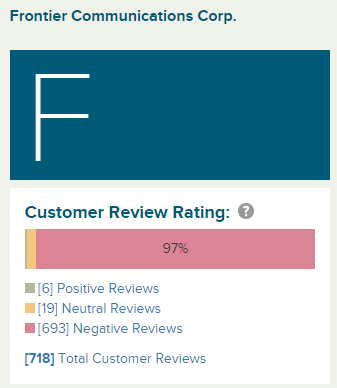
We will mail it to you on floppy disks because your internet connection is too slow to download it.
While FCC Chairman Ajit Pai and Sen. Ron Johnson (R-Wisc.) decry government regulation as responsible for destroying capital and incentives to invest, the state of Kansas this week ended its all-out experiment with deregulation and trickle-down economics on steroids, with a Republican-dominated state legislature calling it a giant flop.
In charge of the Grand Experiment in Trickle-Down, Doubled-Down is Gov. Sam Brownback, who has systematically hobbled the state’s social spending and investment programs since becoming governor in 2011. He adopted his ‘vision thing’ from Reaganomics proponent Art Laffer, who apparently forgot the Reagan Administration’s penchant for all things deregulation was not all sweetness and light and had to be tempered by President George H.W. Bush after he was elected in 1988.
But what if history could have a second chance? What if a state kept its pledge of no new taxes and slashed regulation and oversight to the bone. Would it result in a free market paradise where government got out of the way for the public good? Would lower taxes result in more tax revenue as Kansas businesses boomed? Would infrastructure take care of itself?
To find out, Brownback slashed the state’s income tax, eliminated the top income tax bracket and delivered a disproportionate share of the tax cut benefits to the economic motivators (also known as Kansas’ richest families) who would supposedly use the surplus to invest in businesses and jobs. At the urging of the powerful small business lobby, backed by the Koch Brothers and their octopus of astroturf anti-tax groups demanding reform, Brownback zeroed out taxes on “pass-thru” income, which effectively allowed anyone running a LLC or small business to evade taxes.
There were moderate Republicans in Kansas that warned about the prospects of Brownback’s questionable assertion that low taxes and low funding of the state government would bring a new era of growth and prosperity. But dark money and Koch’s political machine saw to it those politicians were “de-elected” and replaced with Brownback’s army of minions.
In addition to creating budgetary ruin with tax revenue cratering, essential digital infrastructure crashed and burned. Deregulation and a mediocre state broadband expansion effort didn’t make internet service in Kansas better. In fact it got worse, along with the finger-pointing over who was responsible.
Last fall, Kansas Sen. Pat Roberts brought then FCC commissioner Ajit Pai to the community of Allen to meet with executives working for a dozen small telephone companies who were having trouble upgrading their networks across the great expanse of rural Kansas.

