
Pai
FCC Chairman Ajit Pai found a lot to like about the proposed merger of T-Mobile and Sprint and has recommended his fellow commissioners approve the transaction after the companies offered new commitments to ease anti-competitive and anti-trust concerns.
That typically means the FCC’s 3-2 Republican majority will quickly approve the deal in a forthcoming vote, with three Republicans in favor and two Democrats opposed, if tradition holds.
Pai’s support for the merger is hardly surprising. Since joining the FCC as a commissioner in the second half of the Obama Administration, Pai has consistently opposed every pro-consumer item on the FCC’s docket. He loves industry-consolidating mergers, hates telecom companies being forced to open their businesses to competition on things like set-top boxes, and considers almost all pro-consumer protection policies from net neutrality to merger deal conditions examples of “overregulation” that he argues are harmful to the free market and investment.
The troubled merger, which would create what we will call T-Sprint, has remained under review for months, recently stalled over revelations the two companies tailored the transaction to appeal to President Trump. T-Mobile executives spent $195,000 repeatedly renting rooms at the Trump International Hotel in Washington and spent large sums hiring Trump-connected “advisors” including Reince Priebus and Corey Lewandowski. The merger pitch was changed to emphasize its impact on rapidly growing 5G networks, a talking point favorite of President Trump, who wants to beat the Chinese over the development of next generation wireless networks.
The merger must win approval from both the FCC and the Justice Department. The latter is said to be troubled about the anti-competitive impact of reducing the number of national wireless carriers from four to three. Such a consolidation would likely permanently change the wireless competition paradigm, because there has been no interest among new entrants to construct multi-billion dollar national cellular networks to compete with established wireless companies.
On Monday, T-Mobile and Sprint delivered additional concessions which seem to have won the approval of Mr. Pai.
“Two of the FCC’s top priorities are closing the digital divide in rural America and advancing United States leadership in 5G, the next generation of wireless connectivity,” Pai said in a statement Monday. “The commitments made today by T-Mobile and Sprint would substantially advance each of these critical objectives.”
But a closer examination of “T-Sprint’s concessions” shows there is remarkably little there to protect competition and consumers:
- A proposed spin off of prepaid Boost Mobile, which relies on the weaker Sprint network, is hardly much of a concession considering it will likely be impacted by the decommissioning of Sprint’s network, requiring at least some customers to buy new equipment that works on T-Mobile’s network. T-Sprint would also continue to control Boost competitors Virgin Mobile and MetroPCS, putting Boost at a distinct disadvantage.
- The “nationwide” 5G network promised by T-Sprint is replete with fine print. The company will not be formally assessed on its expansion progress for three years, has demanded that T-Mobile’s own employees be allowed to conduct network performance tests — a conflict of interest, and that if it fails to meet its own proposed metrics, the FCC must forego the use of its regulatory forfeiture powers. Instead, the company agrees to pay “voluntary” fines if it fails coverage expansion commitments that are open to wide interpretation and litigation.
- T-Sprint agreed to expand its “5G” coverage, but will rely heavily on existing macro cell towers and low and mid-band spectrum, shared by a much larger number of users than millimeter wave/small cell technology. That will probably deliver a more modest, incremental upgrade over existing 4G LTE technology, not a game-changer that can deliver gigabit speeds to wireless customers. Nothing precludes AT&T and Verizon from deploying similar upgrades without a competition-crushing merger between the third and fourth largest competitors.
- T-Sprint’s proposed wireless home broadband replacement does not include a commitment to provide unlimited service. In fact, vague language in the commitment letter suggests T-Sprint will offer the service with a performance and usage expectation akin to other fixed wireless networks. That likely means customers will endure a data cap and speeds that are not comparable to wired technology. Once the company has signed up 9.5 million home broadband customers, any commitments offered to regulators about that service automatically expire.
- The FCC is expected to give up much of its regulatory authority in return for T-Sprint’s commitments. If T-Sprint walks away from its commitments and not invest billions on its network expansion, it can pay a much smaller fine and have its merger obligations disappear. The FCC will not be able to use its more effective compliance power: forfeiture penalties.
