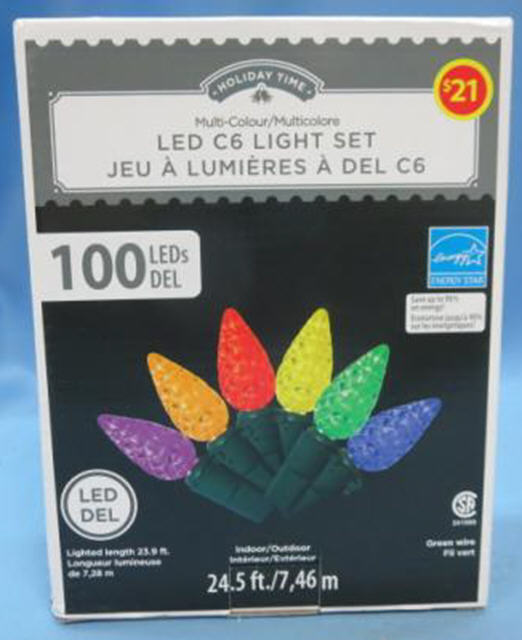

Despite the UL label on the cord, these Walmart-sold Christmas lights have been recalled in Canada for causing “unfortunate incidents.” In the U.S. they are still on the market and consumers are on their own.
The increasing prevalence of energy-saving LED holiday lights may help reduce your energy bill this Christmas, but are probably not doing any favors to your in-home Wi-Fi.
Chinese factories that produce billions of light string sets annually often have the attitude that quality control should take a back seat to selling price, and as such many of these cheaply produced sets experience a growing number of issues the longer they are in use. This year, Canadian regulators have ordered complete recalls of holiday lights manufactured by Taizhou Hongpeng Colour Lanterns or Ningbo EGO International Co. Ltd. The sets were implicated for interference, overheating, fire, shock, toxicity, and more.
The affected lights, sold until the fall of 2015, were available across North America in dollar stores, hardware warehouses, supermarkets, and department stores. Many were sold by Loblaws, Michaels (the CELEBRATE IT series) and Walmart’s “Holiday Time” brand lights. Up north, it’s time for those lights to go after sampling and evaluation by the federal agency led to clear evidence they posed serious safety risks.
In the United States, consumers are on their own. Despite adopting new safety regulations in June, the Consumer Product Safety Commission remains satisfied with a hands-off/business-friendly approach that relies primarily on voluntary recalls that begin after consumers self-report injuries from defective products.
The CPSC does not test Christmas light sets, despite the fact seasonal and decorative lighting products have been responsible for hundreds of fire and shock-related deaths and injuries over the years. CPSC is aware of 132 fatal incidents that occurred from 1980 through 2014 which led to 258 deaths, and 1,405 nonfatal incidents associated with seasonal and decorative lighting products.
Despite clear warnings from Health Canada’s own testing, the CPSC continues to allow manufacturers to sell dangerous light sets that are now recalled in Canada.
Assuming your Christmas tree lights don’t overheat or short out, regulators are also turning their attention to a less serious problem with the light sets: their potential to create interference problems.

Wi-Fi trouble waiting to happen.
Ofcom, the United Kingdom’s independent telecom regulator, has seen enough reports of Wi-Fi problems tracked back to Christmas lights to issue a caution.
The problem isn’t so much with the LED bulbs. The interference problems usually develop from the cheap transformers/switched mode power supplies used to regulate voltage for certain energy-saving lights. A poor quality unshielded light set, especially those with a built-in, programmed light show, is likely to throw audible hash across the AM radio dial. But it can also interfere with Wi-Fi reception in certain cases, especially if you turn your home and yard into the equivalent of the Vegas strip.
Despite the timely holiday themed Ofcom announcement, most of the lights sold in the United States have offered negligible interference so far — typically when the wireless router is located very near a Christmas tree or a powered holiday decoration. The biggest culprit that obliterates Wi-Fi is still the microwave oven. When running, many models can wipe out reception across a home or apartment.
Other factors that can make a difference include the distance between you and your router and whether the neighbors are sharing the same Wi-Fi channel you use.
