
Phillip “The new unofficial spokesperson for Time Warner Cable?” Dampier
I testified last evening at the Buffalo Public Information Meeting held by the New York Public Service Commission on the merger of Comcast and Time Warner Cable.
The regulator invited four witnesses to testify about the merger last evening. The other three:
- Mark E. Reilly, Comcast’s senior vice president of government affair, northeast division (for);
- Aaron Bartley, executive director of PUSH Buffalo (against);
- Christine Carr, executive director of Computers for Children (neutral).
The meeting was sparsely attended with only about two dozen in the audience, a good number of those arriving from Rochester. Also in attendance were groups with direct financial connections to Comcast, some partly disclosed during the evening, others not. Readers will not be surprised they were strongly in favor of the merger. Common Cause was represented and was clearly against the merger, although their representative also had harsh words for Time Warner Cable.
Niagara County Legislator David E. Godfrey (R-Wilson) and Orleans County Legislator Lynne M. Johnson (R-Lyndonville), representing the Niagara Orleans Regional Alliance, spoke on behalf of rural New Yorkers who lack broadband service. Neither went on record opposing the merger but seemed to suggest its approval be tied to a rural broadband solution. The record on successfully pulling that off in earlier deals has been mixed at best. The cable industry treats its Return On Investment formulas like a biblical text. If expanding service isn’t going to make the companies money in the short term, it is very unlikely to happen. We believe New York’s broadband subsidy program is a better deal for consumers if it means keeping Comcast out of New York.
The audience was almost entirely silent during the event and it wrapped up earlier than originally planned. Buffalo seemed less engaged on broadband issues than I would have expected. Had the hearing been held in Rochester, I have no doubt the audience would have been far larger. Broadband matters in Rochester have always drawn crowds and significant news coverage. One Buffalo resident offered that the PSC chose its meeting location poorly — on “an out of the way” college campus in Amherst now in summer session that charges for parking (although we did park for free). Others have told us the meetings were poorly advertised. Thankfully, the PSC is keeping the record open for comments in writing and by phone.
The strongest contrast of views came from testimony from Mr. Reilly and myself, although the meeting was not configured as a debate.

Reilly
Mr. Reilly did not seem well-informed about specifics regarding Comcast’s products and pricing. He stumbled through incomplete answers when asked directly (twice) to compare Comcast’s prices against Time Warner Cable. Unfortunately, the question and answer session did not allow for interjection from other witnesses, because if it did, I was more than ready to help Mr. Reilly answer that question because I brought the rate cards for both companies with me. Perhaps he did not want to answer, because as the evidence clearly shows, Comcast costs more.
He also implied Comcast had widely deployed up to 505Mbps broadband service in its service area. Speeds of 300-500Mbps are offered only to a limited number of customers that can, number one afford the high asking price ($300/month plus installation fee) and second are passed by Comcast’s fiber or Metro Ethernet networks.
We also disagreed over usage caps. Reilly claimed the average Comcast customer used just 17GB a month. Comcast’s own website claims median monthly data usage is 20-25GB per month. But according to Digital Trends, the average family with Internet-only service uses 212GB of data each month — more than seven times those who watch traditional television. That is because after cutting cable-TVs cord, they are watching shows over their broadband connection. That number is rising, and fast. Over the four years Comcast had a nationwide cap, it did not adjust it upwards even once to account for broadband growth.
Independent analysis from Sandvine found that Internet users, in general, are accessing increasingly larger amounts of data. The overall mean usage on North American fixed-access networks (as opposed to mobile networks) was 51.4 GB in March, which is up from the 44.5 GB noted in Sandvine’s most recent previous study. Cord-cutters as a whole now dominate network usage, accounting for a 54-percent majority of total monthly network traffic. Cord-cutters are also responsible for some of the cable industry’s biggest revenue challenges with their television packages.
The old industry meme that usage caps affect only a tiny minority of customers was also trotted out. We did not have the opportunity to ask, “if only a tiny percentage of customers exceed their allowance, why bother with usage caps at all?”
Time Warner Cable was not represented at the meeting, and in an ironic twist, that left me as their unofficial spokesbooster. In fact, nobody seemed aware of Time Warner Cable’s Maxx upgrade program which is delivering faster, more affordable Internet access than Comcast offers over its cable broadband network without the threat of looming usage caps.

