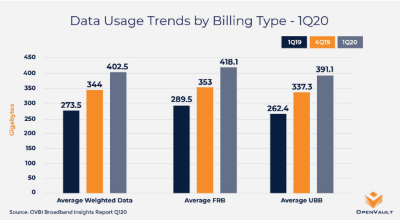
Note that data usage is slightly higher for users with “flat rate billing (FRB)” plans vs. those stuck with “usage-based billing (UBB).” (Source: OpenVault)
A record 10 percent of U.S. households now exceed 1 TB of data usage per month, putting some customers at risk of overlimit fees for exceeding data allowances that are usually enforced by AT&T, Comcast, Cox, and other telecom companies. Those caps are temporarily suspended because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
OpenVault, which collects average data usage from several service providers, reports a dramatic increase in the number of homes it designates as “power users” that consume at least 1 TB of data each month. In the first quarter of 2019, 4.2% of customers regularly exceeded 1 TB of usage. During the same period this year, that number shot up 138% to 10% of customers. “Extreme power users” that consume 2+ TB of data increased a record 215% from just one year ago, now representing 1.2% of broadband households. Last year it was 0.38%.
Overall total broadband usage across all users increased 47% in the first quarter of 2020, reaching an average of 402.5 GB a month. But that number mostly comprises average usage before the COVID-19 pandemic forced many to work from home. OpenVault originally predicted in January 2020 that monthly usage would reach 425 GB by the end of 2020. But with most Americans sheltering at home, measurements now suggest average broadband usage already exceeds that, reaching a record high of 460 GB in April.
“Nearly all the growth in broadband usage we would have expected for 2020 has now been achieved in the first quarter, with much of it concentrated in the last two weeks of the quarter,” OpenVault reported.
Despite usage growth, broadband providers in the United States are universally confident their networks are more than capable of sustaining the increased traffic. In fact, many providers report a spike in new customers, upgrades to higher speed tiers, and at least one — Spectrum, is confident enough of its network capacity to give away two months of broadband service to households with school-age children for free.
NCTA–The Internet & Television Association reports the biggest increases in broadband traffic are occurring on the upstream side, likely because of video teleconferencing. Although downstream traffic also spiked after the pandemic forced many businesses to close their offices, that traffic has flattened out and most recently has even decreased slightly.

Source: NCTA
Broadband providers may have lost key arguments to support reimposing data allowances and usage caps after the pandemic eases. Not only have broadband networks managed dramatic spikes in traffic with no significant difficulties, there are no signs of any “data tsunamis” in the future, even as broadband usage growth exceeds predictions. NCTA reports that 99.8% of the time broadband providers had “ample” or “excess” capacity available, not only to sustain current traffic levels but also potential future spikes in traffic. Peak traffic usage reaching levels where reduced capacity was available was identified just 0.2% of the time, causing a “minor impact on performance and customer experience.”
The current crisis is likely to bring a flood of new revenue to many broadband companies, even without usage overlimit fees. Since the pandemic began, OpenVault reports a 3.75% growth in premium-priced gigabit speed upgrades, up 97% from the same time last year. In the New York City area, gigabit service subscriptions at Altice/Optimum increased 56% as many workers began to telecommute.
The biggest challenge the cable broadband industry faces as a result of this year’s usage growth is a need to accelerate plans already under development to increase upload speeds. Much of the recent traffic growth came from upstream traffic, which is cable broadband’s biggest Achilles’ Heel. Cable broadband networks devote most available bandwidth to downloads, with only a small fraction devoted to upload speed. Cable companies are expected to modestly increase upload speeds in a few months and will eventually deploy the next DOCSIS standard, supporting far faster upload speeds, beginning sometime next year.


 Subscribe
Subscribe