 Is your cable television service included in your rent or condo “services” fee? Have you ever called another provider and told service was not available at your address even through others outside of your condo neighborhood or apartment complex can sign up for service today? Chances are your landlord or property management company is receiving a kickback to keep competition off the property, while you may be stuck paying for substandard services you neither want or need. Worst of all, chances are it’s all legal and everyone is getting a piece of the action… except you.
Is your cable television service included in your rent or condo “services” fee? Have you ever called another provider and told service was not available at your address even through others outside of your condo neighborhood or apartment complex can sign up for service today? Chances are your landlord or property management company is receiving a kickback to keep competition off the property, while you may be stuck paying for substandard services you neither want or need. Worst of all, chances are it’s all legal and everyone is getting a piece of the action… except you.
Welcome to the world of Multiple Dwelling Unit (MDU) Bulk Service Agreements, the seedy underbelly of the anti-competitive cable and telco-TV world. When cable TV first got going, most people wanted access. In the early days, cable franchises were typically exclusive and cable companies maintained the upper hand in negotiations with apartment owners and property owners. Since the service was in demand, many property owners were told to sign whatever “Right Of Entry” Agreement (ROE) was put in front of them. Most contained clauses that guaranteed that cable company would get exclusive access to the property for as long as it was given a franchise to operate within that community. In other words, basically forever.
This turned out very handy when competitors started showing up. First on the scene were satellite television providers, which had a rough time dealing with landlords who loathed tenants installing satellite dishes that “ruined the aesthetics” of the property. Many rental agreements still restrict satellite television dishes in ways that make their use untenable. But things got much more serious when Verizon and AT&T got into the cable business. Initially, both companies found extending FiOS and U-verse to some rental and gated communities was blocked by the exclusive agreements held by cable operators. By 2007, the FCC finally acted to forbid exclusive service contracts, but the cable industry and property developers have played cat and mouse games with the FCC’s loopholes ever since.
Property Developers, Management Companies, Landlords, and Homeowner Associations With Their Hands Out
 With the FCC’s 2007 declaration that exclusive contracts between cable companies and property owners were “null and void,” the power of the cable industry to negotiate on their terms was markedly diminished. Although many property owners applauded their new-found freedom to tell the local cable company to take a hike if they did not offer better service to their tenants, many others saw dollar signs in their eyes. With leverage now in the hands of the property owner, if the local cable company wanted to stay, in many cases it had to pay. Only the most brazen property owners kicked uncooperative cable companies off their properties, putting tenants at a serious inconvenience. Instead, many found life more peaceful and lucrative to stick with the existing cable company, signing a new contract for “bulk billing” tenants. On the surface, it seemed like a good deal. Property owners advertised that cable TV was included in the rent (and they paid a deeply discounted price per tenant) and the cable operator had a guaranteed number of customers, whether they wanted the service or not.
With the FCC’s 2007 declaration that exclusive contracts between cable companies and property owners were “null and void,” the power of the cable industry to negotiate on their terms was markedly diminished. Although many property owners applauded their new-found freedom to tell the local cable company to take a hike if they did not offer better service to their tenants, many others saw dollar signs in their eyes. With leverage now in the hands of the property owner, if the local cable company wanted to stay, in many cases it had to pay. Only the most brazen property owners kicked uncooperative cable companies off their properties, putting tenants at a serious inconvenience. Instead, many found life more peaceful and lucrative to stick with the existing cable company, signing a new contract for “bulk billing” tenants. On the surface, it seemed like a good deal. Property owners advertised that cable TV was included in the rent (and they paid a deeply discounted price per tenant) and the cable operator had a guaranteed number of customers, whether they wanted the service or not.
Bulk billing also proved a very effective deterrent for would-be competitors, who had to overcome the challenge of marketing their service while the tenant was already paying for another as part of their rent. As a result, telco TV competitors often stayed away from properties with bulk billing arrangements.
As broadband has become more prominent and threatens to become more important than the cable TV package, the cable industry has refined its weapons of non-competition. While they cannot force competitors off properties, they can make life very expensive for them. The latest generation of ROE agreements often grant access rights to the building’s telecommunications conduit, cabling, and equipment exclusively to the cable operator.