Jump through hoops for $9.95 Internet
Internet affordability emerged as a major topic last evening. Predictably Comcast touted its $9.95 Internet Essentials program without mentioning its highly restrictive pre-qualification requirements:
The program is only available to households that (i) are located where Comcast offers Internet service; (ii) have at least one child who receives free/reduced rate school lunches through the National School Lunch Program (the “NSLP”) and as confirmed annually while enrolled in the program; (iii) do not have an overdue Comcast bill or unreturned equipment; and (iv) have not subscribed to any Comcast Internet service within the last ninety (90) days (sections 1(i)-(iv) collectively are defined as “Eligibility Criteria”). The program will accept new customers for three (3) full school years, unless extended at the sole election of Comcast. Comcast reserves the right to establish enrollment periods at the beginning of each academic year in which it accepts new customers that may limit the period of time each year in which you have to enroll in the program.
2. In order to confirm your eligibility for the program, Comcast will need to verify that your children receive free/reduced rate school lunches through the NSLP in the initial enrollment year and each subsequent year you are enrolled in the program. In order to confirm eligibility, participants in the program will be required to provide copies of official documents establishing that a child in the household is currently receive free/reduced rate school lunches through the NSLP. Each year you will be required to reconfirm your household’s current eligibility by providing Comcast or its authorized agent with up-to-date documentation. If you fail to provide documentation proving your eligibility in the program, you will be deemed no longer eligible to participate in the program.
3. You will no longer be eligible to participate in the program if (i) you no longer have at least one child living in your household who receives free/reduced rate school lunches under the NSLP; (ii) you fail to maintain your Comcast account in good standing; (iii) Comcast ceases to provide the Covered Service to your location; or (iv) your account opened under the program is closed. A change in address may result in your account being closed, even if you continue to receive Comcast services at a different address. Program participation also may be terminated if the Covered Service is upgraded, altered or changed by you for any reason. If you are no longer eligible for the program, but continue to receive the Covered Service from Comcast, regular rates, and any other applicable terms and conditions will apply to the Covered Service.
In brief, you can only qualify if you don’t have Comcast Internet service already. If you do, Comcast demands you stay without Comcast Internet service for at least 90 days before applying (good luck making that work). This is nothing more than a revenue protection mechanism for Comcast so that customers don’t downgrade to discounted Internet. Only poor families with school age children qualify and Comcast intrusively re-verifies eligibility regularly. Had a past due bill in the past or loss/stolen equipment? You are not qualified. Miss a payment? Comcast can kick you off the program. Try to upgrade any part of your Comcast package? You are done with Internet Essentials. Move to a new address? Your Internet discount isn’t going with you.
John Randall from the Roosevelt Institute came to a similar conclusion:
Comcast’s Internet Essentials program does more to benefit Comcast’s customer acquisition, public relations, and lobbying departments than to help people in America who need high-speed Internet access at a reasonable price. The reality is that the program is a cleverly designed customer acquisition program that benefits Comcast’s bottom line.
It was also a cynical way to help Comcast win approval of its merger with NBCUniversal. Comcast held back the program until they could use it as a political chip in their merger lobbying campaign. As we reported back in 2012:
In 2009, Comcast insiders were hard at work on a discount program for the disadvantaged who could not afford Comcast’s regular prices for broadband service. But the program was stalled at the direction of Cohen, who wanted it to be a chip with regulators to win approval of its acquisition of NBC-Universal. The program, sure to be popular among advocates of the digitally disadvantaged, was a key part of approving the $30 billion deal.
“I held back because I knew it may be the type of voluntary commitment that would be attractive to the chairman [of the FCC],” Cohen said in a recent interview.

You would probably take this used car to a mechanic before deciding whether to buy. Why doesn’t Comcast know the state of Time Warner’s cable systems before they made a $45 billion offer?
Lastly, Mr. Reilly repeatedly confessed Comcast did not know the state of Time Warner Cable’s system and equipment and could not answer questions about precisely how much Comcast would invest in upgrades. He admitted Comcast’s part-acquisition of Adelphia Cable (its systems were largely divided up between Comcast and Time Warner) resulted in a major under-estimate of repair and upgrade work required.
If I buy a used car, I take it to an expert who can describe its current condition, alert me to likely service required both now and in the near future, and predictions about the vehicle’s anticipated lifetime. Apparently Comcast buys cable systems sight-unseen.
It was widely known in the industry at the time that troubled Adelphia Cable properties were neglected as the company neared bankruptcy. Imagine Adelphia as a metaphor for the state of Sears or K-Mart these days.
Two members of the Rigas family that founded Adelphia were convicted on multiple charges of securities fraud, conspiracy to commit bank fraud and bank fraud. Prosecutors said the Rigases hid the fact the company was dangerously overextended with $2.3 billion in unreported debts. The family used the company’s bank accounts to finance a range of personal follies, including 100 pairs of slippers for Timothy Rigas and more than $3 million to produce a film by John Rigas’ daughter. We don’t know if the film was actually any good.
At the end of the evening in Buffalo, we were still left with the impression Comcast’s promises and commitments were vague and the much-touted benefits were much to be desired as soon as you began reading the fine print.
But frankly, I was disappointed by the low turnout. Consumers who do not want Comcast to be their next Internet provider -must- make their feelings known or that is precisely what is going to happen. We need all New Yorkers within travel distance of Albany or New York City to pack the PSC’s meeting rooms and have the courage to get up and speak. You can talk for 30 seconds or 3-5 minutes. You can also write or call the PSC if you want to extend your remarks in writing. New Yorkers have the power to throw a major wrench into a deal very few of us wants. But only if they make their voices heard:
Wednesday, June 18
SUNY Albany
Performing Arts Center
1400 Washington Avenue
Albany
6:00 pm: Informational Forum
7:30 pm: Public Statement Hearing
Thursday, June 19
NYS DPS Office
90 Church Street
New York
Please bring ID with you.
6:00 pm: Informational Forum
7:30 pm: Public Statement Hearing
Those who cannot attend or prefer not to speak at a public statement hearing may comment electronically to Hon. Kathleen H. Burgess, Secretary, at [email protected] or by mail or delivery to the Secretary at the Public Service Commission, Three Empire State Plaza, Albany, New York 12223-1350. Comments should refer to “Case 14-M-0183, Petition of Comcast Corporation and Time Warner Cable Inc.”
Toll-Free Opinion Line: You may call the Commission’s Opinion Line at 1-800-335-2120. This number is set up to take comments about pending cases from in-state callers, 24 hours a day. Press “1″ to leave comments, mentioning the Comcast/Time Warner merger.
All comments provided through these alternative methods should be submitted, or mailed and postmarked, no later than July 31, 2014. All such statements and comments will become part of the record and be reported to the Commission for its consideration.
All submitted comments may be accessed on the Commission’s Web site at www.dps.ny.gov, by searching Case 14-M-0183.


