
Phillip “Free Trade in Bad Broadband” Dampier
Sure we’ve had our cultural skirmishes in the past, but on one thing we can all mostly agree: our largest cable, phone, and broadband providers generally suck.
Outside of hockey season, Canada’s national pastime is hating Bell, Rogers, Vidéotron, Telus, and Shaw. The chorus of complaints is unending on overbilling, bundling of dozens of channels almost nobody watches but everybody pays for, outrageous long-term contracts, and bloodsucking Internet overlimit fees. In fact, dissatisfaction is so pervasive, the Conservative government of Stephen Harper spent this past summer waving shiny keys of distraction promising Canadians telecom relief while hoping voters didn’t notice their tax dollars were being spent by the country’s national security apparatus to spy on Brazil for big energy companies.
The Montreal Gazette is now collecting horror stories about dreadful service, mysterious price hikes, and promised credits gone missing on behalf of readers fed up with Bell and Vidéotron.
Rogers Cable, always thoughtful and pleasant, punished a Ottawa man coping with multiple sclerosis and cancer with a $1,288 bill, quickly turned over to a collection agency after his home burned to the ground. It took headlines spread across Ontario newspapers to get the cable company to relent.
Things are no better in the United States where the American Customer Satisfaction Index rates telecom companies worse than the post office, health insurers airlines, and the bird flu. National Public Radio opened the floodgates when it asked listeners to rate their personal satisfaction with their Internet Service Provider — almost always the local cable or telephone company.

The phone company Canadians love to hate.
Many responded their Internet access is horribly slow, often goes out, and is hugely overpriced. In response, the cable industry’s hack-in-chief did little more than shrug his shoulders — knowing full well American broadband exists in a cozy monopoly or duopoly in most American cities.
Breann Neal of Hudson, Ill., told NPR she has one choice — DSL, which is much slower than advertised. Hudson is Frontier Communications country, and it is a comfortable area to serve because local cable competition from Mediacom, America’s worst cable company, is miles away from Neal’s home.
“There’s no incentive for them to make it better for us because we’re still paying them every month … and there’s no competition,” Neal says.
Samantha Laws, who gets her Internet through her cable provider, says she also only has one option.
“It goes out at least once a day, and it’s been getting worse the last few months,” Laws says. She works with a pet-sitting company that handles all of its scheduling through email and the company website. At times she can’t do her job because of the unreliable connection.
Chicago is in Comcast’s territory and the company is quite comfortable cashing your check while AT&T takes its sweet time launching U-verse in the Windy City. AT&T isn’t about to throw money at improving DSL while local residents wait for U-verse and Comcast doesn’t need to spend a lot in Chicago when the alternative is AT&T.
 Where there is no disruptive new player in town to shake things up, there is little incentive to speed broadband service up. But there is plenty of room to keep increasing prices for a service that is becoming as important as a working telephone. Companies are using broadband profits to cover increasing losses from pay television service, investing in stock buybacks, paying dividends to shareholders, or just putting the money in a bank, often offshore.
Where there is no disruptive new player in town to shake things up, there is little incentive to speed broadband service up. But there is plenty of room to keep increasing prices for a service that is becoming as important as a working telephone. Companies are using broadband profits to cover increasing losses from pay television service, investing in stock buybacks, paying dividends to shareholders, or just putting the money in a bank, often offshore.
“[For] at least 77 percent of the country, your only choice for a high-capacity, high-speed Internet connection is your local cable monopoly,” says Susan Crawford, a visiting professor at Harvard Law School. She is also the author of Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age.
Crawford says that today’s high-speed Internet infrastructure is equivalent to when the railroad lines were controlled by a very few moguls who divided up the country between themselves and gouged everybody on prices.
She says the U.S. has fallen behind other countries in providing broadband. At best, Crawford says, the U.S. is at the middle of the pack and is far below many countries when it comes to fiber optic penetration. Given that the Internet was developed in the U.S., she says the gap is a result of failures in policy.
“These major infrastructure businesses aren’t like other market businesses,” Crawford says. “It is very expensive to install them in the first place, and then they build up enormous barriers of entry around them. It really doesn’t make sense to try to compete with a player like Comcast or Time Warner Cable.”
So Crawford is calling for is a major public works projects to install fiber optic infrastructure — a public grid that private companies could then use to deliver Internet service.