 If Google Fiber, AT&T U-verse or Verizon FiOS sought to offer service on one of these properties, they would have to overcome the investment insanity of wiring each building with its own infrastructure, including duplicate cables, in separate conduits and spaces not already designated for the exclusive use of the cable company. Verizon in New York City has faced numerous obstacles wiring some buildings, including gaining access to the building itself. Intransigent on site employees, bureaucratic and unresponsive property management companies, and developers have all made life difficult for Verizon’s fiber upgrade.
If Google Fiber, AT&T U-verse or Verizon FiOS sought to offer service on one of these properties, they would have to overcome the investment insanity of wiring each building with its own infrastructure, including duplicate cables, in separate conduits and spaces not already designated for the exclusive use of the cable company. Verizon in New York City has faced numerous obstacles wiring some buildings, including gaining access to the building itself. Intransigent on site employees, bureaucratic and unresponsive property management companies, and developers have all made life difficult for Verizon’s fiber upgrade.
AT&T often takes the approach “if you can’t beat ’em, join ’em” and offers its own bulk billing incentives, along with occasional commitments for fiber upgrades. Google Fiber can afford to skip places where it isn’t wanted, although with recent revelations that landlords can raise the rent by up to 11% with the arrival of Google Fiber alone, it may hurt to alienate that fiber to the home provider.
Kickbacks for New Developments = Windfall
Kickbacks for existing properties are lucrative, but nothing compared to the lucrative windfall new property developments can achieve with the right deal.
In 2013, one property developer in Maryland went all out for an exclusive deal with a provider that was going to get de facto exclusivity by using a convoluted series of entities and agreements designed to insulate the company from competition and a challenge from the FCC. A court later ruled the provider used an “elaborate game of regulatory subterfuge” using various corporate entities to escape potential competition.
Some lawyers devote a substantial amount of their practice to the issue of bulk contracts and ROE agreements. Carl Kandutsch serves clients nationwide, many trying to extricate themselves from bad deals of the past. In many cases, an attorney may be needed to find a way out of contracts that don’t meet FCC rules. Other communities sometimes have to buy out an existing contract. Many have to sit and suffer the consequences for years. One residential community found itself trapped with a service provider that was quietly protected by an “airtight contract” negotiated not with the property management company or the homeowner association, but the development’s original builder. The provider delivered lousy service and the community spent six years trying to get rid of the offending firm with no result until they hired an attorney. Although happy to be rid of the bad provider, the homeowner association ended up illustrating how pervasive this problem is after it signed a similar contract with another provider also handing out kickbacks.
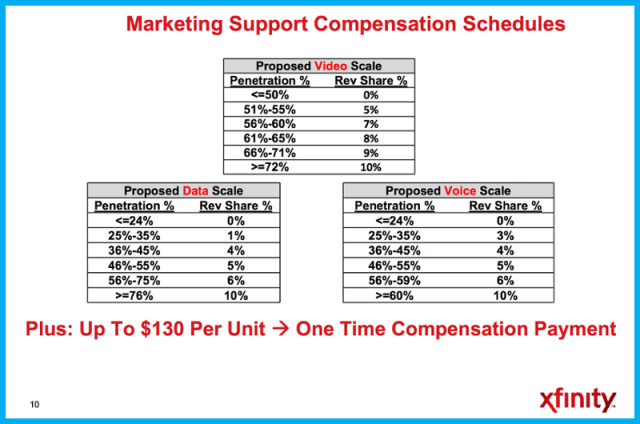
Comcast pays up to 10% of a renter’s cable bill to the landlord. (Image: Susan Crawford)
Comcast is more creative than most. It calls its handouts: “Marketing Support Compensation.” The property owner gets an increasing reward for every tenant signed up for Comcast service. Once around two-thirds of tenants are subscribed, the owner gets up to a 10% take of each bill, plus a one time payment of up to $130 per tenant.
