
Nick Jeffery will be appointed president and CEO of Frontier Communications effective March 1, 2021, succeeding Bernie Han.
Frontier Communications today announced a “holistic transformation” of its business from a copper-based landline company to a fiber to the home internet service provider, with plans to eventually offer fiber to the home service to nearly six million residential customers, approximately three million already served by fiber networks acquired from Verizon and AT&T.
As part of that transformation, Frontier today announced yet another new CEO, Nick Jeffery, will take over from current CEO Bernie Han in March 2021. Jeffery was CEO of Vodafone UK, one of Great Britain’s largest mobile operators. Jeffery agreed to replace Han, who became CEO and president only a year ago, in return for a $3.75 million signing bonus, a $1.3 million annual salary, and eligibility for more than $8 million in annual bonuses and equity awards.
“I am honored to be appointed Frontier’s next CEO, and I am excited to lead the company in its next phase,” Jeffery said in a statement. “Frontier owns a unique set of assets and maintains a competitive market position. My immediate focus will be on serving our customers as we enhance the network through investments in our existing footprint and in adjacent markets while building operational excellence across the organization.”
Frontier has been in Chapter 11 bankruptcy since April 2020 and is being reorganized to eliminate about $10 billion in debt and another billion annually in debt-servicing interest payments. Frontier’s bankruptcy plan will give four investment firms — Elliott Management, Franklin Mutual, Golden Tree Asset Management, and HG Vora, effective control over Frontier. The four are reportedly behind the decision to install Jeffery as Frontier’s new CEO to protect their financial interests. He has a reputation of repairing damaged customer relationships and improving sales, while also being willing to cut costs and simplify services sold to customers. Jeffery will also be joined by former Verizon executive John Stratton, who has accepted a position of executive chairman of the board. Jeffery is expected to lead the company out of bankruptcy sometime in early 2021.
Frontier has repeatedly promised to retire significant parts of its copper wire network and expand fiber to the home service, but over the last decade most of Frontier’s fiber footprint has been acquired from other phone companies, notably Verizon and AT&T. Most of Frontier’s own fiber expansion has come from installing service in new housing developments and in rural areas where it received taxpayer or ratepayer-funded subsidies to expand service to unserved areas.
In a conference call held earlier today, Frontier executives signaled the company will not hurry to deliver fiber upgrades to Frontier customers. In some of the most opaque language ever uttered in a Frontier conference call, company officials warned some Frontier customers may actually find themselves sold to another service provider. The company plans to divide its copper customers into two categories: those destined to be a part of Frontier’s fiber future and those left stuck on copper or sold off after Frontier “strategically reevaluates individual state operating performance employing a virtual separation framework” — all to “optimize our returns on invested capital.”
Frontier emphasizes its planned total of “nearly 6 million fiber-enabled households” will come to fruition “over the long term.” In 2020, the company plans to bring fiber service to approximately 60,000 new households in six states, many in new housing developments Frontier was already expected to serve.
Frontier’s modernization plan will likely sell unprofitable service areas and selectively upgrade many customers over a ten-year period to fiber optics. (Source: Frontier Communications)
“We have completed construction of about 60% of our target locations and continue to ramp quickly and remain on target to reach our year-end goals,” said Han. “Although, it is still very early in the process, our offer is very appealing to customers. While we are successfully converting existing copper customers to fiber, most of our early gains are coming from winning net new customers. Early penetration and ARPUs are performing at or above targets.”
 In 2021, the company announced it had “planning and engineering” underway for unspecified fiber to the home service upgrades in copper service areas “in select regions.” But most of Frontier’s fiber upgrades will take place over the next decade. Specifically, Frontier plans to wire up to 2.9 million homes with fiber using a combination of its own money and subsidy funds provided by the FCC. Frontier’s new owners have signaled they will not go out on a limb to finance rapid fiber upgrades, and you better live in a state where fiber upgrades are being given priority.
In 2021, the company announced it had “planning and engineering” underway for unspecified fiber to the home service upgrades in copper service areas “in select regions.” But most of Frontier’s fiber upgrades will take place over the next decade. Specifically, Frontier plans to wire up to 2.9 million homes with fiber using a combination of its own money and subsidy funds provided by the FCC. Frontier’s new owners have signaled they will not go out on a limb to finance rapid fiber upgrades, and you better live in a state where fiber upgrades are being given priority.
“Of the 2.9 million new fiber homes passed for the modernization plan, roughly 2.6 million of them are in […] California, Texas, Florida and Connecticut and […] West Virginia, Illinois, New York and Ohio,” Han noted.
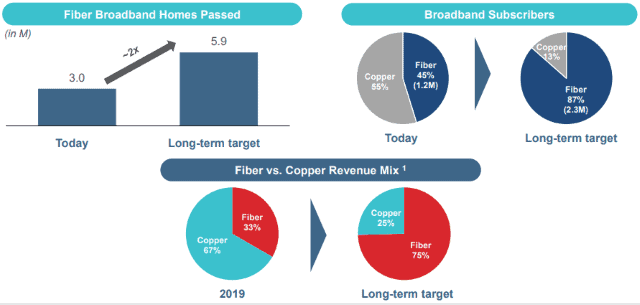
“The modernization plan is expected to be completely self-funding […] and has been developed with strict return on capital hurdles, allowing for very attractive returns,” said Robert A. Schriesheim, chairman of the Frontier’s Finance Committee of the Board. “The expected shift in the subscriber base from the modernization plan will increase the percent of fiber subs from 45% today to 87% over the plan horizon and will drive a transformation of business mix that is expected to result in 75% of revenue coming from fiber products in the long-term as compared to about one-third today.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 The FCC
The FCC  Verizon customers in over 1,800 cities across the United States can now get a speed boost with the launch of Verizon’s nationwide Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) 5G, which runs simultaneously with existing 4G LTE on the same lower band spectrum, giving customers with 5G-capable devices faster service.
Verizon customers in over 1,800 cities across the United States can now get a speed boost with the launch of Verizon’s nationwide Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) 5G, which runs simultaneously with existing 4G LTE on the same lower band spectrum, giving customers with 5G-capable devices faster service. AT&T stopped accepting orders for traditional DSL service from customers across its landline service area on Oct. 1, and will no longer allow existing customers to change speeds or transfer DSL service if they move to a new address.
AT&T stopped accepting orders for traditional DSL service from customers across its landline service area on Oct. 1, and will no longer allow existing customers to change speeds or transfer DSL service if they move to a new address. Only AT&T’s DSL service has been discontinued. The company claims about a half million customers still get DSL service from AT&T as of the second quarter of 2020. Most don’t choose DSL by choice. It is often the only option, because the customer lives in a rural area where no other options for internet service exist. That may leave some new customers with no options for wired internet service at all.
Only AT&T’s DSL service has been discontinued. The company claims about a half million customers still get DSL service from AT&T as of the second quarter of 2020. Most don’t choose DSL by choice. It is often the only option, because the customer lives in a rural area where no other options for internet service exist. That may leave some new customers with no options for wired internet service at all.