The United States is rapidly losing its place among the world’s fastest broadband countries, dropping out of the top-10 this year and falling behind Chile, Liechtenstein, and Romania.
While other countries and internet providers are investing billions to improve their standing in an increasingly competitive global broadband marketplace, a comfortable duopoly of phone and cable companies in the United States has successfully kept regulators at bay and allowed many of the largest internet service providers to divert investment away from upgrades and towards stock buybacks, dividend payouts, debt reduction, and ongoing merger and acquisition activities.
Internet speed testing firm Ookla has watched the United States slip in its fixed broadband speed standings over the last three years, dropping from 8th place (2019) to 9th place (2020), to being dropped from its top 10 list this year (it now scores 14th). Canada has never made the list.
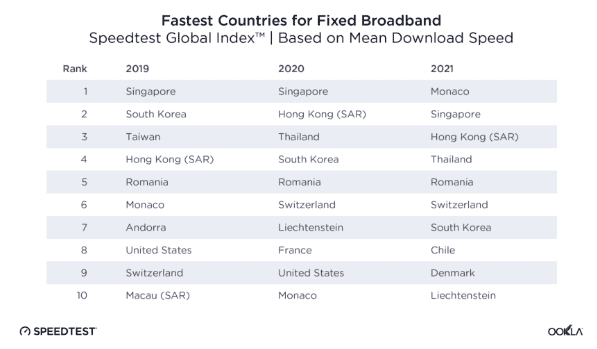
This year, the countries with the fastest internet download speeds are: Monaco, Singapore, Hong Kong, Thailand, Romania, Switzerland, South Korea, Chile, Denmark and Liechtenstein. The only other countries to fall off the top-10 list in the last three years are Taiwan, Andorra, Macau, and France.
Globally, wireless internet speeds are benefitting from 4G and 5G upgrades on cell towers, with overall speed increasing nearly 60% in the last year. Fixed broadband speeds are up 32% year over year, primarily from an increase in the amount of fiber to the home connections providers are making as they move away from traditional copper wiring. Heavy investment in network upgrades can deliver remarkable boosts in internet speeds.
 “South Korea and the United Arab Emirates stood out with mean mobile download speeds that were more than 240% faster than the global average and fixed broadband downloads that were more than 70% faster than the global average,” said Ookla’s Isla McKetta. “China’s mobile download speed was more than 180% faster than the global average and the country was more than 70% faster than the global average for fixed broadband. Switzerland’s mobile and fixed broadband download speeds were close to 100% faster than the global average.”
“South Korea and the United Arab Emirates stood out with mean mobile download speeds that were more than 240% faster than the global average and fixed broadband downloads that were more than 70% faster than the global average,” said Ookla’s Isla McKetta. “China’s mobile download speed was more than 180% faster than the global average and the country was more than 70% faster than the global average for fixed broadband. Switzerland’s mobile and fixed broadband download speeds were close to 100% faster than the global average.”
All of those countries have invested heavily in fiber connectivity for both their mobile and fixed wired broadband connections.
In contrast, U.S. cable companies have delayed upgrades to DOCSIS 4.0, capable of supporting 10 Gbps connections, and many telephone companies have dragged their feet on fiber upgrades, facing resistance from Wall Street as well as heavy debt burdens from prior mergers and acquisitions.
Most of the countries ranking the fastest have pushed providers to supply gigabit internet speed connections, but U.S. regulators and politicians have reduced pressure on large providers by proposing to subsidize millions of expanded internet connections with U.S. taxpayer funds while reducing required speed minimums to just 100/20 Mbps.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Locast, like Aereo and Ivi before it, has ceased streaming local, over the air television signals on a non-profit basis after a New York federal court judge ruled the service is violating U.S. copyright law by receiving more funding than it needs. But in developments this afternoon, there is word an appeal is planned.
Locast, like Aereo and Ivi before it, has ceased streaming local, over the air television signals on a non-profit basis after a New York federal court judge ruled the service is violating U.S. copyright law by receiving more funding than it needs. But in developments this afternoon, there is word an appeal is planned. Judge Louis L. Stanton rejected Locast’s claim it was exempt from Section 111 (a) (5) of the U.S. Copyright Act, which allowed it to stream over the air signals without getting permission from those stations in advance. That section of the Copyright Act was designed to provide a loophole for independent non-profit translator stations, which in some rural areas pick up difficult to receive TV stations and rebroadcast them locally on other channels. Some of these translator operations existed before the days of cable and satellite television, and well before the internet as we know it ever existed. But many of these services were provided through low-power transmitters operated inside large apartment complexes or hotels for the enjoyment of tenants or guests. The Copyright Act allowed groups to retransmit TV signals as long as they lacked “direct or indirect commercial advantage” and did not charge viewers in excess of the “actual and reasonable costs of maintaining and operating the secondary transmission service.”
Judge Louis L. Stanton rejected Locast’s claim it was exempt from Section 111 (a) (5) of the U.S. Copyright Act, which allowed it to stream over the air signals without getting permission from those stations in advance. That section of the Copyright Act was designed to provide a loophole for independent non-profit translator stations, which in some rural areas pick up difficult to receive TV stations and rebroadcast them locally on other channels. Some of these translator operations existed before the days of cable and satellite television, and well before the internet as we know it ever existed. But many of these services were provided through low-power transmitters operated inside large apartment complexes or hotels for the enjoyment of tenants or guests. The Copyright Act allowed groups to retransmit TV signals as long as they lacked “direct or indirect commercial advantage” and did not charge viewers in excess of the “actual and reasonable costs of maintaining and operating the secondary transmission service.”

 A
A  After weeks of tense negotiations to secure bipartisan support for the Biden Administration’s $1 trillion infrastructure stimulus measure, the White House appears to have largely capitulated to Republican efforts to water down funding to expand broadband service into a $65 billion package that will doubtless be a financial bonanza to the country’s largest phone and cable operators.
After weeks of tense negotiations to secure bipartisan support for the Biden Administration’s $1 trillion infrastructure stimulus measure, the White House appears to have largely capitulated to Republican efforts to water down funding to expand broadband service into a $65 billion package that will doubtless be a financial bonanza to the country’s largest phone and cable operators. The latest proposal’s idea of solving the broadband affordability issue is to admit there is a problem and declare the need for some kind of low-cost broadband option, but apparently does not specify pricing, who is qualified to get cheaper service, and who will oversee that such programs remain affordable. That allows providers to keep writing the rules of their own token, voluntary efforts to offer discounted internet, like those that disqualify current customers and requires enrollees to jump through various qualification hoops to sign up. The stimulus program will also spend billions of dollars effectively paying a portion of disadvantaged Americans’ internet bills, at the current high prices many ISP’s charge. That is a direct subsidy to big cable and phone companies that can continue charging whatever they please for access, knowing the government will now pay $30-50 of the bill.
The latest proposal’s idea of solving the broadband affordability issue is to admit there is a problem and declare the need for some kind of low-cost broadband option, but apparently does not specify pricing, who is qualified to get cheaper service, and who will oversee that such programs remain affordable. That allows providers to keep writing the rules of their own token, voluntary efforts to offer discounted internet, like those that disqualify current customers and requires enrollees to jump through various qualification hoops to sign up. The stimulus program will also spend billions of dollars effectively paying a portion of disadvantaged Americans’ internet bills, at the current high prices many ISP’s charge. That is a direct subsidy to big cable and phone companies that can continue charging whatever they please for access, knowing the government will now pay $30-50 of the bill.