
Rural Roane County, Tenn.
Earlier this month, a standing room only crowd packed the offices of Rockwood Electric Utility (REU) in Rockwood, Tenn., despite the fact the meeting was held at 10 a.m. on a Friday morning.
Local residents were there on a work day to listen to area providers and local officials discuss rural broadband access. Most wanted to know exactly when the local phone or cable company planned to expand to bring internet access to the far corners of the region between Knoxville and Chattanooga in east Tennessee.
Comcast, Charter, and AT&T told Roane County Commissioners Ron Berry and Darryl Meadows, State Sen. Ken Yager (R-Kingston), and the crowd they all had a long wait because the companies couldn’t profit offering rural broadband service to the county.
“That is what our shareholders expect and the way we operate in a capitalistic society,” declared Andy Macke, vice president of external affairs at Comcast.
“The biggest challenge for all of you in this room is what they call the last mile,” said Alan L. Hill, the regional director of external and legislative affairs at AT&T Tennessee. “It is a challenge. We all face these challenges.”
In short, nothing much had changed in Roane County, or other rural counties in southeastern Tennessee, to convince service providers to spend money to bring internet service to the region. Until that changed, AT&T, Comcast and others should not be expected to be on the front lines addressing rural internet access. Successive governors of Tennessee have long complained about the rural broadband problem, but the state legislature remains cool to the idea of the state government intervening to help resolve it.

Gov. Haslam
In 2017, Tennessee Gov. Bill Haslam noted Tennessee currently ranked 29th in the U.S. for broadband access, with 34 percent of rural Tennessee residents lacking access at recognized minimum standards. In splashy news releases and media events, Haslam sold his solution to the problem — the Broadband Accessibility Act, offering up to $45 million over three years to assist making broadband available to unserved homes and businesses.
In reality, the law authorized spending no more than $9.5 million annually on rural broadband grants over the next three years. It also slashed the FCC’s broadband standard from 25/3 Mbps to 10/1 Mbps, presumably a gift to the phone companies who prefer to offer less-capable DSL service in rural areas. In the first year of awards, 13 Tennessee counties, none in the southeastern region where Roane County lies, divided the money, diluting the impact to almost homeopathic strength.
Critics called Haslam’s broadband improvement program “The Smoke and Mirrors Act” for promising a lot and delivering little. At current funding levels, broadband service can only be expanded to 5,000 of the estimated 422,000 households that lack access to internet service, and then only with the award winner’s matching financial contribution.
The demand for rural broadband financial assistance is obvious from the $66 million in requests received from 71 different utilities, co-ops, and communications companies in the first year of the program, all seeking state funding to expand rural broadband. Only a small fraction of those requests were approved. AT&T applied for money targeting Roane County and was turned down. AT&T’s Hill expressed sympathy for the county’s school children who need to complete homework assignments by borrowing Wi-Fi access from fast food establishments, area businesses, and larger libraries. But AT&T’s sympathy will not solve Roane County’s broadband problems.
What might is Rockwood Electric Utility, the municipal power company that sponsored the broadband event.
 REU is a not-for-profit, municipally owned utility that has successfully served portions of Roane, Cumberland, and Morgan counties since 1939. By itself, the community-owned utility is no threat to companies like Comcast, because it offers service in places the cable company won’t. But if REU partnered with other municipal providers and offered internet service in larger nearby towns and communities to achieve economy of scale and a more secure financial position, that is a competitive threat apparently so perilous that the telecom industry spent millions of lobbying dollars on state legislatures like the one in Tennessee to ghost-write legislation to discourage utilities like REU from getting into the broadband business, much less dare to compete directly with them. AT&T, Charter, and Comcast also fear how they will compete against municipal utilities that have successfully delivered electric service and maintained an excellent reputation in the community for decades.
REU is a not-for-profit, municipally owned utility that has successfully served portions of Roane, Cumberland, and Morgan counties since 1939. By itself, the community-owned utility is no threat to companies like Comcast, because it offers service in places the cable company won’t. But if REU partnered with other municipal providers and offered internet service in larger nearby towns and communities to achieve economy of scale and a more secure financial position, that is a competitive threat apparently so perilous that the telecom industry spent millions of lobbying dollars on state legislatures like the one in Tennessee to ghost-write legislation to discourage utilities like REU from getting into the broadband business, much less dare to compete directly with them. AT&T, Charter, and Comcast also fear how they will compete against municipal utilities that have successfully delivered electric service and maintained an excellent reputation in the community for decades.
Tennessee law is decidedly stacked in favor of AT&T, Charter, and Comcast and against municipal utilities. Although the state allows municipal providers to supply broadband, it can come only after satisfying a series of regulatory rules designed to protect commercial cable and phone companies. It also prohibits municipal providers from offering service outside of existing service areas. That leaves communities served by a for-profit, investor-owned utility out of luck, as well as residents in areas where a rural utility lacked adequate resources to supply broadband service on its own.
 Haslam’s Broadband Accessibility Act cynically retained these restrictions and blockades, hampering the rural broadband expansion the law was supposed to address.
Haslam’s Broadband Accessibility Act cynically retained these restrictions and blockades, hampering the rural broadband expansion the law was supposed to address.
For several years, Sen. Janice Bowling (R-Coffee, Franklin, Grundy, Marion, Sequatchie, Van Buren and Warren Counties), has tried to cut one section of Tennessee’s broadband-related laws that prohibits municipal providers from offering service outside of their existing utility service area. Her proposed legislation would authorize municipalities to provide telecommunication service, including broadband service, either on its own or by joint venture or other business relationship with one or more third parties and in geographical areas that are inside and outside the electric plant’s service area.
In her sprawling State Senate District 16, a municipal provider already offers fiber broadband service, but Tennessee’s current protectionist laws prohibit LightTUBe from offering service to nearby towns where service is absent or severely lacking. That has left homes and businesses in her district at a major disadvantage economically.
Sen. Janice Bowling (R-Tenn.) discusses rural broadband challenges in her 16th district south of Nashville and her bill to help municipal utilities provide broadband service. (4:20)
“In rural Tennessee, if we have what is called an industrial park, and we have electricity, you have running water, you have some paved roads, but if you do not have access to fiber at this point, what you have is an electrified cow pasture with running water and walking trails. It is not an industrial park,” she complained, noting that the only reason her bill is prevented from becoming law is lobbying by the state’s cable and phone companies. “We can no longer leave the people of Tennessee hostage to profit margins of large corporations. We appreciate what they’re doing. We appreciate where they do it, but in rural Tennessee we will never meet their profit margins and so we can no longer be held hostage when we have the ability to help ourselves.”