Because Comcast’s reputation often precedes it, customers reluctant to sign up without considering other providers will find that tougher to do because Comcast bans other providers from marketing their services to tenants with the support or cooperation of the landlord. In other words, no door hangers, free coffee, brochures in the lobby, or any other on-site promotions. In case a property owner forgets, Comcast sends reminders in the mail:

Comcast likes to remind landlords it has an exclusive. (Image: Susan Crawford)
Susan Crawford calls it “astounding, enormous, decentralized payola” and claims it affects millions of renters.

Crawford
“These shenanigans will only stop when cities and national leaders require that every building have neutral fiber/wireless facilities that make it easy for residents to switch services when they want to,” Crawford wrote. “We’ve got to take landlords out of the equation — all they’re doing is looking for payments and deals (understandably: they’re addicted to the revenue stream they’ve been getting), and the giant telecom providers in our country are more than happy to pay up. The market is stuck. Residents have little idea these deals are happening. The current way of doing business is great for landlords and ISPs but destructive in every other way.”
One real world example of how this deters competition comes from Webpass (recently acquired by Google), which offers gigabit Ethernet speeds in select MDUs in San Francisco, San Diego, Miami, Chicago, and Boston. The service comes with a low price, but that doesn’t get the company in the door, according to its president, Charles Barr.
Barr has been refused entry by multiple building owners who have agreements with Comcast, AT&T, or others.
“Tenants want us, but we can’t get in,” Barr said.
Crawford argues the FCC has once again been outmaneuvered by ISPs and their attorneys.
“Sure, a landlord can’t enter into an exclusive agreement granting just one ISP the right to provide Internet access service to an MDU, but a landlord can refuse to sign agreements with anyone other than Big Company X, in exchange for payments labeled in any one of a zillion ways,” added Crawford. “Exclusivity by any other name still feels just as abusive.”
This isn’t a new problem. Stop the Cap! first reported on these kinds of bulk buying arrangements back in 2010, all made possible by the FCC’s regulatory loopholes. Six years later, the problem appears to be getting worse.
 Time Warner Cable subscribers in Otsego County, N.Y. have been able to watch WBNG-TV, the CBS affiliate in Binghamton, since there has been a cable company called Time Warner Cable. But as of yesterday, that is no longer the case. In Baxter County, Ark., Suddenlink customers suddenly lost KARK (NBC) and KTHV (CBS), two stations from Little Rock, after the cable company decided it would henceforth only carry KYTV (NBC) and KOLR (CBS) instead. Part of the problem for subscribers is those two stations are located in Springfield, Missouri, a different state.
Time Warner Cable subscribers in Otsego County, N.Y. have been able to watch WBNG-TV, the CBS affiliate in Binghamton, since there has been a cable company called Time Warner Cable. But as of yesterday, that is no longer the case. In Baxter County, Ark., Suddenlink customers suddenly lost KARK (NBC) and KTHV (CBS), two stations from Little Rock, after the cable company decided it would henceforth only carry KYTV (NBC) and KOLR (CBS) instead. Part of the problem for subscribers is those two stations are located in Springfield, Missouri, a different state.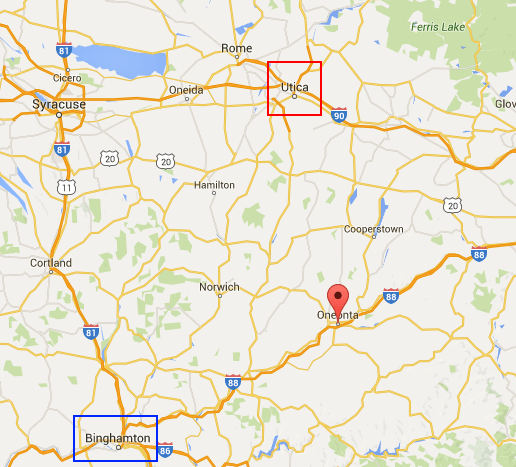
 Another cable company with cost-cutting fever is Altice-owned Suddenlink, which stopped carrying the two Little Rock-based broadcast stations in northern Arkansas on June 7, leaving KATV (ABC) as the only central Arkansas-based news outlet on the cable provider’s Mountain Home-area system.
