This is the second part of a two-part series reflecting on Verizon’s 5G millimeter wave wireless home broadband service and how Wall Street complicates its potential. Be sure to read part one, “How a Wall Street Analyst Complicates AT&T and Verizon’s Upgrade and Investment Plans” for the full story.
 “Put simply, the cost of building a second network is so high that its builder simply can’t earn a passable return based on the market share available to a second player,” Craig Moffett, an important telecom industry analyst working on behalf of Wall Street investors, argued over Verizon’s fiber to the home project dubbed FiOS. “Virtually every overbuilder, from telephone companies to competitive cable companies to municipalities, has learned this lesson the hard way; almost all such efforts have ended in bankruptcy. Verizon’s own FiOS network was an economic failure; there is no longer any debate about whether FiOS did or didn’t earn its cost of capital. It didn’t, and it wasn’t even close.”
“Put simply, the cost of building a second network is so high that its builder simply can’t earn a passable return based on the market share available to a second player,” Craig Moffett, an important telecom industry analyst working on behalf of Wall Street investors, argued over Verizon’s fiber to the home project dubbed FiOS. “Virtually every overbuilder, from telephone companies to competitive cable companies to municipalities, has learned this lesson the hard way; almost all such efforts have ended in bankruptcy. Verizon’s own FiOS network was an economic failure; there is no longer any debate about whether FiOS did or didn’t earn its cost of capital. It didn’t, and it wasn’t even close.”
Moffett’s philosophy about emerging broadband technology and competition is heavily influenced by his personal and professional belief that broadband competition is bad for business and investors. His distaste for Verizon FiOS, a plan to scrap old copper phone wiring in favor of fiber optics, was well-known across the industry and trade press. But Verizon kept going with the project under the leadership of then-CEO Ivan Seidenberg, who was a telephone man through and through. But by 2010, Seidenberg had decided to retire, and his successor, Lowell McAdam, had a very different perspective about Verizon’s future. McAdam spent almost his entire career from the early 1990s forward in the wireless business. In 2006, McAdam was named the chief operating officer and CEO of Verizon Wireless. When he succeeded Seidenberg in late 2010, Verizon had already announced it was winding down further FiOS expansion. That seemed to suit McAdam just fine, because under his leadership as CEO of Verizon, Verizon Wireless became the dominant focus of the company. Heavy investment in wireless continued, while Verizon’s landline network was allowed to deteriorate.
Moffett told his clients the end of FiOS expansion would be good news for cable companies because they would lose fewer subscribers as a result.
Verizon’s marketing machine carefully lays its business case for 5G home broadband
More than a decade later, Verizon’s decision to embark on another major technology upgrade requiring billions in new spending quickly raised eyebrows on Wall Street. This time, however, Verizon executives attempted to be better prepared to defend their 5G vision from the reflexive investor argument that it was too expensive and extravagant.

Moffett
“First, their fixed wireless broadband business will leverage investments that Verizon argues they will need to make anyway to support their wireless network,” Moffett wrote in a report to his clients, acknowledging Verizon’s claimed reasons for entering the wireless home broadband business. “Second, Verizon argues that it will be cheaper to connect homes wirelessly than it is to connect them with fiber, making it economic to deploy fixed wireless in markets where fiber to the home hasn’t been economically justifiable.”
Most of the expenses cited by Moffett relate to bringing fiber networks into neighborhoods to support the small cell technology Verizon is relying on for its 5G home broadband and mobile services.
Moffett also believes the only attractive market for 5G service will be in more upscale suburban rings around cities, not densely populated urban centers or rural areas. Moffett argues fiber providers are likely already providing service in urban areas and rural areas simply lack enough customers to justify the cost of either a fiber optic network or a small cell network. Ironically, that conclusion means the same suburban ring Moffett rejected 5-10 years ago as economically unsuitable for fiber service is now precisely the area Moffett argues is the only attractive market for fiber service, to bring 5G.
From a short-term results perspective, laying fiber optics is a costly proposition unlikely to return much revenue gain in a few short years. That reality has kept many investor-owned phone companies away from expensive network upgrades. These legacy telephone companies recognize they are going to continue to lose customers to faster technologies like cable, fiber, and perhaps, wireless. But managing an existing low-speed DSL business seems preferable to facing the wrath of investors upset over the prospect of shareholder dividends and share buybacks being curtailed to redirect money into a full-scale upgrade effort, even if it results in better returns and greater revenue a few years down the road.
