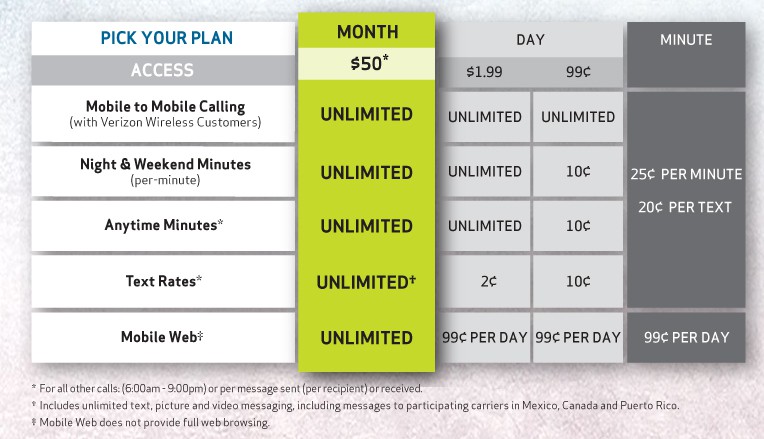
Mirroring AT&T’s announcement last month that it would begin implementing speed throttles for wireless unlimited data plan customers who are among the “top 5% of users,” Verizon Wireless quietly made changes last week allowing the company to throttle its own unlimited data plan “heavy users” who consume more than 2GB of usage per month on its 3G network.
But Verizon claims it isn’t actually throttling the speeds of customers, it is simply engaging in “network optimization practices” and using “network intelligence” to reduce speeds (sometimes to near-dial-up) while connected to a “congested cell site.”
That will prove a distinction without much difference to customers who rely on 3G data usage using cell sites Verizon deems congested. They may also find the time spent in Verizon’s penalty box unusually long.
“You may experience [reduced speeds] for the remainder of your then current bill cycle and immediately following bill cycle,” Verizon’s FAQ states.
That can mean customers paying $30 a month for an “unlimited data plan” may find 3G usage a very slow experience for a maximum of two months before they are off Verizon’s throttle list.
The new speed throttle policy began Sept. 15. Verizon:
Network Optimization practices and throttling is network intelligence. With throttling, your wireless data speed is reduced for your entire cycle, 100% of the time, no matter where you are. Network Optimization is based on the theory that all customers should have the best network possible, and if you’re not causing congestion for others, even if you are using a high amount of data, your connection speed should be as good as possible. So, if you’re in the top 5% of data users, your speed is reduced only when you are connected to a congested cell site. Once you are no longer connected to a congested site, your speed will return to normal. This could mean a matter of seconds or hours, depending on your location and time of day.
Verizon has not said exactly how many of its cell sites it deems as “congested,” at what times that congestion is most likely to occur, and admits there is currently no way customers can learn when they are connected to a congested site so they can make an informed decision about their usage.
But the company does say customers can avoid the penalty:
- Upgrade to a 4G phone and hope for good 4G LTE coverage. Customers using Verizon’s 4G network are not currently subject to a speed penalty for “excessive use.”
- “Upgrade” to a tiered data plan with usage allowances. Verizon will not throttle the speeds of customers who are not on unlimited data plans.
- Reduce your data usage, especially in areas where congestion is likely.

Choke collars are in season at AT&T and Verizon Wireless, leaving Sprint's unlimited service looking more consumer-friendly by the day.
Those suggestions require potentially pricey new handsets, require customers to abandon their existing unlimited data usage plan, or simply get you thinking twice before launching a data session, fearing being grounded for up to two months with a dramatically reduced level of service.
The biggest impact of the network speed throttles will be among data-heavy iPhone users. Apple’s iPhone doesn’t support 4G, and is likely to continue to rely on 3G network coverage when the next version of the popular phone is introduced in October. Ultimately, Verizon’s new policy means iPhone devotees using more than 2GB per month may have to abandon their phone or their unlimited data plan if they want to avoid the throttle.
Verizon also found a way to keep customers from canceling penalty-free, noting contract changes that reserved the right to implement network management techniques were made in February. The 60-day window for the “materially-adverse” contract change cancellation policy expired in April. Verizon:
By alerting customers in February 2011, and including the notice in our terms and conditions as of February 3, 2011, we made sure customers knew we began reserving the right to implement Network Optimization practices. In February 2011, we began alerting customers:
- Data Management – (note: now named “Network Optimization” to more accurately describe the tools) – Verizon Wireless may reduce data throughput speeds in a given bill cycle for customers who use an extraordinary amount of data and fall within the top 5% of data users. The reduction will only apply to those using congested cell sites and can last for the remainder of the current and immediately following billing cycle. The reductions will only apply when appropriate in locations and at times of peak demand.
- Data Optimization – (note: now named “Video Optimization” to more accurately describe its function) – Verizon Wireless is implementing optimization and transcoding technologies in its network to transmit data files in a more efficient manner to allow available network capacity to benefit the greatest number of users, and although unlikely, the process may minimally impact the appearance of the file as displayed on the mobile device.
Interestingly, AT&T’s own speed throttle penalty was estimated to kick in after 4GB of usage, not the 2GB Verizon is using as its benchmark for “network optimization.” Verizon also says customers with their Mobile Hotspot feature will find that usage exempted from counting towards the 2GB threshold.
Verizon has opened up a new web page explaining the throttling policy.
[Thanks to Stop the Cap! reader Mileena, among many others, who shared the news with us.]


 Subscribe
Subscribe