Brownback
Roberts wasn’t ready to claim federal government regulation was responsible for the mess. But Pai’s reflexive claims that deregulation incentivizes for-profit companies to invest in better broadband simply wasn’t working in Kansas either. The only solution for The Free Marketeers in rural Kansas turns out to be handing out government money to expand rural broadband, except in Kansas, there was very little money to be had after Brownback took an ax to the state budget.
The Wichita Eagle unintentionally drew a contrast between the thinking of providers that want to blame everyone else for the problem and plain reality for Brian Thomas, who works for the Blue Valley Tele-Communications Company.
“It really all comes down to a quality of life perspective,” Thomas told the newspaper. “I think we all live that. That’s our jobs, to provide that.”
The newspaper noted that without government money, the only way private companies could afford to pay to replace thousands of miles of ancient copper phone wiring in favor of fiber would be to make internet service so expensive that only businesses and the ultra-wealthy would be able to afford it.
So while Brownback’s great social experiment carried on, internet expansion and upgrades stalled in many communities across Kansas. In Allen, where Pai met to extol the virtues of private investment, the town librarian at Allen’s public library got some help from the Manhattan (Kansas) library system to install an inexpensive Wi-Fi hotspot that, once switched on, almost immediately filled its parking lot day and night with what the newspaper called “internet-starved townspeople.”
Allen County, Kan.
“There are several people who will watch movies outside” after hours, town librarian Nikki Plankington said. “The kids use it for the Pokemon Go thing. I don’t know what that’s all about, but the kids use it.”
While the public library did its part, Kansas’ for-profit private internet providers are going in a different direction – complaining a lot and asking for handouts with no strings attached.
The Eagle reported Pai’s meeting with rural telecom executives turned into a ‘whine and cheese’ reception. The phone companies had a laundry list of dislikes they wanted the deregulation-minded Pai to fix for them while they pondered upgrades:
- The Universal Service Fund/Connect America Fund, financed by ratepayers through surcharges on their phone bills, was “obsolete” and didn’t provide enough money.
- The federal government didn’t allow ISPs to chase after the deepest pockets to pay for their upgrades — popular online websites like Netflix and Amazon.com.
- The FCC’s definition of broadband as 25Mbps ignored the fact Kansas phone companies wanted to deliver considerably lower speed service, claiming customers don’t want more than 10Mbps.
If the government could be lobbied to lower standards, eliminate regulation, and deliver or at least compel a cash welfare infusion from content providers and ratepayers, there was no need to ask rich Kansans to stop counting their money long enough to invest some of it in better broadband.
 Catherine Moyer from Pioneer Communications claimed it was unfair to ask companies and customers to pay for upgrades when those internet titans like Netflix, Amazon, and Google make countless billions in profits using Pioneer’s network with absolutely no compensation for doing so.
Catherine Moyer from Pioneer Communications claimed it was unfair to ask companies and customers to pay for upgrades when those internet titans like Netflix, Amazon, and Google make countless billions in profits using Pioneer’s network with absolutely no compensation for doing so.
“My customers and the customers here in Allen and all the customers in Wichita for that matter that have voice service pay a proportion of their bill,” she said. But, “there’s a whole group of people and companies utilizing the network that don’t pay into the fund in any meaningful way … so they haven’t helped build out this network.”
When the newspaper suggested she was effectively asking for higher taxes and paid lanes for internet content companies like Netflix that Moyer claimed was consuming 35% of Pioneer’s available bandwidth, she didn’t seem to have any objections.
“It’s not necessarily what people want to see, but in the same light, if you want these networks and you want these speeds, you have to somehow fund that. And who should fund it?” Moyer asked.
The next issue that doesn’t work for Kansas telecom companies is the FCC’s standard that broadband service be at least 25Mbps, and if a phone or cable company wants public dollars to build out their networks, they better choose a technology capable of delivering that kind of speed.
 “One thing that kind of concerns me a little bit is having the FCC dictate, or Washington dictate, the level of speed I’m required to have in order to maintain a certain level of funding,” said Archie Macias of Wheat State Telephone, which serves rural communities in Butler, Cowley, Chase and Lyon counties. Macias is upset because his system uses fiber optics that can easily handle 25Mbps, but his customers only want to pay for 10Mbps.
“One thing that kind of concerns me a little bit is having the FCC dictate, or Washington dictate, the level of speed I’m required to have in order to maintain a certain level of funding,” said Archie Macias of Wheat State Telephone, which serves rural communities in Butler, Cowley, Chase and Lyon counties. Macias is upset because his system uses fiber optics that can easily handle 25Mbps, but his customers only want to pay for 10Mbps.
“I’m not going to build a network that’s like having 500 channels on a TV that you’re going to watch 12 or 13,” he told the newspaper.
Wheat State currently offers four broadband plans in areas where fiber service is available:
- $39.99 Pro (10/2Mbps)
- $49.99 Multi-Pro (15/3Mbps)
- $69.99 Power-Pro (25/5Mbps)
- $79.99 Mega-Pro (50/20Mbps)
- $10 discount when bundled with other services
What customers choose for broadband service is often an issue of pricing, not speed.
In more populated parts of Kansas, customers are still trying to cope with DSL service that has not seen significant upgrades for a decade. Since Brownback isn’t doing much to help, and tax cuts and deregulation have failed to inspire the kind of robust broadband expansion “light touch” regulation is supposed to provoke, a lot of Kansans are leaving the state for good.

An abandoned farm.
One of those threatening to flee is Christianne Parks, who lives in Allen and endures not-even-close-to-being-broadband.
“Eventually, I probably would get bored out of my mind and leave,” 19-year old Parks told the newspaper when asked what she would do if her broadband situation did not change.
Last fall, the newspaper pinpointed some of the real problems afflicting the state’s economy and missing from the list were taxes and regulation. Deregulation-inspired consolidation in the state’s critical agribusiness sector decimated rural farms and the local economies that depended on them. When the farmers leave, Main Street businesses soon follow. The 1970s and 1980s was the era of the Rust Belt in the northeast and midwest. Now parts of the midwest including Kansas risk being labeled a Wheat Belt of economic deterioration.
Since 2000, 81 of Kansas’ 105 counties have lost population, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. The consensus is that trend will get worse, according to the newspaper – especially among young people – until and unless someone can find a way to get better internet service to the outlands. Brownback’s hands-off policies favoring providers are in contrast to New York’s more aggressive rural broadband funding program that seeks to achieve near 100% penetration of broadband service in the state over the next few years. New York regulators also compel companies doing business in the state to share some of their wealth from mergers and acquisitions, most recently requiring Charter Communications and Altice to expand their broadband networks to improve service and reach customers they don’t serve today.
The free-market-solves-everything concept celebrated by Pai and the Koch Brothers has now been tested and failed in Kansas. Among the few bright spots for broadband in Kansas are civic-minded telephone or cable providers that look beyond return on investment formulas in their community, and more commonly community-owned broadband networks or co-ops with a motive beyond profit — delivering decent broadband to maintain, sustain, and grow their local economies.
Recovery from the “free market miracle” train wreck started last fall, when a wave of moderate Democrats and Republicans were elected with a pledge to do everything possible to kill Brownback’s vision of paradise. This week, the Republican-dominated legislature had enough of living in Brownback’s PretendLand and overrode his veto of their plan to raise income taxes across the board and kill his legalized tax evasion scheme for business owners to bring in an additional $1.2 billion over the next two years to invest in Kansas.
The improved broadband that could result may give something for the state’s wealthiest citizens to do in their free time besides count their money.
 As Cox Communications continues to expand its arbitrary data cap program on its broadband customers, the company has announced a ‘cap relief’ option for customers willing to pay $50 more for the same service they enjoyed last year without a data cap.
As Cox Communications continues to expand its arbitrary data cap program on its broadband customers, the company has announced a ‘cap relief’ option for customers willing to pay $50 more for the same service they enjoyed last year without a data cap.

 Subscribe
Subscribe