Verizon is depending on its wireless division’s extremely high profitability to counter the usual objections to major upgrades, and by focusing on how 5G will enhance the wireless experience. It also benefits from media hype surrounding 5G technology, exciting some investors. But Verizon is also downplaying exactly what it will cost to lay fiber optic networks deep into neighborhoods to deliver it.
Moffett investigates Verizon’s first 5G city — Sacramento, Calif., and discovers alarming results
Moffett decided to bypass the traditional cost-benefit analysis of laying mile after mile of optical fiber and decided to test Verizon’s case for wireless 5G home broadband instead.
Six months after launch, Moffett investigated Verizon’s 5G millimeter wave network in Sacramento, examining how the service is initially performing. Moffett identified seven zip codes in Sacramento where service was most likely to be available, based on cell tower/small cell records. As of late February, Moffett found Sacramento had 391 Verizon small cells installed, with 273 used for millimeter wave 5G service (the rest are likely designed to bolster Verizon’s 4G LTE network).
Verizon has admitted small cell technology is vulnerable to distance, so Moffett relied on earlier purported claims of 5G coverage to limit the number of addresses to be sampled. Moffett’s team identified 45,000 out of 70,000 possible addresses, based on if those homes were located within a radius of 0.7 miles of a 5G small cell. Then, Moffett’s team devised a method of hitting Verizon’s 5G availability website with each of those 45,000 addresses to learn which ones Verizon qualified for 5G service.
The results, so far, are underwhelming:
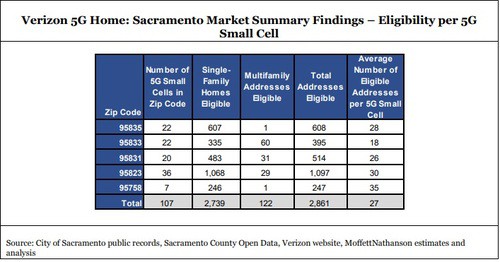
- Only an average of 6% of the queried addresses were actually eligible to receive Verizon’s fixed wireless service. That could mean Verizon has installed 5G small cells, but some are not yet operational in all areas or the network is performing much worse than originally anticipated. Some zip codes did better than others, but not by much. The best offered just an 18% pre-qualified acceptance rate. Apparently Verizon’s qualification website also informs applicants if they already have service, which proved to be a good way of finding out how many addresses actually have signed up. Moffett claims only 3% of eligible customers have decided to subscribe to Verizon’s 5G home broadband service so far.
- Coverage appears to a problem. As Moffett checked addresses further away from each small cell, more and more were deemed ineligible for service. In fact, despite Verizon’s claims that its 5G signal reached customers more than 1,900 feet away, the company’s own website refused to actually sell service to customers that far away. Moffett found subscribers were deemed ineligible for service as little as 400 feet away from a small cell. At that distance, less than 50% of checked addresses could sign up. For those 700 feet or more away, almost no addresses were qualified for service.
With those results, Moffett was able to extrapolate some important numbers about how much Verizon’s infrastructure is being utilized:
- Each small cell serves approximately 27 eligible addresses.
- Verizon’s 5G home broadband has a 0.1% market share in Sacramento.
- Excluding areas where multi-dwelling properties dominate, Verizon has achieved a penetration of roughly one subscribed single-family home per 1.5 5G small cell.
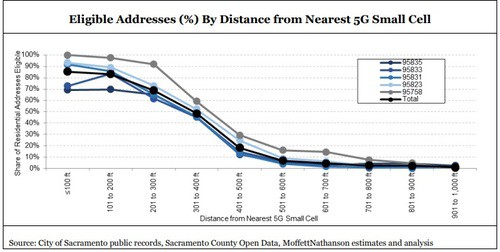
“Our findings in Sacramento — limited coverage, low penetration — preliminary though they may be, suggest that earning an attractive return will be challenging, at best,” Moffett concluded.
Because Verizon has attracted so few subscribers thus far, the total cost per connected home for 5G wireless service could far exceed what it would cost to just lay down fiber to the home service to each customer, which might actually give Verizon more business.
“Our analysis suggests that costs will likely be much higher (that is, cell radii appear smaller) and penetration rates lower than initially expected,” the report explained. “If those patterns are indicative of what is to come in a broader rollout, it would mean a much higher cost per connected home, and therefore much lower returns on capital, than what might have been expected from Verizon’s advance billing.”
If Moffett’s estimate of 27 residences served per small cell was proven true, Verizon would have to deploy well over five million small cells to deliver 5G wireless service across America.
