A new report critical of broadband providers’ implementation of usage-based billing and data caps finds providers are not using them to handle traffic congestion, instead implementing them to monetize broadband usage and protect pay television from online video competition.
 The New America Foundation and the Open Technology Institute today released its report, “Capping the Nation’s Broadband Future?,” which takes a hard look at the increasingly common practice of limiting subscribers’ broadband usage.
The New America Foundation and the Open Technology Institute today released its report, “Capping the Nation’s Broadband Future?,” which takes a hard look at the increasingly common practice of limiting subscribers’ broadband usage.
The paper finds that provider arguments for limiting broadband traffic don’t make sense, but do earn more dollars from customers forced to upgrade their service to win a larger monthly usage allowance.
“Although traffic on U.S. broadband networks is increasing at a steady rate, the costs to provide broadband service are also declining, including the cost of Internet connectivity or IP transit as well as equipment and other operational costs,” the reports argues. “The result is that broadband is an incredibly profitable business, particularly for cable ISPs. Tiered pricing and data caps have also become a cash cow for the two largest mobile providers, Verizon and AT&T, who already were making impressive margins on their mobile data service before abandoning unlimited plans.”
The study finds providers are attempting to invent a climate of broadband scarcity, particularly on the nation’s wired networks, to defend the introduction of various forms of Internet Overcharging, including data caps, usage-based billing, and overlimit fees.
The New America Foundation is calling on policymakers to take a more active role in defending online innovation and controlling provider zeal to cap the nation’s broadband future.
The False Argument of Network Congestion

Providers’ tall tales.
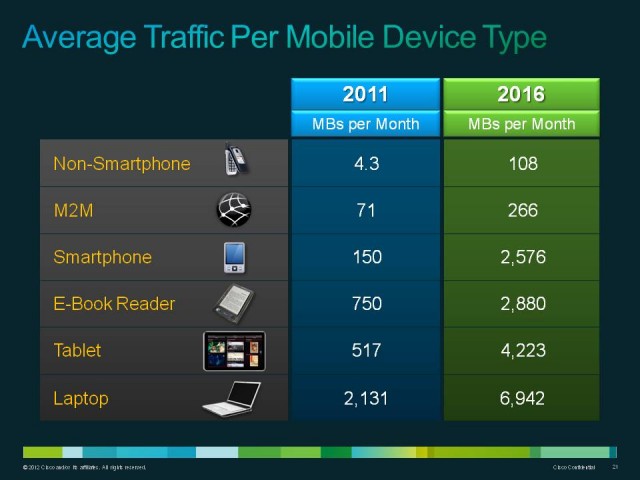
The most common defense for usage caps providers put forward is that they curb “excessive use” and impact almost none of their customers. The report points out many of the providers implementing usage caps have left them largely unchanged, despite ongoing usage growth patterns. In 2008, the report notes Comcast measured the average monthly usage of each broadband customer at around 2.5GB. Just four years later that number has quadrupled to 8-10GB. While many customers rely on Comcast’s broadband service for basic e-mail and web browsing, the cable operator has begun to entice customers into utilizing its online video platform, which in certain cases can dramatically eat into a customer’s monthly usage allowance, which remained unchanged until earlier this year.
Many broadband providers are less generous than Comcast, some imposing caps as low as 5GB of usage per month.
“Data caps encourage a climate of scarcity in an increasingly data-driven world,” the report concludes. “Broadband appears to be one of few industries that seek to discourage their customers from consuming more of their product. Thus, even as the economic and engineering rationale for data caps on wireline broadband does not hold up given the declining costs of providing service and rapid technological advancement, the proliferation of data caps is increasing. The trend is driven in large part by a woefully uncompetitive market that allows the nation’s largest providers to generate enormous profits as well as protect legacy business models from new services and innovators.”
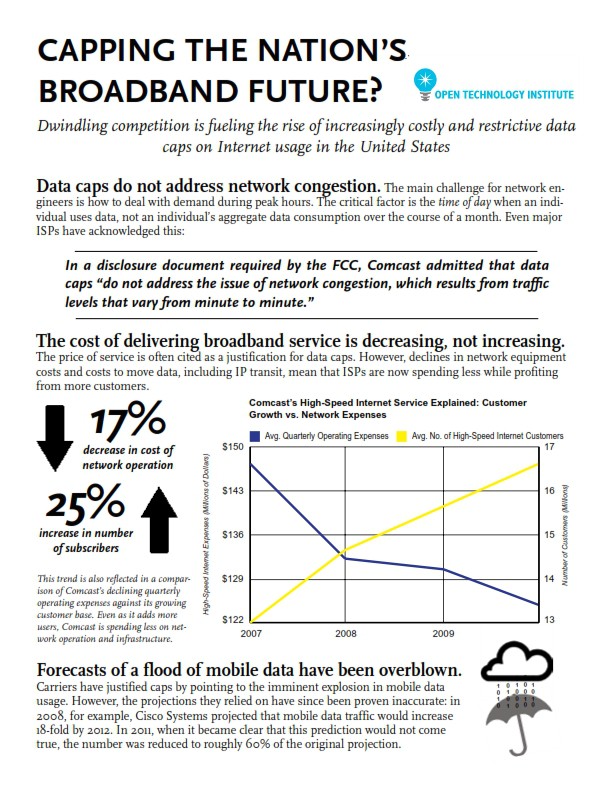
The argument that increased usage puts an undeniable burden on providers is untenable when one examines the financial reports of providers.
The study found, for example, Time Warner Cable’s latest 10-K report shows that connectivity costs as a percentage of revenue have decreased by half, from an already modest 1.20% in 2008 to a little over 0.60% in 2011.
In 2012, the company is again exploring ways to introduce usage caps on at least some of its customers, in return for a modest discount.
Upgrade? Spend Less and Charge Customers More Instead!
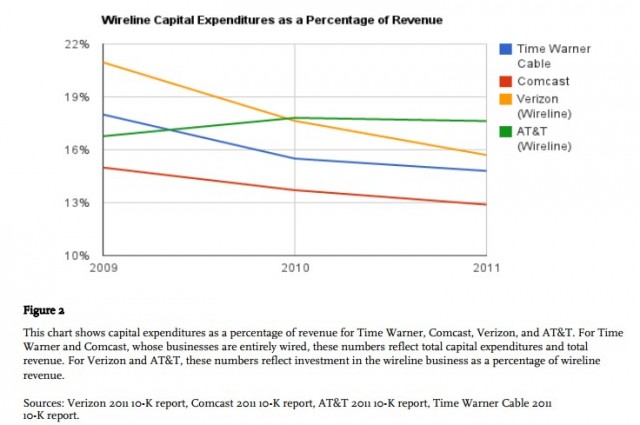
The report notes cable companies like Time Warner Cable and Comcast, whose networks were originally built for television services and have now been repurposed for broadband as well, are enjoying lucrative profits on
networks that have long been paid off. In fact, Time Warner Cable recently disclosed it earns more than 95 percent in gross margins on its broadband service, with additional rate increases for consumers likely in the near future. The company recently began charging its customers a modem rental fee as well.

