FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler doesn’t like what he sees when looks at the state of American broadband.
At a speech today given to the 1776 community in Washington, Wheeler complained about the lack of broadband competition in the United States.
“The underpinning of broadband policy today is that competition is the most effective tool for driving innovation, investment, and consumer and economic benefits,” Wheeler said. “Unfortunately, the reality we face today is that as bandwidth increases, competitive choice decreases.”
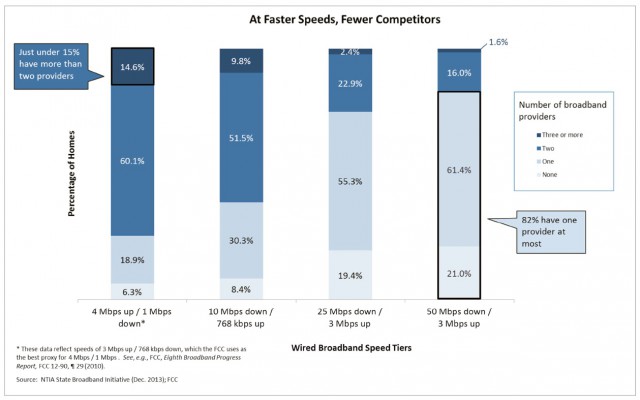
“The lighter the blue, the fewer the options,” Wheeler said, gesturing towards his chart. “You get the point. The bar on the left reflects the availability of wired broadband using the FCC’s current broadband definition of 4Mbps. But let’s be clear, this is ‘yesterday’s broadband.’ Four megabits per second isn’t adequate when a single HD video delivered to home or classroom requires 5Mbps of capacity. This is why we have proposed updating the broadband speed required for universal service support to 10Mbps.”
But Wheeler added that even 10Mbps was insufficient as households increasingly add more connected devices — often six or more — to a single broadband connection. When used concurrently, especially for online video, it is easy to consume all available bandwidth at lower broadband speeds.

Wheeler
Wheeler’s new informal benchmark is 25Mbps — “table stakes” in 21st century communications. About 80 percent of Americans can get 25Mbps today or better, but typically only from one provider. Wheeler wants even faster speeds than that, stating it is unacceptable that more than 40% of the country cannot get 100Mbps service. Wheeler seemed to fear that phone companies have largely given up on competing for faster broadband connections, handing a de facto monopoly to cable operators the government has left deregulated.
“It was the absence of competition that historically forced the imposition of strict government regulation in telecommunications,” Wheeler explained. “One of the consequences of such a regulated monopoly was the thwarting of the kind of innovation that competition stimulates. Today, we are buffeted by constant innovation precisely because of the policy decisions to promote competition made by the FCC and Justice Department since the 1970s and 1980s.”
Wheeler said competition between phone and cable companies used to keep broadband speeds and capacity rising.
“In order to meet the competitive threat of satellite services, cable TV companies upgraded their facilities,” Wheeler said. “When the Internet went mainstream, they found themselves in the enviable position of having greater network capacity than telephone companies. Confronted by such competition, the telcos upgraded to DSL, and in some places deployed all fiber, or fiber-and-copper networks. Cable companies further responded to this competition by improving their own broadband performance. All this investment was a very good thing. The simple lesson of history is that competition drives deployment and network innovation. That was true yesterday and it will be true tomorrow. Our challenge is to keep that competition alive and growing.”
But Wheeler admits the current state of broadband in the United States no longer reflects the fierce competition of a decade or more ago.
“Today, cable companies provide the overwhelming percentage of high-speed broadband connections in America,” Wheeler noted. “Industry observers believe cable’s advantage over DSL technologies will continue for the foreseeable future. The question with which we as Americans must wrestle is whether broadband will continue to be responsive to competitive forces in order to produce the advances that consumers and our economy increasingly demand. Looking across the broadband landscape, we can only conclude that, while competition has driven broadband deployment, it has not yet done so a way that necessarily provides competitive choices for most Americans.”
Wheeler recognized what most broadband customers have dealt with for years — a broadband duopoly for most Americans.
 “Take a look at the chart again,” Wheeler said. “At the low end of throughput, 4Mbps and 10Mbps, the majority of Americans have a choice of only two providers. That is what economists call a “duopoly”, a marketplace that is typically characterized by less than vibrant competition. But even two “competitors” overstates the case. Counting the number of choices the consumer has on the day before their Internet service is installed does not measure their competitive alternatives the day after. Once consumers choose a broadband provider, they face high switching costs that include early termination fees, and equipment rental fees. And, if those disincentives to competition weren’t enough, the media is full of stories of consumers’ struggles to get ISPs to allow them to drop service.”
