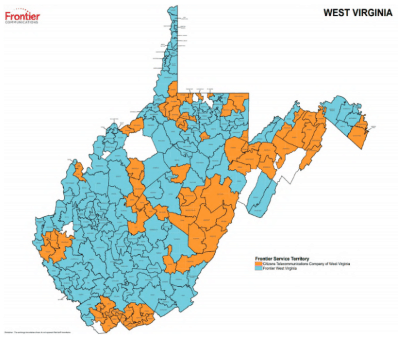
Frontier provides service to all but around a half dozen communities in West Virginia.
A comprehensive independent audit of Frontier Communications operations in West Virginia found the phone company is not keeping up with network maintenance, causing increased service problems for the company’s customers.
The significantly redacted 164-page report produced by Schumaker and Company found plenty of room for improvement for Frontier’s landline and broadband services.
The report was commissioned under order by the West Virginia Public Service Commission after the regulator received almost 2,000 customer complaints about Frontier’s service. The PSC’s demand for an audit also received the support of over 700 Frontier customers in the state.
Despite several redactions, the report offers clues about the quality of Frontier’s infrastructure for landline and internet services in West Virginia.
Frontier provides service for all but a half dozen localities in the state. Because of West Virginia’s mountainous topology, significant portions of the state do not receive adequate cellular service, making wired landlines still an essential safety tool in some areas. Despite that, Frontier’s relatively poor performance has driven away a significant number of its customers. Some subscribe to cable phone service, but most now depend on cell phones.

A Frontier crossbox in use in West Virginia.
The PSC allowed Frontier to offer a redacted public version of the auditor’s report after Frontier cited confidential business information and the Commission’s lack of regulatory oversight over the company’s DSL internet service. The redactions were substantial, blotting out significant information such as the age of Frontier’s network and equipment in different corners of the state, the condition of the company’s large number of utility poles, outage statistics, budgeting and investment numbers, repair programs, and basic information about the company’s employees and its broadband service offerings. The PSC staff filed its own recommendation that such redactions be rejected, noting Frontier is the unique carrier of last resort in West Virginia, with no competitor likely to attempt similar service. Staff members also claimed the telecom industry would find data specific to West Virginia not very useful elsewhere.
Despite the redactions, it is easy to deduce Frontier has a significant problem. Its copper landline network is gradually succumbing to a lack of regular maintenance, which can cause prolonged service degradation and outages. The audit specifically cites Frontier’s growing challenges dealing with a copper wire network that has been on utility poles for decades. Some wiring is likely to have been installed during the Johnson or Nixon Administration. The audit found that previous owner Verizon embarked on two significant copper line replacement programs, one in 1974 and the other in 1983 — 46 and 37 years ago, respectively. No large scale replacements have been undertaken since.
Phone companies like Frontier have been losing landline customers for years. The audit estimated that “more than half (57%) of American homes only have wireless communications. The displacement is even more pronounced when viewed through the prism of demographics. Over three quarters (76.5%) of young adults (aged 25-34) live in homes with only wireless connections.” In 2018, Frontier told the PSC 37 percent of its access lines were permanently disconnected between 2010 and 2017, bringing the number of customers down from 613,443 to 385,832. A 2017 Center for Health Statistics study found that roughly 53 percent of all West Virginia adults use wireless services exclusively, while another 10 percent use wireless services most of the time, with almost 22 percent of West Virginia adults still using landline services exclusively or most of the time. Frontier holds on to a larger percentage of customers than that with the sale of its rural DSL internet service.