Verizon’s choice of cities to launch its 5G millimeter wave network may be partly designed to test the differences in topology, building density and foliage levels, and there may be dramatic differences between Houston, Sacramento, Indianapolis, and Los Angeles.
Moffett’s overall conclusion is that should Verizon move forward on rolling out 5G wireless home broadband to around 25% of the country, as it planned, reaching those 30 million homes “will take a very, very long time, and it will cost a great deal of money.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe
The 5G story is strange because it doesn’t fit the traditional telecom model very well. Probably the best scenario for millimeter wave fixed wireless is “cherry picking” favorable locations where somebody can put up an antenna and serve a lot of people. For instance: https://webpass.net/metros For instance an antenna on a large building could deliver service line-of-site to an apartment building: the costs of the radio equipment can be spread over all of the tenants so this could be very low cost, e.g. “gigabit” service for $30-40 a month per sub. It is strange that many millimeter wave bands have… Read more »
The problem is the 5G signal doesn’t go above a certain height (don’t remember what the limit was in Los Angeles) from small cells placed on light poles, so they would have to install them much higher up, perhaps on top of buildings. But line of sight is very critical. Google is doing their own mesh Wi-Fi-like concept in urban multi-dwelling unit areas, but notice that growth has slowed way down as well. I remain skeptical that fixed wireless 5G will be the useful home broadband replacement it claims to be. FTTH is still a much better option. I am… Read more »
Moffet makes huge assumptions while Verizon investigated actual use in 11 test markets for nearly two years. Verizon stopped activating 5G when manufacturers told them 5G NR certified equipment that they had already said they would replace would be upgraded at no cost to the customer. 5G fixed is an adjunct service that will be offered anywhere they build out for 5G mobile using the same fiber they bought two years ago – almost 50 million miles worth. Any revenue they get from that will just help pay the cost of the mobile build out. The fiber itself is part… Read more »
Agreed… it’s ironic investors will throw money at Silicon Valley fraud and BS (Theranos) and ridiculous start-ups that have no prospect of making money while counting every nickel over telecom infrastructure projects. I can’t tell you how many times I’ve argued with big investors over Frontier’s need to overhaul its business, scrap copper, and upgrade to compete. They don’t want to hear about it, even if it means Frontier’s eventual death spiral. They don’t want big spending that cuts into dividends and hurts the share price. It is also clear mobile 5G and IoT would be the primary driver of… Read more »
Since I can’t edit my original post.
Verizon stopped activating 5G when manufacturers told them 5G NR certified equipment that they had already said they would replace would be upgraded at no cost to the customer would be delayed till late 2019, which they thought would be available early 2019.
Moffett is the type of guy you would not want at dinner to discuss the future. He would ruin it by telling you that everyone should have dsl and anything better is too “expensive”. He’s just another pawn for Wall Streets dumbest.
He is part of the “it’s good enough service for you” crowd, at least until competitors race ahead. Then it’s basically too late for that first company, who apparently should just concede and shut its doors.
Can someone put guys like Moffett into a rocket capsule and eject him into the vacuum of space?
There is obviously a detachment from reality in the fact that cable continues to evolve and most HFC networks are (FTTN). Heck my Charter fiber run goes across my front lawn. Keep in mind Moffit was the face of cable before, so his motives are not pure. To me the US is plain stupid. In the swing of wasted money to Afghanistan, the US should have made it a MANDATE to every single house (within reason) have fiber run to it, and then let whatever supplier connect up and use the line. The question is: Is millimeter wave the suburban… Read more »
We do have misplaced priorities. But there are lots of people ready to demagogue tax dollars for broadband buildouts and internet service for the poor. Just read the comment section of this article: https://www.syracuse.com/news/2019/04/syracuses-digital-crisis-1-out-of-4-homes-doesnt-have-internet.html If people want 5G, that is fine, but it still needs fiber all over the place and these small cells appear to need a denser buildout than first thought. If the fiber is there, fiber to the home should be an option, and frankly it will be better than a wireless 5G connection for home internet use. The original thought was that wireless was useful because… Read more »
AT&T actually seems to have changed their mind about fixed wireless at least using a mid band spectrum. https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/att-changes-its-tune-on-5g-fixed-wireless/2018/09/ I know Verizon is planning to replace 25% of their copper network with fixed wireless (unless ARS Technica can convince regulators that telcos must maintain a separate parallel copper network so 80 year olds can be connected to diesel generators when the power goes out, lol). There’s only so much regulators can do to force a company to maintain 100+ year outside plant while telling them to improve service at the same time. The rest will go fiber but that process… Read more »