 Frontier Communications is scheduled to announce its emergence from bankruptcy reorganization as early as Friday, beginning a new era with a reduced debt load, new leadership, and a plan to retire a considerable amount of its copper wire network in favor of fiber optics over the next decade.
Frontier Communications is scheduled to announce its emergence from bankruptcy reorganization as early as Friday, beginning a new era with a reduced debt load, new leadership, and a plan to retire a considerable amount of its copper wire network in favor of fiber optics over the next decade.
“Frontier is ready to set a new course as a revitalized public company. Through the restructuring process, the company has stabilized its business and recapitalized its balance sheet, while making significant progress on the early stages of implementing our initial fiber expansion plan,” said John Stratton, incoming executive chairman of the board. “Frontier’s success with the Fiber-to-the-Home pilot program, which upgraded more than 60,000 locations from copper to fiber optic service in 2020, is just one example of the important work already underway. Frontier’s future is bright. I’m eager to work closely with our new board, our CEO Nick Jeffery, and the rest of the leadership team to build the new Frontier.”
As part of its reorganization, Frontier shed nearly $10 billion in debt, most attributable to its earlier buying spree of castoff landline customers formerly served by AT&T and Verizon. The company’s budget busting 2016 acquisition of Verizon service areas in California, Texas, and Florida was called “a textbook
For at least a decade covering 2010-2020, Frontier was regarded as one of the worst phone companies in America in consumer surveys. Most of its legacy customers still suffer with Frontier’s dilapidated and deteriorating copper wire network and the slow speed DSL service barely supported on it. Speeds of 1-3 Mbps maximum are still common in some places, even in urban areas. Frontier’s acquisition of Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse service areas in states like Indiana, Washington, Connecticut, Florida, Texas and California gave a minority of customers access to pre-built fiber to the home networks, but Frontier’s notoriously poor switchover from Verizon and AT&T’s billing systems to their own effectively drove off hundreds of thousands of formerly loyal customers.
Under the leadership of former CEOs Maggie Wilderotter and Dan McCarthy, Frontier dragged from one quarter to the next, promising improvements that failed to materialize for most customers. The company’s $10.5 billion acquisition of landlines in California, Texas and Florida was particularly costly as the company sold bonds offering astonishing 10.5-11% interest rates to investors to cover more than $5 billion in debt coming due for repayment. A year after the Verizon deal, a half million Frontier customers left for good and the company lost $262 million.
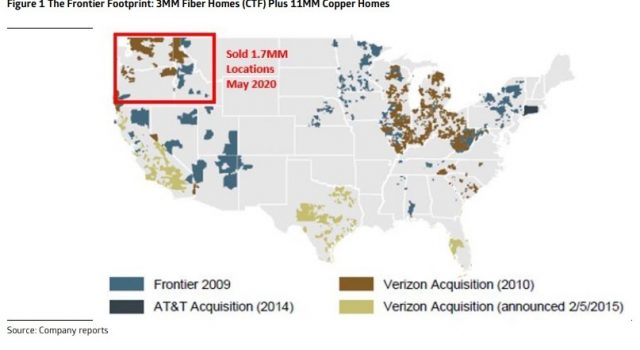
Frontier’s latest fiber plan is to target upgrades in its legacy service areas, noted in blue on this map. These areas are all almost entirely served by copper wire, provide slow speed DSL, and are long overdue for fiber upgrades. Frontier will also expand fiber in its acquired service areas, represented by other colors on the map. Note that Frontier sold its Pacific Northwest region, marked by the red box, to Zipply Fiber, which also plans to scrap Frontier’s copper wire network in favor of fiber. (Map courtesy of Light Reading)
By the time bankruptcy was inevitable, Frontier was saddled with billions in debt and no financial ability to embark on fiber upgrades the company should have committed to a decade ago. Almost all of its existing fiber footprint was acquired from other companies.

Stratton
Frontier’s new management includes John Stratton, a former Verizon executive. Stratton believes Frontier’s future depends on the company expanding its fiber footprint. In 2020, it put that plan to the test by expanding fiber to the home service to 60,000 additional homes in a pilot project proving Frontier can plan and execute fiber upgrades on time and on budget. But a closer look at the numbers shows the majority of homes Frontier “upgraded” were brand new. Of the 60,000 homes, 44,000 were located in new housing developments or were unwired previously. These “greenfield” locations are typically easier to provision and much less expensive to service than pre-existing homes where Frontier first needs to decommission its existing copper wiring and replace it with fiber optics. Only around 16,000 pre-existing homes saw copper wire replaced with fiber in so-called “brownfield” locations.
For Frontier to succeed, it will need to move a lot more copper customers to fiber optics to remain competitive in the marketplace. Currently, Frontier serves approximately three million fiber homes and 11 million copper homes. Frontier is expected to announce fiber upgrades for an additional six million homes and target about 85% of its footprint to be serviced by fiber… eventually.
Some proposals hint the company could take five years or more to complete upgrades at the same time independent fiber to the home providers, next generation satellite internet, and wireless home 4G/5G internet plans are expanding. Much of Frontier’s service area is serviced by cable companies already providing high speed internet. Frontier’s plan assumes it will capture about 40% of the market — a tall order in communities like Rochester, N.Y., where dominant cable provider Charter Spectrum is assumed to have 70+% of the home broadband market. When competing fiber providers enter the market, Spectrum often slashes promotional pricing to $30 a month for 400 Mbps internet service for two years. Spectrum will probably offer similar pricing in newly competitive markets to retain customers threatening to cancel service and switch to Frontier.
Frontier plans to discuss its exit from bankruptcy and where the company will go in the future in a webcast presentation this Friday, April 30, 2021 at 10:00am ET.
 Almost 20% of Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers now consume over 1 TB of data per month, with the average cord-cutting Spectrum customer now reaching 700 GB of usage.
Almost 20% of Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers now consume over 1 TB of data per month, with the average cord-cutting Spectrum customer now reaching 700 GB of usage.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Frontier Communications
Frontier Communications 


 Cleveland, Ohio area residents now have access to over 70 over-the-air channels from northeast Ohio thanks to the efforts of
Cleveland, Ohio area residents now have access to over 70 over-the-air channels from northeast Ohio thanks to the efforts of 