Frontier heavily redacted the independent audit about its performance.
Frontier’s largest service problems result from its indefinite reliance on splicing damaged or degraded line pairs servicing individual customers. With fewer customers, the company has more choices of alternative line pairs it can use to restore service for customers affected by service interruptions. The audit found many line splices were decades old and often were responsible for eventual larger scale service outages, especially when repairs were inadequately completed exposing the entire cable to the elements. The audit also found no formal tree trimming operation was in place at the company, which meant trees inevitably overgrew into the company’s lines. In storms, trees can disrupt service by blowing into cables or even tearing wires off utility poles. The report also noted that technicians often drove around and spotted network defects and other problems likely to eventually cause service outages, but there was no formal reporting and mitigation strategy, which often left repairs delayed for months or years.
Frontier is also facing a talent flight, as network engineers that have serviced the lines since they were operated by Verizon are preparing to retire in large numbers. That could create even greater problems as inexperienced new technicians unfamiliar with the state of Frontier’s network gradually replace them.
Despite these problems, the auditors found Frontier was still earning a healthy amount of revenue in West Virginia. Oddly, that assertion was hotly disputed by Frontier itself, claiming that conclusion was “flatly wrong” and it had been losing money in the state every year since 2012.
“The auditors did not properly account for pensions, post-employment healthcare, and other benefits paid by Frontier nor for interest costs on the money Frontier borrowed to invest in West Virginia,” wrote Allison Ellis, Frontier’s senior vice president of regulatory affairs. “When those expenses are taken into account, it is clear that Frontier has invested more in the state than it has recouped.”
Auditors recommend that Frontier establish a more robust network engineering effort, aggressively repairing line issues before they become apparent to customers and improving its reporting systems to track service problems from start to finish. It also recommended increasing the amount of fiber in the network to reduce service issues and maintenance expenses and allow for better internet speeds. Finally, it recommends customers receive additional compensation for repeated service outages.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 In reality, 5G is nothing more than an overhyped wireless technology upgrade that can either be slightly faster than existing 4G LTE networks, or considerably faster if adequate wireless spectrum is available for short distance communications. In either case, the energy emitted by traditional cell towers or small cells is infinitesimal compared to much stronger local TV and radio stations. In fact, the fastest 5G networks operate on millimeter wave frequencies that cannot penetrate walls and doors and are capable of reaching only a few blocks away at most.
In reality, 5G is nothing more than an overhyped wireless technology upgrade that can either be slightly faster than existing 4G LTE networks, or considerably faster if adequate wireless spectrum is available for short distance communications. In either case, the energy emitted by traditional cell towers or small cells is infinitesimal compared to much stronger local TV and radio stations. In fact, the fastest 5G networks operate on millimeter wave frequencies that cannot penetrate walls and doors and are capable of reaching only a few blocks away at most.
 “One lady coughed repeatedly at me as she tried to move some of her personal property out of the way so I could drill a hole to bring in a cable line,” Ralph said. “She started turning blue and her husband had to help her to a chair. I couldn’t get back to my truck fast enough that morning. I have a wife and three kids and the last thing I need to do is bring this virus back to them.”
“One lady coughed repeatedly at me as she tried to move some of her personal property out of the way so I could drill a hole to bring in a cable line,” Ralph said. “She started turning blue and her husband had to help her to a chair. I couldn’t get back to my truck fast enough that morning. I have a wife and three kids and the last thing I need to do is bring this virus back to them.” Spectrum technicians are being offered a weekly $25 restaurant gift card if they agree to brave service calls in customer homes.
Spectrum technicians are being offered a weekly $25 restaurant gift card if they agree to brave service calls in customer homes. Frontier Communications has revealed to investors what many probably realized long ago — the independent phone company chronically underinvested in network upgrades and repairs for years, giving customers an excuse to switch providers.
Frontier Communications has revealed to investors what many probably realized long ago — the independent phone company chronically underinvested in network upgrades and repairs for years, giving customers an excuse to switch providers. About 51% of Frontier’s revenue comes from its residential customers. That number has been declining about 5% annually, year over year as customers leave. Frontier’s internet products are now crucial to the company’s ability to stay in business. Less than 30% of Frontier’s revenue comes from selling home phone lines. For Frontier to remain viable, the company must attract and keep internet customers. For the last several years, it has failed to do either.
About 51% of Frontier’s revenue comes from its residential customers. That number has been declining about 5% annually, year over year as customers leave. Frontier’s internet products are now crucial to the company’s ability to stay in business. Less than 30% of Frontier’s revenue comes from selling home phone lines. For Frontier to remain viable, the company must attract and keep internet customers. For the last several years, it has failed to do either.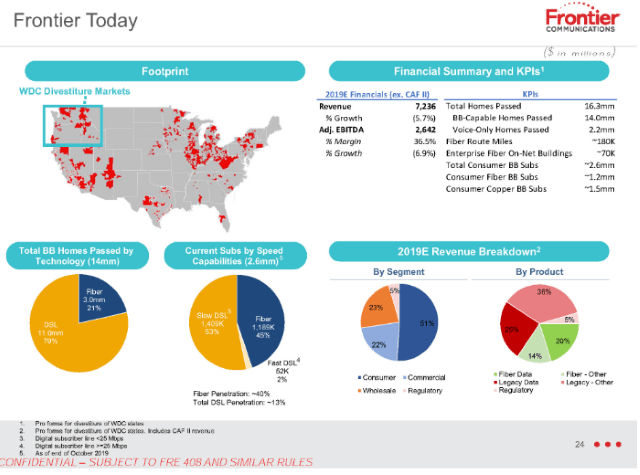

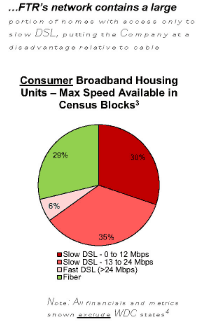 So why would a company like Frontier not immediately hit the upgrade button and start a massive copper retirement-fiber upgrade plan to keep the company in the black? In short, Frontier has survived chronic underinvestment because of a lack of broadband competition. Nearly two million Frontier customers have only one choice for internet access: Frontier. For another 11.3 million, there is only one other choice – a cable company that many detest. Frontier has enjoyed its broadband monopoly/duopoly for at least two decades. So long as its customers have fewer options, Frontier is under less pressure to invest in upgrades.
So why would a company like Frontier not immediately hit the upgrade button and start a massive copper retirement-fiber upgrade plan to keep the company in the black? In short, Frontier has survived chronic underinvestment because of a lack of broadband competition. Nearly two million Frontier customers have only one choice for internet access: Frontier. For another 11.3 million, there is only one other choice – a cable company that many detest. Frontier has enjoyed its broadband monopoly/duopoly for at least two decades. So long as its customers have fewer options, Frontier is under less pressure to invest in upgrades.
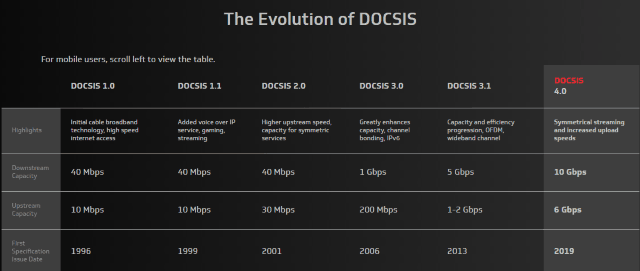
 CableLabs unveiled the final DOCSIS 4.0 specification today, dramatically improving upload speeds and offering the potential of much faster internet service from cable operators in the next few years.
CableLabs unveiled the final DOCSIS 4.0 specification today, dramatically improving upload speeds and offering the potential of much faster internet service from cable operators in the next few years.