Phillip Dampier
The Wall Street Journal’s not-living-in-the-real-world editorial page strikes again.
The commentary pages have always been the weakest part of the Journal, primarily because they screech pro-corporate talking points in contrast to the more balanced reporting in the rest of the newspaper.
Mr. Holman W. Jenkins, Jr. decided to distort broadband reality (again) in yesterday’s edition with a glowing commentary on how wonderful broadband providers are in his piece, “Springtime for Broadband.” The only thing missing was a border in fine print labeled, “Sponsored by Verizon, AT&T, and your cable company.”
While your Internet bill is being hiked at the same time your provider is slapping usage limits on your connection, Jenkins dismisses consumer-fueled complaints about broadband price gouging, assaulting Net Neutrality, and overall poor customer service as part of Washington’s “broadband policy circus.”
Charges fly hourly that Google or some other company is guilty of gross insult to net neutrality (that sacred principle nobody can define). Oregon Sen. Ron Wyden has introduced legislation to regulate data caps and Internet pricing. Law professor Susan Crawford, until recently a White House technology adviser, clearly craves to be America’s next go-to talking head on broadband. Lately she’s been everywhere calling for a crackdown on the competing “monopolists” who supply Internet access.
How dare they complain, decries Jenkins in a robust defense of the 21st century version of the railway robber barons.
Comfortably playing patty cake with provider-fed talking points from the industry echo chamber, Jenkins is ready for battle, facts or not.
But wireless providers have invested big money to deploy high-speed mobile networks, and fixed and mobile are inevitably beginning to compete. The latest evidence: Australia recently predicted that up to 30% of households will go the all-wireless route and won’t be customers for its vaunted national broadband project.

Jenkins
Not exactly. The basis for this 30% figure is the National Broadband Network’s own business plan, which warns –if– the company raised prices to a maximum theoretical level, up to 30 percent of its customers would rely on wireless instead… by the year 2039. That is 26 years from now. You have nothing better to do in the meantime, right?
In fact, conservative critics of the fiber network, some defending the big wireless cell phone industry in Australia, have suggested fiber optics is a big waste of money because “wireless is the future.”
That old chestnut again.
“Now you can present a bulletin without touching a typewriter … it’s just there on the computer system, you don’t need a reel to reel tape recorder. I’ve got a touchscreen in front of me. Back then I had a big cartridge deck,” said Ray Hadley on 2GB radio. “Can you imagine the advances in technology in the next 26 years? I can’t. I can’t comprehend it. By the time they finish the NBN, it could be superseded by something we don’t even know about.”
NBN Myths, a website set up to tackle the disinformation campaign from political and industry opponents has one simple fact to convey: “Despite what you may have read from certain clueless commentators, there is not a single country or telecommunications company anywhere in the world that is attempting to replace fixed networks with wireless in urban areas, or even planning to do so in the future.”

