
Morrow
Australia is learning a costly lesson finding ways to extend broadband service to rural areas in the country, choosing fixed wireless and satellite networks that will ultimately cost more than extending fiber optic broadband to rural customers.
Australia’s National Broadband Network (NBN) is tasked with supplying virtually all of Australia with internet access, using fiber/wired broadband in urban and suburban areas and fixed wireless and satellite internet access in the country’s most remote locations.
But just a few years after debuting satellite broadband and fixed LTE 4G wireless service in many parts of the country, demand has quickly begun to overwhelm capacity, forcing costly upgrades and punitive measures against so-called “heavy superusers.” The NBN has also scrapped plans to introduce higher-speed fixed wireless services, fearing it will only create additional demands on a network that was not envisioned to manage heavy broadband usage from video streaming.
NBN CEO Bill Morrow has elected to place most of the blame on his customers, specifically “superusers” that he characterized as “online gamers” who spend hours during the day and peak usage periods consuming large parts of the fixed wireless network’s available capacity.
“In the fixed wireless, there’s a large portion [of end users] that are using terabytes of data,” Morrow said. “We’re evaluating a form of fair use policy to say, ‘We would groom these extreme users.’ Now the grooming could be that, during the busy period of the day when these heavy users are impacting the majority, that they actually get throttled back to where they’re taking down what everybody else is taking down.”
 Under the current NBN fair use policy, monthly downloads per household are capped at 400 GB, with maximum usage during peak usage periods limited to 150 GB a month, which is already significantly less than what most average American households consume each month. With expensive and unexpected early upgrades to more than 3,100 cell towers to manage rapidly growing usage, the cost of service is starting to rise substantially, even as usage limits and speed reductions make these networks less useful for consumers.
Under the current NBN fair use policy, monthly downloads per household are capped at 400 GB, with maximum usage during peak usage periods limited to 150 GB a month, which is already significantly less than what most average American households consume each month. With expensive and unexpected early upgrades to more than 3,100 cell towers to manage rapidly growing usage, the cost of service is starting to rise substantially, even as usage limits and speed reductions make these networks less useful for consumers.
In areas where the NBN extends a fiber optic network, the fixed wholesale price for a 50/20 Mbps connection is $32.00 (U.S.) per month. (A 100/40 Mbps connection costs $46.25). For fixed wireless, prices are rising. A 50/20 Mbps fixed wireless connection (with usage cap) will now cost $46.25 a month.
Morrow took heat from members of Parliament over his claim that online gamers were chiefly responsible for slowing down the NBN’s fixed wireless network.
“With great respect to everything you said over the last 15 minutes, you have been saying to us the problem here is gamers,” said MP Stephen Jones (Whitlam).
Morrow clarified that online gamers were not the principal cause of congestion. The main issue is concurrency, which drags down network speeds when multiple family members unexpectedly use an internet connection at the same time. The worst congestion results when several family members launch internet video streams at the same time. Online video not only leads average users’ traffic, it can also quickly outstrip available cell tower capacity. High quality video streaming can quickly impact 4G LTE service during peak usage periods, driving speeds down for all users. The NBN now considers these newly revealed capacity constraints a limit on the feasibility of using wireless technology like LTE to supply internet access.
The current mitigation strategy includes limiting video bandwidth, discouraging video streaming with usage caps or speed throttles, capacity upgrades at cell towers, and public education requesting responsible usage during peak usage times. With capacity issues becoming more serious, Morrow canceled plans to upgrade fixed wireless to 100 Mbps speeds because of costs. The proposed upgrades would have cost “exponentially” more than wired internet access.