Another cable company with cost-cutting fever is Altice-owned Suddenlink, which stopped carrying the two Little Rock-based broadcast stations in northern Arkansas on June 7, leaving KATV (ABC) as the only central Arkansas-based news outlet on the cable provider’s Mountain Home-area system.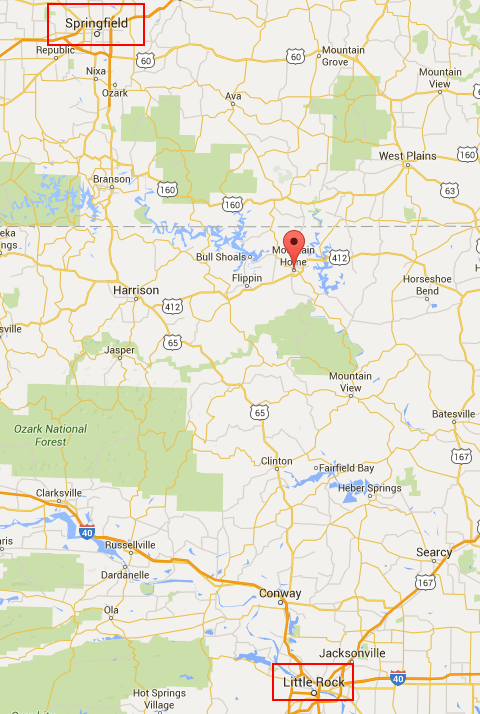 Suddenlink has standing orders from Altice to look for savings wherever possible, but none of those savings are returned to subscribers. The loss of the stations has not reduced anyone’s cable bill and Suddenlink recently moved TBS and INSP — a Christian cable network — to a more costly Expanded Basic tier. In place of the two networks dropped from the Basic package are home shopping networks that actually make Suddenlink money – Evine Live and Jewelry TV.
Suddenlink has standing orders from Altice to look for savings wherever possible, but none of those savings are returned to subscribers. The loss of the stations has not reduced anyone’s cable bill and Suddenlink recently moved TBS and INSP — a Christian cable network — to a more costly Expanded Basic tier. In place of the two networks dropped from the Basic package are home shopping networks that actually make Suddenlink money – Evine Live and Jewelry TV.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Premium movie channels Starz and Encore
Premium movie channels Starz and Encore  First credit cards were tied to your credit score, then auto insurance, and now how much you pay for cable television and what kind of support you receive from customer service may also depend on your creditworthiness, at least at Cable One.
First credit cards were tied to your credit score, then auto insurance, and now how much you pay for cable television and what kind of support you receive from customer service may also depend on your creditworthiness, at least at Cable One. Cable One has even stopped direct marketing its cable service, even though it was winning nine percent of new customer sign-ups. The customers Cable One attracted were so low quality, Might claims the company didn’t make a penny from the marketing effort.
Cable One has even stopped direct marketing its cable service, even though it was winning nine percent of new customer sign-ups. The customers Cable One attracted were so low quality, Might claims the company didn’t make a penny from the marketing effort.
 Despite vociferous denials to New York regulators that Altice’s unique way of cost-cutting expenses in Europe would mean the same in the United States, a Suddenlink employee in the Appalachians found herself visiting a nearby Kroger supermarket recently to pick up some “forever” postage stamps after the office’s postage meter machine stopped working.
Despite vociferous denials to New York regulators that Altice’s unique way of cost-cutting expenses in Europe would mean the same in the United States, a Suddenlink employee in the Appalachians found herself visiting a nearby Kroger supermarket recently to pick up some “forever” postage stamps after the office’s postage meter machine stopped working. When Altice took over Cablevision, employees were stunned when top executives dined in the staff canteen on their first day after the deal closed. That was never the style of former CEO James Dolan and other executives who avoided hobnobbing with anyone too far from the executive suites. Dolan himself often used a helicopter to travel back and forth from the office, occasionally with bodyguards.
When Altice took over Cablevision, employees were stunned when top executives dined in the staff canteen on their first day after the deal closed. That was never the style of former CEO James Dolan and other executives who avoided hobnobbing with anyone too far from the executive suites. Dolan himself often used a helicopter to travel back and forth from the office, occasionally with bodyguards. With a commitment to slash $900 million in expenses out of Cablevision alone during 2016, that’s a lot of discipline. Employees are echoing their French counterparts at Altice’s SFR-Numericable when they call life at Suddenlink and Cablevision “a culture of fear,” watching workers exiting each week without being replaced. Much the same happened in Europe, despite commitments not to engage in job-cutting. In both cases, Altice claims the slow but steady trickle of employee departures are “normal churn,” not layoffs.