Which would you rather have?
Even Telstra, the biggest telecom company in Australia scoffs at such a notion, noting a growing number of its customers have both wired and wireless service, and they do not depend on one over the other.
Research firm Telsyte found that 85 per cent of Australians want speeds of 50Mbps or higher, speeds impossible for wireless to offer. In fact, when the NBN fiber network became available to Australians, almost half the current users as of October last year had chosen an even-faster 100Mbps plan option. But Australians also want mobile broadband, and they are signing up for that as well.
The Australian Bureau of Statistics notes the number of mobile broadband Internet connections also grew by around 40% in Australia between 2009 and 2010. But here is the Achilles heel of wireless: it cannot deliver the same speeds or capacity, and providers charge high prices and deliver low usage caps. As a result, the wireless industry has pulled off a coup: they earn enormous revenues from networks they have successfully rationed. The total amount of data downloaded over Australia’s wireless networks actually fell on a per user basis, despite the growth in customers.
Much of Jenkins’ commentary is spoon-fed by the industry-funded Information Technology and Innovation Foundation, which produces industry-sponsored studies designed to tell America all is well in our broadband duopoly.
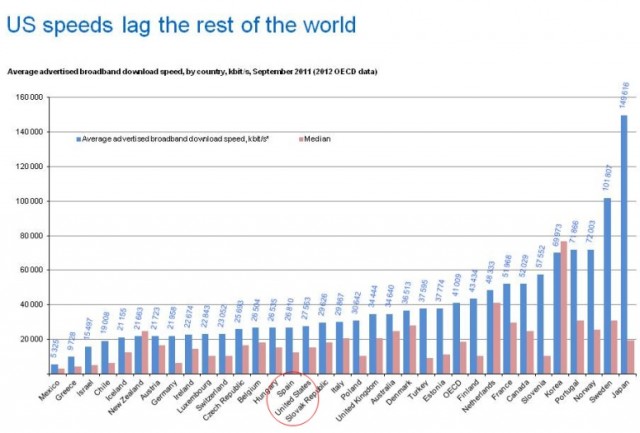
In the latest federal survey, the average broadband speed in America is up to 15.6 megabits per second, from 14.3 a year earlier. Nearly half of customers who six months ago made do with one megabit or less have now moved up to higher speeds. Since 2009, the U.S. has gone from 22nd fastest Internet to the eighth fastest.
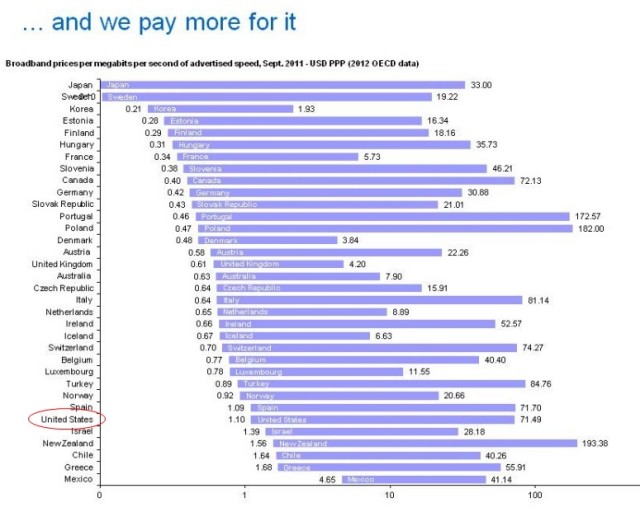
The 15.6Mbps figure comes from the Federal Communications Commission. The statistics about our global speed ranking come from Akamai’s voluntary speed test program. Other studies rate America much lower. More importantly, while providers in the U.S. try to squeeze out more performance from their copper networks, other countries are laying speedier fiber networks that are destined to once again leapfrog over the United States. Most charge less for their broadband connections as well.
Jenkins also quotes the ITIF which touts 20 million miles of fiber were laid in America last year. But the ITIF, when pressed, will admit the majority of that fiber was “middle mile” connections, institutional or business network fiber you cannot access, or fiber to cell towers. Fiber to the home expansion has stalled, primarily because Verizon has suspended expansion of its FiOS network to new areas after Wall Street loudly complained about the cost.
Jenkins argues that if we leave providers alone and stop criticizing their growing prices, declining competition, and fat profits, the marketplace will suddenly decide to invest in network upgrades yet again.
“The day may come when even Verizon, which visibly soured on its $23 billion FiOS bet, rediscovers an urge to invest in fixed broadband infrastructure to meet growing consumer lust for hi-def services,” writes Jenkins.
Would Wall Street rather see providers invest in network upgrades or return profits to shareholders? Investment expansion in the broadband industry comes when a company senses if they do not spend the money, their business will be swept away by others that will. Cable broadband threatens telephone company DSL, so AT&T cherry-picked communities for investment in its half-measure U-verse fiber to the neighborhood network. Google Fiber, should it choose to expand, will be an even bigger threat to both cable and phone companies. Municipal fiber to the home networks upset the incumbent players so much, they spend millions of ratepayer dollars in efforts to legislate them out of existence.
Jenkins’ view that giving the industry carte blanche to do and charge as it pleases to stimulate a better broadband future is as fanciful as NBN critics in Australia suggesting fiber upgrades should be canceled in favor of waiting 20+ years for improved wireless to come along.
He even approves of Internet Overcharging schemes like usage caps and consumption billing, calling it proper price discrimination in a “fiercely competitive” environment to defray a network’s fixed costs.
Do you think there is fierce competition for your broadband dollar?
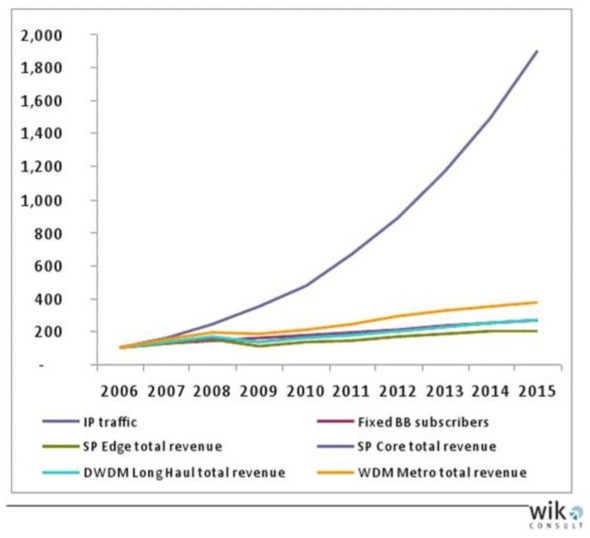
Broadband’s fixed costs are so low and predictable, it literally calls out consumption pricing as just the latest overreach for enhanced profits. As Suddenlink’s CEO himself admitted, the era of big expensive cable upgrades are over. Incremental upgrades are cheap, the costs to offer broadband are declining, so it is time to reap the profits.
Jenkins closes with one recommendation we can agree with: “A low-tech way to stir up broadband competition would be to relax the regulatory obstacles to the actual physical provision of broadband.”
We can start by scrapping all the state laws the industry lobbied to enact that prohibit community-owned broadband competition. If big cable and phone companies won’t provide communities with the quality of broadband service they need to compete for 21st century jobs, let those communities do it themselves.


 Subscribe
Subscribe


 It’s time to take a look inside Time Warner Cable’s latest quarterly financial report and pick out some interesting developments that will impact customers during the first quarter of 2013.
It’s time to take a look inside Time Warner Cable’s latest quarterly financial report and pick out some interesting developments that will impact customers during the first quarter of 2013.