Ofcom’s advice:
Move your router away from electrical devices: Halogen lamps, electrical dimmer switches, stereo or computer speakers, Christmas lights, TVs and monitors and AC power cords have all been known to cause interference to broadband routers. It’s important to use quality key materials in modern electronics. Keep your router as far away as possible from other electrical devices as well as those which emit wireless signals such as baby monitors etc.
Move your router to a different part of your home: The walls and furniture in your house act as an obstacle to the Wi-Fi radio frequencies. Ideally routers should be kept centrally within the home and placed on a table or shelf rather than on the floor.
Try restarting your wireless router: This may automatically select a less busy Wi-Fi radio frequency.
Our advice is to consider replacing or upgrading a misbehaving router that will not hold a Wi-Fi connection even in the best of circumstances and above all, make sure you have enabled wireless security to keep uninvited guests off your network.


 Subscribe
Subscribe The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission is asking some hard questions of Quebec-based mobile provider Vidéotron, which began zero-rating preferred partner music streaming services last summer that allow customers to stream all the music they want without it counting against their data cap.
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission is asking some hard questions of Quebec-based mobile provider Vidéotron, which began zero-rating preferred partner music streaming services last summer that allow customers to stream all the music they want without it counting against their data cap. Observers say zero-rating enhances a customer’s perception that data has a measurable financial value, often arbitrarily assigned by competitors in a marketplace. If providers charge an average of $10 per gigabyte, customers will gradually accept that as the base value for wireless data, despite the fact many providers used to sell unlimited data plans for around $30. Zero rating content can be used in marketing campaigns to suggest customers are getting added value when a provider turns off the usage meter while using those services. Stream 3GB of music and a provider can claim that has a value of $30, but provided to you at “no charge.”
Observers say zero-rating enhances a customer’s perception that data has a measurable financial value, often arbitrarily assigned by competitors in a marketplace. If providers charge an average of $10 per gigabyte, customers will gradually accept that as the base value for wireless data, despite the fact many providers used to sell unlimited data plans for around $30. Zero rating content can be used in marketing campaigns to suggest customers are getting added value when a provider turns off the usage meter while using those services. Stream 3GB of music and a provider can claim that has a value of $30, but provided to you at “no charge.”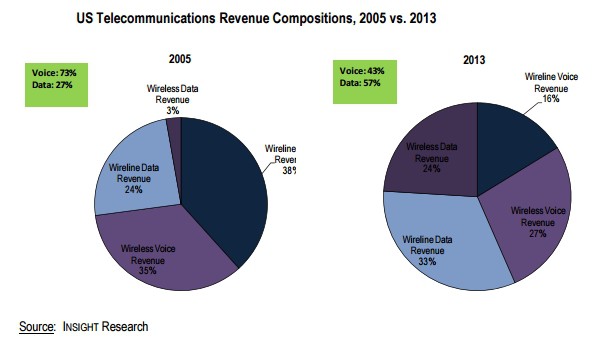 The year 2013 marked a significant turning point for phone companies that have handled voice telephone calls for over 100 years. For the first time,
The year 2013 marked a significant turning point for phone companies that have handled voice telephone calls for over 100 years. For the first time,  Starting in 2008, wireless industry executives noticed something peculiar. While revenue from texting add-on plans was surging, the growth in calling began to level off. Wireless voice usage per subscriber peaked at an average of 769 minutes in 2007 and began falling after that year. By 2011, the average customer was making 615 minutes of calls a month. As customers began downgrading calling plans, wireless carriers shifted their quest for revenue towards text messaging.