Sen. Yager
Her sentiment in shared by many other Tennessee legislators who serve rural districts, and her Senate bill (and House companion bill) routinely receive little, if any, public opposition. But private lobbying by telecom industry lobbyists makes sure the bill never reaches the governor’s desk, usually dying in an obscure committee unlikely to attract media attention.
That reality is why residents of Roane County were meeting in a crowded room to get answers about why broadband still remained elusive after several years, despite the high-profile attention it seems to get in the legislature and governor’s office.
“‘It is a critical issue as I said. It is not a luxury. It is a necessity. I certainly understand your frustration,” responded Sen. Ken Yager. “This problem is so big I don’t think one person can do it alone, one entity. It’s going to have to have partnerships. One thing this bill encourages is for your co-ops to partner with one another to bring broadband in.”
The bill Sen. Yager refers to and endorsed at the meeting was written by Sen. Bowling. Sen. Yager must be very familiar with Bowling’s proposals, because she has appeared before the Senate Commerce & Labor Committee he belongs to year after year to promote it. On March 3, 2018, the bill failed again in a 4-3 vote. But unbeknownst to those in attendance at the public meeting, Sen. Yager himself delivered the fourth “no” vote that killed the bill.
Undeterred, Bowling promises to be back next year with the same bill language as before. Perhaps next time, voters will know who their friends are in the legislature, and who actually represents the interests of big corporate cable and phone companies.


 Subscribe
Subscribe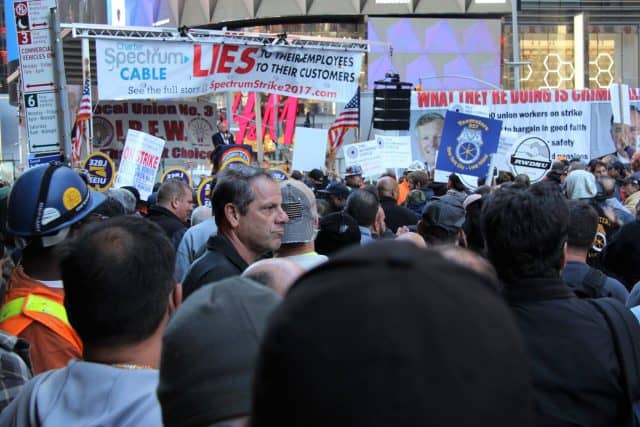 For the last year and a half, while Charter/Spectrum has been accused of dragging its feet on rural broadband rollouts across New York State and is now threatened with franchise revocation, the company had plenty of time to spare waiting out the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 3, who have been on strike to protest a pay-and-benefits-race-to-the-bottom in the New York City.
For the last year and a half, while Charter/Spectrum has been accused of dragging its feet on rural broadband rollouts across New York State and is now threatened with franchise revocation, the company had plenty of time to spare waiting out the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 3, who have been on strike to protest a pay-and-benefits-race-to-the-bottom in the New York City. The David vs. Goliath battle has also put enormous strain on some affected families. Some have quit the company and looked for employment elsewhere, some others have returned to work and abandoned the strike, leaving holdouts hoping for a breakthrough.
The David vs. Goliath battle has also put enormous strain on some affected families. Some have quit the company and looked for employment elsewhere, some others have returned to work and abandoned the strike, leaving holdouts hoping for a breakthrough.





 After the inspector general of the Federal Communications Commission opened an investigation into FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s close relationship with executives at Sinclair Broadcasting, Pai stopped returning Sinclair’s phone calls and refused any further meetings with America’s largest local TV station owner, at least until last Tuesday when Pai called Sinclair’s general counsel to say its multi-billion dollar merger with Tribune Media was in trouble.
After the inspector general of the Federal Communications Commission opened an investigation into FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s close relationship with executives at Sinclair Broadcasting, Pai stopped returning Sinclair’s phone calls and refused any further meetings with America’s largest local TV station owner, at least until last Tuesday when Pai called Sinclair’s general counsel to say its multi-billion dollar merger with Tribune Media was in trouble.

