Parks Associates: Broadband VAS Adoption & Awareness
Cable and phone companies may increasingly turn to selling broadband subscription add-ons to restore the high level of profitability investors expect from the nation’s internet service providers.
With an increasing number of people deciding to ditch cable TV subscriptions, cable and phone companies are seeing lower growth in the average amount they charge subscribers every month, leaving many to consider finding new broadband “value-added” products and services to sell.
Falling video subscription revenue and increased programming costs have made it difficult for operators to report the glowing results Wall Street has come to expect over the last 20 years. In 2017, only 34% of customers were signed up for broadband-only service. By the first quarter of this year, that number had risen to 42%. Broadband only customers pay less than customers who choose a bundle of services. Parks Associates found the average internet-only customer paid $60 a month for service, with rates up 36% from the first quarter of 2012 to the third quarter of 2019. In comparison, cable operators only managed to raise rates for bundled video/internet packages from $107 to $127 a month over the same period. When a customer downgrades to internet-only service, the average revenue per subscriber (also known as “ARPU”) drops significantly, sometimes by as much as half.
To keep revenue growing, providers have a few options:
- Raise prices: Cable and phone companies have traditionally raised prices on services least likely to be dropped as a result of price hikes. For years, cable operators could significantly raise prices for cable TV packages with little fear customers would cancel service. Cord-cutting changed that, and as a result video-related rate hikes have slowed. Instead, operators have found broadband to be the service most cannot do without, and have shifted rate hikes accordingly.
- Offer upgraded services: The most popular and effective revenue enhancer is upselling customers to better packages and services. For broadband, that traditionally means a faster speed package. Most companies charge a comparatively small amount (often $10-20 more) for a considerably faster speed tier.
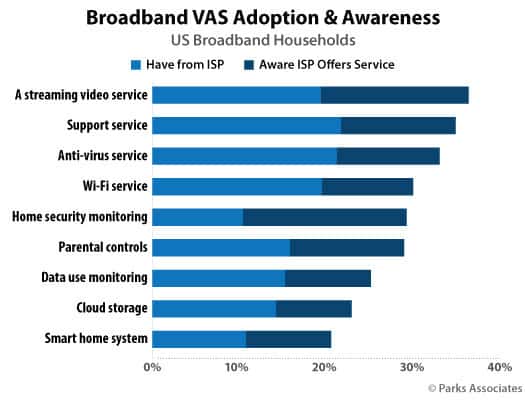
- Sell value-added services: These are ancillary services that offer subscribers more value from their existing subscription. Examples include: Unlimited Access (waiving data caps), Enhanced Technical Support, Anti-Virus/Malware Protection, Enhanced Streaming Video Services, Enhanced Network Performance for Gameplay, Wiring Maintenance/Insurance, Home Security/Automation, and Cloud Backups.
 Currently, only a few providers aggressively promote value-added services. Many already provide anti-virus/malware software as part of their broadband service offering. Others, like Charter/Spectrum, have soured on selling value-added services in favor of a simplified menu of services and options. Spectrum ceased supporting Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks’ legacy home security/automation services in early 2020. Some phone companies, notably Frontier Communications, have long depended on value-added services to bolster revenue for its increasingly beleaguered DSL internet service. Frontier heavily markets anti-virus, enhanced tech support, and wiring maintenance services to customers, which can add a considerable amount to a customer’s bill.
Currently, only a few providers aggressively promote value-added services. Many already provide anti-virus/malware software as part of their broadband service offering. Others, like Charter/Spectrum, have soured on selling value-added services in favor of a simplified menu of services and options. Spectrum ceased supporting Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks’ legacy home security/automation services in early 2020. Some phone companies, notably Frontier Communications, have long depended on value-added services to bolster revenue for its increasingly beleaguered DSL internet service. Frontier heavily markets anti-virus, enhanced tech support, and wiring maintenance services to customers, which can add a considerable amount to a customer’s bill.
Parks Associates, a market research and consulting company, is now offering insight on value-added services to phone and cable companies in its latest research report, 360 Deep Dive: Broadband Value-added Services (for $7,500 a copy):
As the broadband market becomes increasingly commoditized, broadband providers are seeking way to differentiate themselves through new products and services. This research investigates consumer perception and interest in value-added services from service providers including Wi-Fi services, network optimization, and data security and monitoring services.
The report finds most consumers have traditionally ignored or were unaware of value-added services from internet providers. As a result, the impact on revenue from sales of such services has been usually negligible.
“Value-added services (VAS) have little impact on ARPUs because [internet] speed, which correlates with VAS adoption, is the primary driver of ARPUs,” said David Drury, Parks’ research director. “In other words, speed rather than the number of VAS broadly determines ARPU levels, even though those with higher speeds also have a higher number of VAS.”
But Parks suggests the ongoing coronavirus pandemic may open fresh opportunities to introduce customers to value-added services. Among the services consumers may now be using for the first time are telehealth services, which allow for virtual online doctor visits, video conferencing with friends, family, and colleagues, and remote learning tools. After the COVID-19 crisis passes, providers could begin marketing service and support for these applications, either directly or in partnership with other companies.
Still undetermined is whether companies should bundle these types of services into existing subscriptions for free as a customer retention tool, or offer them for sale to customers.
“Broadband growth has plateaued, so the next opportunity is in VAS,” Drury said. “Providers have generally used VAS as a marketing tool to attract and retain subscribers, so for them to make the transition to a revenue source, companies need a clear understanding of the gaps in consumer satisfaction and demand for strategic and successful VAS deployments.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe The cable industry’s public affairs network — C-SPAN, gave a friendly reception to a top telecom industry lobbyist over the weekend, responding to soft ball questions about rural broadband and telecommunications public policy debates.
The cable industry’s public affairs network — C-SPAN, gave a friendly reception to a top telecom industry lobbyist over the weekend, responding to soft ball questions about rural broadband and telecommunications public policy debates.
 Planning to launch during the second half of 2020 in:
Planning to launch during the second half of 2020 in: Several Spectrum employees have contacted Stop the Cap! to let us know a rate increase is planned for Spectrum services that will raise rates for cable television customers beginning as early as next month.
Several Spectrum employees have contacted Stop the Cap! to let us know a rate increase is planned for Spectrum services that will raise rates for cable television customers beginning as early as next month. AT&T has
AT&T has