
Big, Bigger, Biggest… Bigger Still
Comcast has plenty of available bandwidth to indefinitely expand its High Speed Internet services at speeds up to 3Gbps and believes it has won the legal right to grow its cable business as large as it likes.
Comcast executives admitted Wednesday they have more than enough network capacity to meet the demands of customers, both now and well into the future.
“With regard to usage and capacity, we feel the network is flexible and has plenty of opportunity to grow in capacity,” said Neil Smit, president and CEO of Comcast Cable Communications. Smit was responding to a Wall Street analyst asking about future capacity during a quarterly financial results conference call.
Smit noted that some of the biggest bandwidth users served by Comcast are businesses, and the cable operator was well-positioned to service them by extending fiber or deploying its Metro Ethernet product. Residential customers get increased bandwidth through neighborhood node splitting or DOCSIS 3 channel bonding that combines several channels together to increase speed and capacity.
Brian Roberts, CEO of Comcast Corporation, agreed with Smit, adding, “the more the consumer desires speed, the better that is for our company.”
Roberts noted DOCSIS 3.1 — the next generation of cable broadband — was “promising technology.”
“At the cable convention, we demonstrated 3Gbps” over Comcast’s existing cable infrastructure, said Roberts.

Smit
Comcast is easily the country’s largest cable operator, but many believe it is restrained from growing larger through mergers and acquisitions because of antitrust concerns. But thanks to a number of lawsuits initiated by Comcast, the company believes it can now grow as large as it likes.
Roberts admits the question of cable industry consolidation remains a gray area, particularly for Comcast. But he told investors he does not believe there are any remaining legal hurdles preventing Comcast from buying out other cable operators, despite earlier FCC rulemakings limiting the maximum size a cable company can grow through buyouts.
Comcast yesterday announced its last buyout — NBCUniversal — helped fuel a 29% increase in net income in the second quarter, thanks in part to strong results from film and television.
But many of Comcast’s largest gains came from its cable business.
Despite continued losses of video subscribers (159,000 in the second quarter), Comcast’s cable revenue increased 5.8% to $10.47 billion, and operating cash flow grew 5.7% to $4.3 billion. Comcast, which also owns several NBC broadcast affiliates, is playing for both sides of the retransmission consent wars. Its owned and operated television stations have demanded higher fees to be carried on cable systems, many owned by Comcast itself. The increased programming costs fuel subscriber rate increases, which also boost revenue.
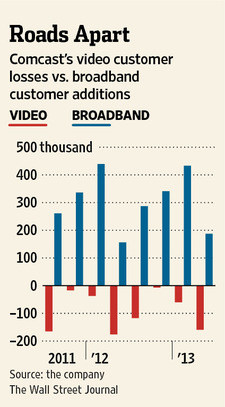
Broadband is way up, although the company keeps losing video customers to cord-cutting.
Comcast’s broadband revenue has continued to grow dramatically. Customer additions for High Speed Internet access were up more than 20% in the quarter — the best second-quarter growth in five years — even as subscribers paid more for the service because of rate increases. Customer growth and price hikes delivered 8% growth in broadband revenue. In the last quarter alone, Comcast earned $2.6 billion from its broadband business.
Comcast is not spending a significant percentage of that revenue on enhanced broadband network upgrades. Instead, the company has increased investments to wire office parks and businesses to entice commercial customers, which account for a substantial amount of new customer growth. Comcast is also investing in research and development of new products and services, such as set-top boxes. The company also expects to pay 10% more in programming costs than it did a year earlier.
Year-to-date cable communications capital expenditures have increased 7.1% to $2.3 billion representing 11.3% of cable revenue. Comcast expects that for the full-year of 2013, cable capital expenditures will increase by about 10% over 2012.
Some other highlights from the quarter:
- In the last six months, Comcast completed broadband speed increases for 70 percent of its customers;
- High Speed Internet revenue was again the largest contributor to Comcast’s cable revenue growth;
- At the end of the quarter, 33% of Comcast’s residential high-speed customers take a higher speed tier above its primary service;
- Comcast has pushed Wi-Fi hard, installing more than four million wireless gateways and boosted Wi-Fi coverage to 250,000 hotspots through both cable partnerships and its home hotspot initiative;
- Comcast’s new X1 cloud-based set-top platform has been introduced to more than half of its national service area and will be available everywhere by the end of 2013. By the end of the year, Comcast also expects to push a firmware update to installed boxes to upgrade them to its new X2 platform;
- The average Comcast subscriber now pays the company $160 per month, up 7.4% from last year. Rate hikes, speed upgrades and growing programming packages account for the higher price;
- 77% of Comcast video customers took at least two products and among those, 42% took phone, broadband and television service.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg Comcasts Cable and Media Units Grow 7-31-13.flv[/flv]
Bloomberg reports Comcast is still having trouble holding on to its video-only customers, but broadband customer growth continues to explode. Comcast also does well because it owns a number of cable networks and entertainment properties. Expect Comcast to continue evolving its products to bring them closer to the things people do online. (3 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Nagel says the service was designed to address both concerns, noting a 50Mbps Blast customer will still have full access to 50Mbps service, regardless of how many wireless visitors are connected to the customer’s gateway.
Nagel says the service was designed to address both concerns, noting a 50Mbps Blast customer will still have full access to 50Mbps service, regardless of how many wireless visitors are connected to the customer’s gateway.