 T-Sprint’s argument is that this transaction will accelerate the deployment of 5G technology in a war for 5G supremacy with China. But exactly what technology is deployed, on what spectrum, using small cells or macro cell towers, makes a lot of difference. China’s wireless companies are owned and controlled by the Chinese government, which is also underwriting some of the costs. America’s networks are financed with private capital (and customer bills). T-Sprint’s 5G plans are also far less ambitious than those from AT&T and Verizon, and the cost to long-term competition is too high. The FCC should know that.
T-Sprint’s argument is that this transaction will accelerate the deployment of 5G technology in a war for 5G supremacy with China. But exactly what technology is deployed, on what spectrum, using small cells or macro cell towers, makes a lot of difference. China’s wireless companies are owned and controlled by the Chinese government, which is also underwriting some of the costs. America’s networks are financed with private capital (and customer bills). T-Sprint’s 5G plans are also far less ambitious than those from AT&T and Verizon, and the cost to long-term competition is too high. The FCC should know that.
Congress has noticed that this merger has been rejected before during the Obama Administration for being anti competitive. Nothing has changed with respect to that. But T-Mobile’s lobbying sure has — this time trying to appeal to the Trump Administration for approval. Pai is certainly on board, and that could cost American consumers plenty.
Most telling of all is Wall Street’s reaction to today’s news. A merger that is being sold as as an AT&T/Verizon killer appears to be anything but. Verizon stock rose by 4.2% and AT&T by 4%. Investors recognize that consolidation can mean only one thing: higher prices. It means the end of the wireless price war that had Sprint and T-Mobile taking potshots at their larger rivals, forcing them to cut prices and bring back unlimited data plans.
It would be ruinous for T-Sprint to continue slashing prices and taunting AT&T and Verizon with costly promotions and giveaways. AT&T and Verizon expect T-Sprint will join their comfortable cartel with suspiciously similar plans and pricing, while firing up to 30,000 redundant workers and decommissioning Sprint’s wireless network. That last fact is well known on Wall Street, too. Cellphone tower owners took a beating in the stock market on the news they could lose Sprint as a customer. American Tower was down 1.9%, Crown Castle fell 3.2% and SBA Communications Corp. dropped as much as 4.5%.
The deal still must pass muster with the Justice Department, and attorneys general from multiple U.S. states are also opposing the deal on the state level. But the Republican members of the FCC joining up to support the deal make it more likely that it will eventually get approved.



 Subscribe
Subscribe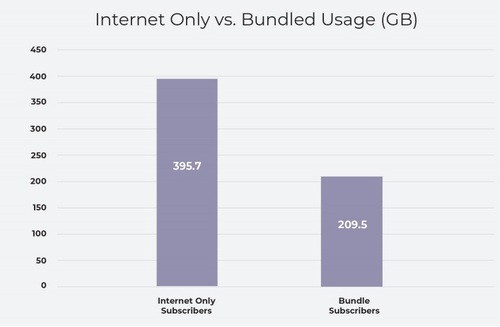

 T-Sprint’s argument is that this transaction will accelerate the deployment of 5G technology in a war for 5G supremacy with China. But exactly what technology is deployed, on what spectrum, using small cells or macro cell towers, makes a lot of difference. China’s wireless companies are owned and controlled by the Chinese government, which is also underwriting some of the costs. America’s networks are financed with private capital (and customer bills). T-Sprint’s 5G plans are also far less ambitious than those from AT&T and Verizon, and the cost to long-term competition is too high. The FCC should know that.
T-Sprint’s argument is that this transaction will accelerate the deployment of 5G technology in a war for 5G supremacy with China. But exactly what technology is deployed, on what spectrum, using small cells or macro cell towers, makes a lot of difference. China’s wireless companies are owned and controlled by the Chinese government, which is also underwriting some of the costs. America’s networks are financed with private capital (and customer bills). T-Sprint’s 5G plans are also far less ambitious than those from AT&T and Verizon, and the cost to long-term competition is too high. The FCC should know that. Cable One has the highest average revenue per customer of any publicly traded cable company in the United States, with
Cable One has the highest average revenue per customer of any publicly traded cable company in the United States, with 
 Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers run up more than double the amount of broadband usage average customers subscribing to both cable TV and broadband use, and that consumption is growing fast.
Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers run up more than double the amount of broadband usage average customers subscribing to both cable TV and broadband use, and that consumption is growing fast.