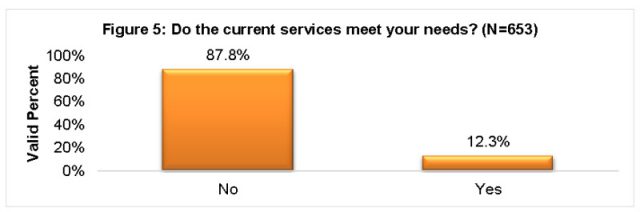
Hype vs. Reality: Most Australians reject fixed wireless and satellite internet as woefully inadequate. (Source: BIRRR)
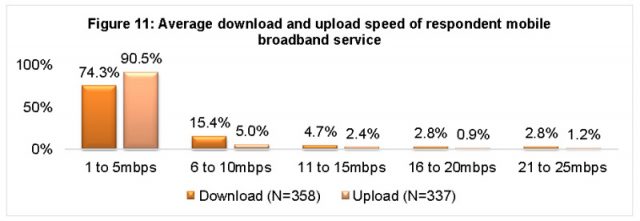
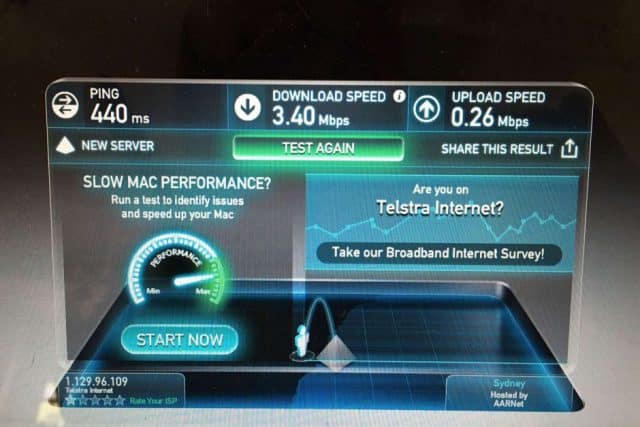
Actual Fixed Wireless speeds
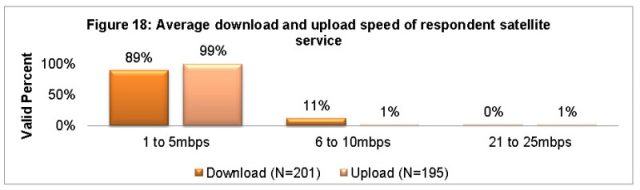
Actual Satellite Internet speeds
The concept of supplying fixed wireless or satellite internet access to rural areas may have made sense a decade ago, but there are growing questions about the suitability of this technology based on growth in consumer usage patterns, which increasingly includes streaming video. The cost to provide a sufficiently robust wireless network could easily rival or even outpace the costs of extending traditional fiber optic wired service to many rural properties currently considered cost prohibitive to serve. In Australia, fixed wireless and satellite has delivered sub-standard access for rural consumers, and requires the imposition of “fair usage” caps and speed throttles that inconvenience customers. For now, Morrow believes that is still the best solution, given that Australia’s national broadband plan relies heavily on wireless access in rural communities.
“[The benefit of a fair usage policy is] big enough to where if we did groom them during the busy time of the day, it would be a substantial [speed] lift for people,” he said. “I don’t think there’s a silver bullet in any of this – this is going to require us to think through a number of different areas.”
Better Internet for Rural, Regional and Rural Australia (a volunteer consumer group) shares horror stories about relying on satellite to solve rural broadband problems. (7:50)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “Our internet here is horrible, our provider is Frontier,” Monica King Von Holtum of Worthington in southwest Minnesota,
“Our internet here is horrible, our provider is Frontier,” Monica King Von Holtum of Worthington in southwest Minnesota, 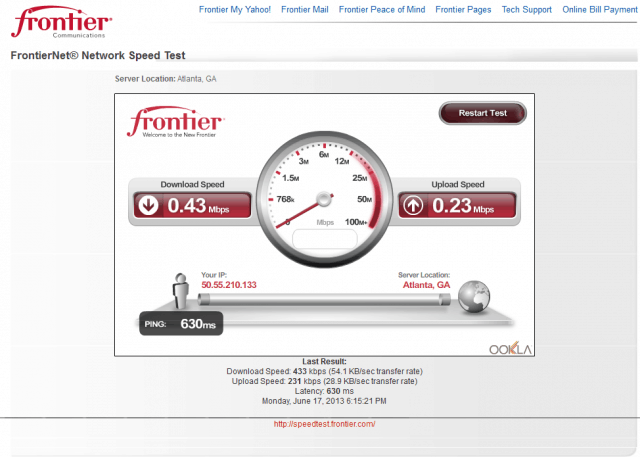


 REU is
REU is  Haslam’s Broadband Accessibility Act cynically retained these restrictions and blockades, hampering the rural broadband expansion the law was supposed to address.
Haslam’s Broadband Accessibility Act cynically retained these restrictions and blockades, hampering the rural broadband expansion the law was supposed to address.


 “Believe it or not, some of the biggest online games use very little data while you’re playing compared to streaming HD video or even high-fidelity audio,” the article stated. “Where streaming 4K video can use as much as 7 gigabytes per hour and high-quality audio streaming gets up to around 125 megabytes per hour, (but usually sits at around half that) certain online games use as little as 10MB per hour.”
“Believe it or not, some of the biggest online games use very little data while you’re playing compared to streaming HD video or even high-fidelity audio,” the article stated. “Where streaming 4K video can use as much as 7 gigabytes per hour and high-quality audio streaming gets up to around 125 megabytes per hour, (but usually sits at around half that) certain online games use as little as 10MB per hour.”