With a commitment to slash $900 million in expenses out of Cablevision alone during 2016, that’s a lot of discipline. Employees are echoing their French counterparts at Altice’s SFR-Numericable when they call life at Suddenlink and Cablevision “a culture of fear,” watching workers exiting each week without being replaced. Much the same happened in Europe, despite commitments not to engage in job-cutting. In both cases, Altice claims the slow but steady trickle of employee departures are “normal churn,” not layoffs. Is your cable television service included in your rent or condo “services” fee? Have you ever called another provider and told service was not available at your address even through others outside of your condo neighborhood or apartment complex can sign up for service today? Chances are your landlord or property management company is receiving a kickback to keep competition off the property, while you may be stuck paying for substandard services you neither want or need. Worst of all, chances are it’s all legal and everyone is getting a piece of the action… except you.
Is your cable television service included in your rent or condo “services” fee? Have you ever called another provider and told service was not available at your address even through others outside of your condo neighborhood or apartment complex can sign up for service today? Chances are your landlord or property management company is receiving a kickback to keep competition off the property, while you may be stuck paying for substandard services you neither want or need. Worst of all, chances are it’s all legal and everyone is getting a piece of the action… except you. With the FCC’s 2007 declaration that exclusive contracts between cable companies and property owners were “null and void,” the power of the cable industry to negotiate on their terms was markedly diminished. Although many property owners applauded their new-found freedom to tell the local cable company to take a hike if they did not offer better service to their tenants, many others saw dollar signs in their eyes. With leverage now in the hands of the property owner, if the local cable company wanted to stay, in many cases it had to pay. Only the most brazen property owners kicked uncooperative cable companies off their properties, putting tenants at a serious inconvenience. Instead, many found life more peaceful and lucrative to stick with the existing cable company, signing a new contract for “bulk billing” tenants. On the surface, it seemed like a good deal. Property owners advertised that cable TV was included in the rent (and they paid a deeply discounted price per tenant) and the cable operator had a guaranteed number of customers, whether they wanted the service or not.
With the FCC’s 2007 declaration that exclusive contracts between cable companies and property owners were “null and void,” the power of the cable industry to negotiate on their terms was markedly diminished. Although many property owners applauded their new-found freedom to tell the local cable company to take a hike if they did not offer better service to their tenants, many others saw dollar signs in their eyes. With leverage now in the hands of the property owner, if the local cable company wanted to stay, in many cases it had to pay. Only the most brazen property owners kicked uncooperative cable companies off their properties, putting tenants at a serious inconvenience. Instead, many found life more peaceful and lucrative to stick with the existing cable company, signing a new contract for “bulk billing” tenants. On the surface, it seemed like a good deal. Property owners advertised that cable TV was included in the rent (and they paid a deeply discounted price per tenant) and the cable operator had a guaranteed number of customers, whether they wanted the service or not. If Google Fiber, AT&T U-verse or Verizon FiOS sought to offer service on one of these properties, they would have to overcome the investment insanity of wiring each building with its own infrastructure, including duplicate cables, in separate conduits and spaces not already designated for the exclusive use of the cable company. Verizon in New York City has faced numerous obstacles wiring some buildings, including gaining access to the building itself. Intransigent on site employees, bureaucratic and unresponsive property management companies, and developers have all made life difficult for Verizon’s fiber upgrade.
If Google Fiber, AT&T U-verse or Verizon FiOS sought to offer service on one of these properties, they would have to overcome the investment insanity of wiring each building with its own infrastructure, including duplicate cables, in separate conduits and spaces not already designated for the exclusive use of the cable company. Verizon in New York City has faced numerous obstacles wiring some buildings, including gaining access to the building itself. Intransigent on site employees, bureaucratic and unresponsive property management companies, and developers have all made life difficult for Verizon’s fiber upgrade.