Powell
That’s an idea met with hand-wringing and concern-trolling Revolving Door Olympian Michael Powell, who made his way from former chairman of the Federal Communications Commission during the first term of George W. Bush’s administration straight into the arms of Big Cable as president of their national trade association, the NCTA.
Powell, well compensated in his new role representing the cable industry, wants Americans to consider wireless 3G and 4G broadband (with usage caps as low as a few hundred megabytes per month) equivalent competitors to the local cable and phone company.
“I think to exclude [wireless] as a substitutable, competitive alternative is an error that leads you to believe the market is substantially more concentrated that it actually is,” Powell says.
Of course, Powell’s new career includes a paycheck large enough to afford the wireless data bills that would shock the rest of us. All that money also apparently blinds him to the reality the two largest wireless providers in America are AT&T and Verizon — the same two companies that are part of the duopoly in wired broadband. It’s even worse in Canada, where Rogers, Bell, and Telus dominate wired and wireless broadband.
Although America isn’t even close to having the fastest broadband speeds, Powell wants you to know the speeds you do get are good enough.
“I think taking a snapshot and declaring us as somehow dangerously falling behind is just not substantiated by the data,” he says. He says it is like taking a snapshot of speed skaters, where there might be a few seconds separating the leaders, but no one is “meaningfully out of the race.”
 That is why we still celebrate and honor Svetlana Radkevich from Belarus who competed in the speed skating competition at the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics. She made it to the finish line and ranked 33rd. Ironically, South Korea ranked fastest overall that year, taking home three gold and two silver medals. In Powell’s world, that’s a distinction without much difference. You don’t need South Korean speed and gold medals when Belarus is enough. That argument always plays well in the United States, where Americans can choose between Amtrak or an airline for a long distance trip. Who needs a non-stop flight when a leisurely train ride will get you there… eventually.
That is why we still celebrate and honor Svetlana Radkevich from Belarus who competed in the speed skating competition at the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics. She made it to the finish line and ranked 33rd. Ironically, South Korea ranked fastest overall that year, taking home three gold and two silver medals. In Powell’s world, that’s a distinction without much difference. You don’t need South Korean speed and gold medals when Belarus is enough. That argument always plays well in the United States, where Americans can choose between Amtrak or an airline for a long distance trip. Who needs a non-stop flight when a leisurely train ride will get you there… eventually.
There are a handful of providers uncomfortable with the mediocre broadband slow lane. Google is among them. So are community broadband providers installing fiber broadband and delivering gigabit Internet speeds. EPB in Chattanooga is among them, and it has already made a difference for that city’s digital economy neither AT&T or Comcast could deliver.
Unsurprisingly, Powell thinks community broadband is a really bad idea because private companies are already delivering broadband service — while laughing all the way to the bank.
If a community really wants gold medal broadband, Powell says, they should be able to have it. But Powell conveniently forgets to mention NCTA’s largest members, including Comcast and Time Warner Cable, spend millions lobbying federal and state governments to make publicly owned broadband illegal. After all, cable companies know what is best.
All Things Considered recently asked its fans on Facebook, “How satisfied are you with your Internet service provider?” Many responded that they didn’t like their Internet service, that it often goes out and that their connection was often “painfully slow.” Listen to the full report first aired Jan. 11, 2014. (11:30)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.


 Subscribe
Subscribe The Weather Channel has been removed from DirecTV’s lineup and replaced with WeatherNation, a much-smaller channel based in St. Paul, Minn., because the popular weather network reportedly sought a $0.01 monthly rate increase.
The Weather Channel has been removed from DirecTV’s lineup and replaced with WeatherNation, a much-smaller channel based in St. Paul, Minn., because the popular weather network reportedly sought a $0.01 monthly rate increase. The Weather Channel has launched a campaign to restore the network that carries the impression DirecTV does not care about the safety of their customers. The Weather Channel executives have stated their severe weather coverage is unparalleled and would leave satellite dish customers in rural areas without important information about dangerous weather.
The Weather Channel has launched a campaign to restore the network that carries the impression DirecTV does not care about the safety of their customers. The Weather Channel executives have stated their severe weather coverage is unparalleled and would leave satellite dish customers in rural areas without important information about dangerous weather.
 As expected for months, Charter Communications, Inc. today formally offered Time Warner Cable shareholders $132.50 per share to assume ownership of the nation’s second largest cable operator in a deal worth more than $61 billion, including debt.
As expected for months, Charter Communications, Inc. today formally offered Time Warner Cable shareholders $132.50 per share to assume ownership of the nation’s second largest cable operator in a deal worth more than $61 billion, including debt.

 “Since we made our first proposal, Time Warner Cable has lost another half million video customers,” Rutledge said. “Their customer service continues to decline in every measure. We can improve it. We have a demonstrated track record of improving customer service. It’s a question of credibility.”
“Since we made our first proposal, Time Warner Cable has lost another half million video customers,” Rutledge said. “Their customer service continues to decline in every measure. We can improve it. We have a demonstrated track record of improving customer service. It’s a question of credibility.” After years of inaction, northern Canada will finally see improved telecommunications services that the rest of us have taken for granted for at least a decade.
After years of inaction, northern Canada will finally see improved telecommunications services that the rest of us have taken for granted for at least a decade.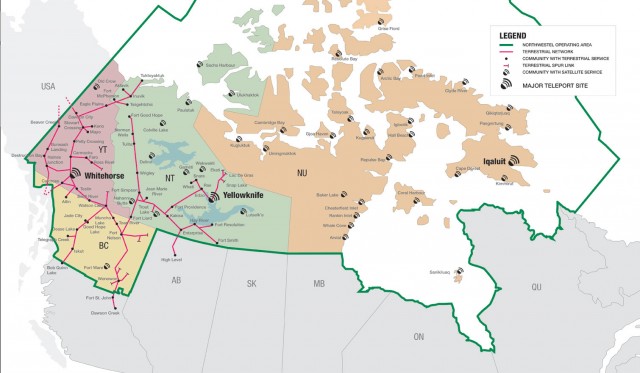
 The CRTC has been unimpressed with the Bell Canada subsidiary’s performance, noting the quality of service is well behind the rest of Canada. The Commission has placed a four-year price cap on services and has broken up NorthwesTel’s near-monopoly on service by ordering it sell landline, Internet, and other voice services separately, which opens the door for new competitors to emerge. New entrants could either develop their own networks or resell service purchased wholesale from the phone company.
The CRTC has been unimpressed with the Bell Canada subsidiary’s performance, noting the quality of service is well behind the rest of Canada. The Commission has placed a four-year price cap on services and has broken up NorthwesTel’s near-monopoly on service by ordering it sell landline, Internet, and other voice services separately, which opens the door for new competitors to emerge. New entrants could either develop their own networks or resell service purchased wholesale from the phone company. Time Warner Cable lost another 215,000 video subscribers during the fourth quarter of 2013, leaving the company with 825,000 fewer subscribers than it had one year ago.
Time Warner Cable lost another 215,000 video subscribers during the fourth quarter of 2013, leaving the company with 825,000 fewer subscribers than it had one year ago.