Starting in 2008, wireless industry executives noticed something peculiar. While revenue from texting add-on plans was surging, the growth in calling began to level off. Wireless voice usage per subscriber peaked at an average of 769 minutes in 2007 and began falling after that year. By 2011, the average customer was making 615 minutes of calls a month. As customers began downgrading calling plans, wireless carriers shifted their quest for revenue towards text messaging.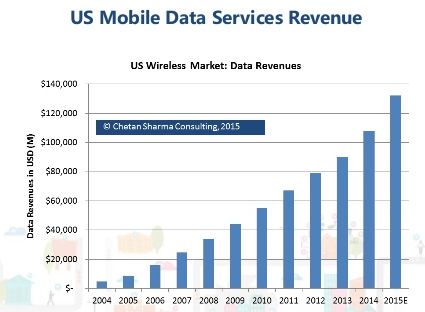 The industry’s demand for profit eventually threatened to kill the goose that laid the golden egg. At the same time wireless carriers were raising prices on text messages and forcing customers into expensive texting add-on plans, free third-party messaging apps began eating into texting volume. By 2012, the use of SMS declined for the first time, with 2.19 trillion text messages sent and received, down 4.9 percent from a year earlier.
The industry’s demand for profit eventually threatened to kill the goose that laid the golden egg. At the same time wireless carriers were raising prices on text messages and forcing customers into expensive texting add-on plans, free third-party messaging apps began eating into texting volume. By 2012, the use of SMS declined for the first time, with 2.19 trillion text messages sent and received, down 4.9 percent from a year earlier. Some even expect carriers to eventually
Some even expect carriers to eventually  Since Verizon Wireless stopped selling unlimited data plans and turned data into a precious commodity usually worth about $10 per gigabyte, the company can afford to give some of it away to their loyal customers.
Since Verizon Wireless stopped selling unlimited data plans and turned data into a precious commodity usually worth about $10 per gigabyte, the company can afford to give some of it away to their loyal customers. While AT&T is in no hurry to expand and upgrade U-verse broadband to its wireline customers in the United States, the Dallas-based company has spent more than $7 billion trying to attract wireless customers in Mexico that so far don’t show much interest in the U.S. company.
While AT&T is in no hurry to expand and upgrade U-verse broadband to its wireline customers in the United States, the Dallas-based company has spent more than $7 billion trying to attract wireless customers in Mexico that so far don’t show much interest in the U.S. company. AT&T’s decision to spend billions in Mexico while it reduces spending on further expansion of its U-verse network has nothing to do with Net Neutrality or Title II enforcement by the Federal Communications Commission. It is all about finding new customers. Wireless penetration has now topped 100 percent in the U.S. (because some families maintain multiple devices, sometimes with different carriers). In Mexico, less than 50% of the population has a cell phone and even fewer own smartphones. AT&T believes that gives it plenty of room to grow. AT&T believes wireless service brings the best potential for profits both inside and outside of the U.S., and the company thinks it can dramatically improve market share in Mexico and charge prices that will bring it a healthy return.
AT&T’s decision to spend billions in Mexico while it reduces spending on further expansion of its U-verse network has nothing to do with Net Neutrality or Title II enforcement by the Federal Communications Commission. It is all about finding new customers. Wireless penetration has now topped 100 percent in the U.S. (because some families maintain multiple devices, sometimes with different carriers). In Mexico, less than 50% of the population has a cell phone and even fewer own smartphones. AT&T believes that gives it plenty of room to grow. AT&T believes wireless service brings the best potential for profits both inside and outside of the U.S., and the company thinks it can dramatically improve market share in Mexico and charge prices that will bring it a healthy return. Their customers apparently disagree. In Mexico, for the first nine months of the year, AT&T lost 689,000 wireless subscribers — a decline of almost 8 percent. Even customers attracted to try AT&T for the first time often decide to leave, giving AT&T Mexico a churn rate exceeding 5% — five times worse than what AT&T experiences in the United States.
Their customers apparently disagree. In Mexico, for the first nine months of the year, AT&T lost 689,000 wireless subscribers — a decline of almost 8 percent. Even customers attracted to try AT&T for the first time often decide to leave, giving AT&T Mexico a churn rate exceeding 5% — five times worse than what AT&T experiences in the United States. Others wonder how AT&T Mexico will be able to introduce the premium priced services it will depend on to get a return on its investment. The Mexican economy is unlikely to allow customers to pay substantially more for wireless service.
Others wonder how AT&T Mexico will be able to introduce the premium priced services it will depend on to get a return on its investment. The Mexican economy is unlikely to allow customers to pay substantially more for wireless service.