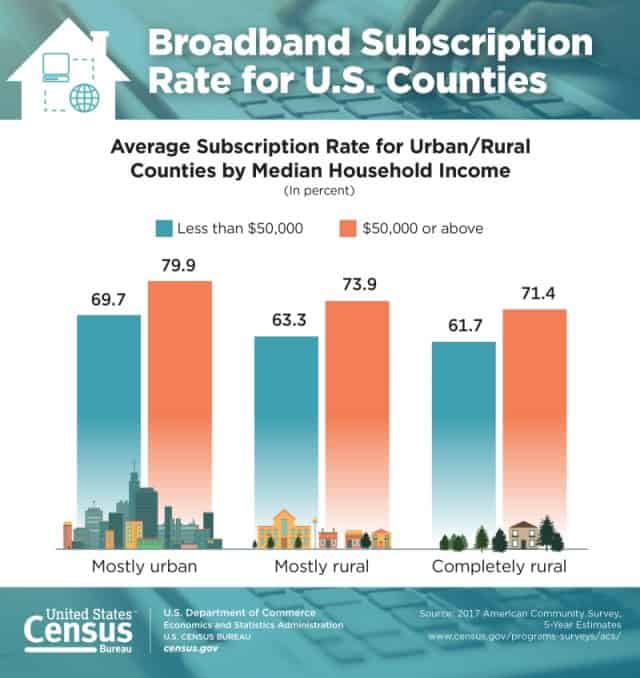
In “mostly urban” counties with median household incomes of $50,000 and over, the average broadband internet subscription rate was roughly 80 percent, while in “completely rural” counties with the similar median incomes, the average broadband internet subscription rate was only 71 percent.
“Mostly urban” counties with median household incomes below $50,000, however, only reported average broadband internet subscription rates of 70 percent while “completely rural” counties with similar median incomes had average broadband internet subscription rates of just 62 percent.
This contrast showed up most dramatically in the South. Of the 21 counties with populations of at least 10,000 and broadband internet subscription rates at or above 90 percent, 12 were in the South, four were in the Midwest, four in the West, and one in the Northeast. Conversely, of the 24 counties with broadband internet subscription rates at or below 45 percent and populations of at least 10,000, 21 were in the South, two were in the West, and one was in the Midwest.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Charter Communications’ ongoing settlement talks with the New York Public Service Commission are “productive” and will likely result in a final settlement agreement allowing Spectrum to continue operating in New York.
Charter Communications’ ongoing settlement talks with the New York Public Service Commission are “productive” and will likely result in a final settlement agreement allowing Spectrum to continue operating in New York.

 Verizon Wireless claims it is not intentionally slowing data services for its customers in North & South Carolina, despite growing complaints from customers about slow speeds.
Verizon Wireless claims it is not intentionally slowing data services for its customers in North & South Carolina, despite growing complaints from customers about slow speeds. “We lost power/cable and were using my Verizon unlimited data plan for internet access, and were very frustrated when attempting to access pages with dynamic content,” he wrote. “This is not typically a problem in central North Carolina, a high-coverage area. It seemed clear our data was being throttled.”
“We lost power/cable and were using my Verizon unlimited data plan for internet access, and were very frustrated when attempting to access pages with dynamic content,” he wrote. “This is not typically a problem in central North Carolina, a high-coverage area. It seemed clear our data was being throttled.” Verizon 5G Home will begin accepting new customer orders for its in-home wireless broadband replacement as of this Thursday, Sept. 13, with a scheduled service launch date of Oct. 1.
Verizon 5G Home will begin accepting new customer orders for its in-home wireless broadband replacement as of this Thursday, Sept. 13, with a scheduled service launch date of Oct. 1. Customers in the first four launch cities will be using equipment built around a draft standard of 5G, as the final release version is still forthcoming. Verizon is holding off on additional expansion of 5G services until the final 5G standard is released, and promises early adopters will receive upgraded technology when that happens.
Customers in the first four launch cities will be using equipment built around a draft standard of 5G, as the final release version is still forthcoming. Verizon is holding off on additional expansion of 5G services until the final 5G standard is released, and promises early adopters will receive upgraded technology when that happens.

 Under the current NBN fair use policy, monthly downloads per household are capped at 400 GB, with maximum usage during peak usage periods limited to 150 GB a month, which is already significantly less than what most average American households consume each month. With expensive and unexpected early upgrades to more than 3,100 cell towers to manage rapidly growing usage, the cost of service is starting to rise substantially, even as usage limits and speed reductions make these networks less useful for consumers.
Under the current NBN fair use policy, monthly downloads per household are capped at 400 GB, with maximum usage during peak usage periods limited to 150 GB a month, which is already significantly less than what most average American households consume each month. With expensive and unexpected early upgrades to more than 3,100 cell towers to manage rapidly growing usage, the cost of service is starting to rise substantially, even as usage limits and speed reductions make these networks less useful for consumers.