 Subscribe
Subscribe


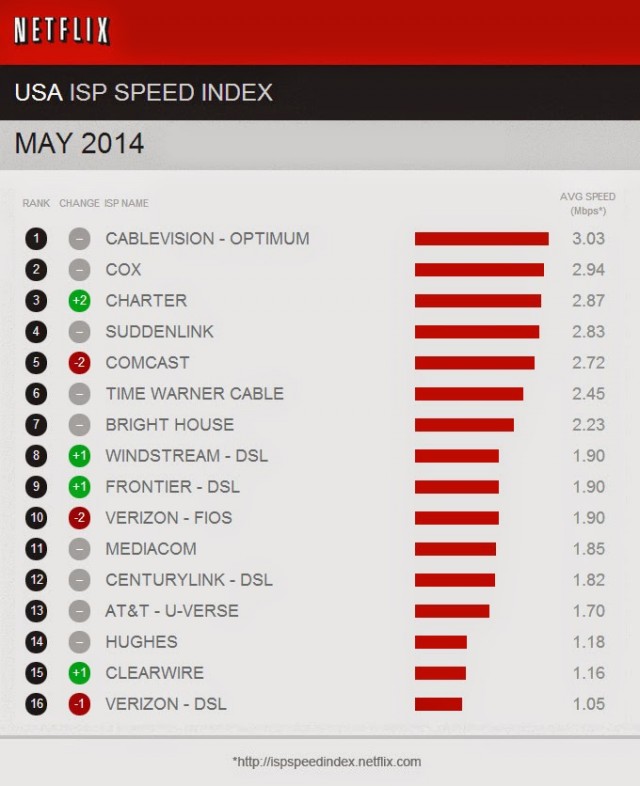


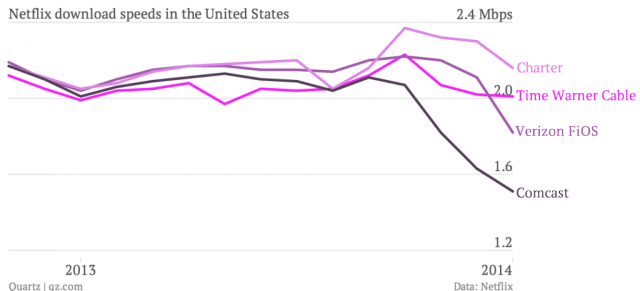
 The companies with the biggest drops in Netflix performance are the same ones strongly advocating special paid “fast lanes” on the Internet for preferred traffic to resolve exactly these kinds of performance problems.
The companies with the biggest drops in Netflix performance are the same ones strongly advocating special paid “fast lanes” on the Internet for preferred traffic to resolve exactly these kinds of performance problems.
 Subscribers of more than 900 independent cable companies may face an unwelcome surprise this summer in the form of a mid-year rate increase.
Subscribers of more than 900 independent cable companies may face an unwelcome surprise this summer in the form of a mid-year rate increase. “I don’t like to do this because it puts me in a difficult position of raising prices, which no one likes, or reducing the product, which no one likes, or cutting back on the quality of our customer service, which no one likes,” said Gessner. “Large media companies control all the TV programming and they are raising the price. The cost of TV programming is rising very rapidly and it is causing this rise in retail prices.”
“I don’t like to do this because it puts me in a difficult position of raising prices, which no one likes, or reducing the product, which no one likes, or cutting back on the quality of our customer service, which no one likes,” said Gessner. “Large media companies control all the TV programming and they are raising the price. The cost of TV programming is rising very rapidly and it is causing this rise in retail prices.”