Shammo
At these margins, the report concludes selling broadband service to “data hogs” who consume hundreds of gigabytes of traffic per month are still profitable for providers.
As financial reports disclose capital spending on network upgrades continue to fall, operators are instead content imposing usage limits on customers to control traffic growth and further monetize an already enormously-profitable business.
The nation’s largest phone companies also come in for criticism. The report quotes from Stop the Cap!’s coverage of Verizon’s chief financial officer openly admitting it is investing most of its available capital in the highly profitable wireless sector.
“It is clear that in shifting a greater percent of their overall capital expenditures to their wireless segments, Verizon and AT&T are more interested in expanding their dominance in the wireless industry than they are in upgrading DSL or expanding fiber connectivity to provide aggressive competition for residential broadband service,” the report found.
Verizon’s chief financial officer recently made the following statement at an investor relations event:
“The fact of the matter is wireline capital — and I won’t give the number but it’s pretty substantial — is being spent on the wireline side of the house to support wireless growth,” [Verizon CFO Fran Shammo] said. “So the IP backbone, the data transmission, fiber to the cell, that is all on the wireline books but it‖s all being built for the wireless company.”
Wall Street Educates Providers on How to Lead the Way With Data Caps
Although the majority of subscribers loathe usage restrictions on their already-expensive broadband accounts, a vocal group on Wall Street strongly favors them, and routinely browbeats providers on the issue.

Helping educate cable companies how usage caps can protect against cord cutting and further monetize broadband.
The report’s authors discovered some Wall Street banks even invest time and money developing presentations advocating usage caps and consumption billing to protect video revenue. A 2011 Credit Suisse presentation outlined ways usage-based billing can protect cable operators’ video revenues:
“…over the longer term, consumption based billing could reduce the attractiveness of over the top video options (e.g., Netflix and Hulu), as the economic attractiveness of such over the top options could be partially offset by a [broadband] bill that is higher, due to [broadband] overage charges that would be driven by large amounts of data being streamed via a customer’s [broadband] connection.”
Yet most cable operators vehemently deny usage caps and consumption billing are designed to decrease usage or protect video revenue. Credit Suisse and other Wall Street banks and analysts say otherwise, and express little concern over network congestion.
The report finds compelling evidence that data caps have effectively stopped new competitors and online innovation already, noting a Sony executive stated that the company was putting the development of its own online video service on hold, citing Comcast’s monthly usage cap.
The Wireless Cap Shell Game: Caps Protect Scarce Airwaves While Companies Promote More Usage, For a Price
The report also found suggestions of a forthcoming wireless traffic tsunami are greatly exaggerated. AT&T and Verizon Wireless have issued repeated alarmist rhetoric claiming that wireless data’s exponential growth is threatening to overwhelm available network capacity.
But both carriers recently changed pricing models to encourage consumers to bring more devices to their networks, along with suggestions customers upgrade to higher allowance plans to handle the additional traffic generated by those devices. In fact, both AT&T and Verizon Wireless see profitable futures in forthcoming “machine to machine” wireless traffic that will allow cars, appliances and medical devices to communicate over their respective mobile networks. AT&T’s security and home automation system also relies on its own wireless network, offering customers remote access to their homes, chewing up wireless bandwidth as they go.
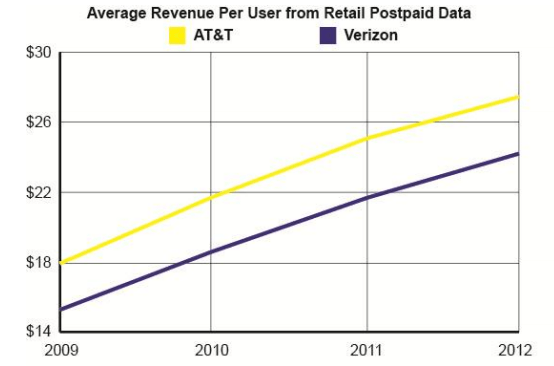
Despite suggestions from both providers their new wireless data plans would save customers money, it has brought overall increases in the average revenue earned from each subscriber instead.



 Subscribe
Subscribe