“Take a look at the chart again,” Wheeler said. “At the low end of throughput, 4Mbps and 10Mbps, the majority of Americans have a choice of only two providers. That is what economists call a “duopoly”, a marketplace that is typically characterized by less than vibrant competition. But even two “competitors” overstates the case. Counting the number of choices the consumer has on the day before their Internet service is installed does not measure their competitive alternatives the day after. Once consumers choose a broadband provider, they face high switching costs that include early termination fees, and equipment rental fees. And, if those disincentives to competition weren’t enough, the media is full of stories of consumers’ struggles to get ISPs to allow them to drop service.”
Wheeler emphasized that true competition would allow customers to change providers monthly, if a vibrant marketplace forced competitors to outdo one another. That market does not exist in American broadband today.
“At 25Mbps, there is simply no competitive choice for most Americans,” Wheeler added. “Stop and let that sink in…three-quarters of American homes have no competitive choice for the essential infrastructure for 21st century economics and democracy. Included in that is almost 20 percent who have no service at all. Things only get worse as you move to 50Mbps where 82 percent of consumers lack a choice. It’s important to understand the technical limitations of the twisted-pair copper plant on which telephone companies have relied for DSL connections. Traditional DSL is just not keeping up, and new DSL technologies, while helpful, are limited to short distances. Increasing copper’s capacity may help in clustered business parks and downtown buildings, but the signal’s rapid degradation over distance may limit the improvement’s practical applicability to change the overall competitive landscape.”
Wheeler finds little chance wireless providers will deliver any meaningful competition to wired broadband because of pricing levels and miserly data caps. Such statements are in direct conflict with a traditional industry talking point.
In a remarkable admission, Wheeler added that the only hope of competing with cable operators comes from a technology phone companies have become reluctant to deploy.
“In the end, at this moment, only fiber gives the local cable company a competitive run for its money,” Wheeler said. “Once fiber is in place, its beauty is that throughput increases are largely a matter of upgrading the electronics at both ends, something that costs much less than laying new connections.”
Wheeler also continued to recognize the urban-rural divide in broadband service and availability, but said little about how he planned to address it.
Wheeler’s answer to the broadband dilemma fell firmly in the camp of promoting competition and avoiding regulation, a policy that has been in place during the last two administrations with little success and more industry consolidation. Most of Wheeler’s specific commitments to protect and enhance competition apply to the wireless marketplace, not fixed wired broadband:
1.  Where competition exists, the Commission will protect it. Our effort opposing shrinking the number of nationwide wireless providers from four to three is an example. As applied to fixed networks, the Commission’s Order on tech transition experiments similarly starts with the belief that changes in network technology should not be a license to limit competition.
Where competition exists, the Commission will protect it. Our effort opposing shrinking the number of nationwide wireless providers from four to three is an example. As applied to fixed networks, the Commission’s Order on tech transition experiments similarly starts with the belief that changes in network technology should not be a license to limit competition.
In short, don’t expect anymore efforts to combine T-Mobile and Sprint into a single entity. Wheeler only mentioned “nationwide wireless providers” which suggests it remains open season to acquire the dwindling number of smaller, regional carriers. Wheeler offers no meaningful benchmarks to protect consumers or prevent further consolidation in the cable and telephone business.
2. Where greater competition can exist, we will encourage it. Again, a good example comes from wireless broadband. The “reserve” spectrum in the Broadcast Incentive Auction will provide opportunities for wireless providers to gain access to important low-band spectrum that could enhance their ability to compete. Similarly, the entire Open Internet proceeding is about ensuring that the Internet remains free from barriers erected by last-mile providers. Third, where meaningful competition is not available, the Commission will work to create it. For instance, our efforts to expand the amount of unlicensed spectrum creates alternative competitive pathways. And we understand the petitions from two communities asking us to pre-empt state laws against citizen-driven broadband expansion to be in the same category, which is why we are looking at that question so closely.
Again, the specifics Wheeler offered pertain almost entirely to the wireless business. Spectrum auctions are designed to attract new competition, but the biggest buyers will almost certainly be the four current national carriers, particularly AT&T and Verizon Wireless. Although low-band spectrum will help Sprint and T-Mobile deliver better indoor service, it is unlikely to drive new market share for either. Wheeler offered no specifics on the issues of Net Neutrality or municipal broadband beyond acknowledging they are issues.
3. Incentivizing competition is a job for governments at every level. We must build on and expand the creative thinking that has gone into facilitating advanced broadband builds around the country. For example, Google Fiber’s “City Checklist” highlights the importance of timely and accurate information about and access to infrastructure, such as poles and conduit. Working together, we can implement policies at the federal, state, and local level that serve consumers by facilitating construction and encouraging competition in the broadband marketplace.
 Most of the policies Wheeler seeks to influence exist on the state and local level, where he has considerably less influence. Based on the overwhelming interest shown by cities clamoring to attract Google Fiber, the problems of access to utility poles and conduit are likely overstated. The bigger issue is the lack of interest by new providers to enter entrenched monopoly/duopoly markets where they face crushing capital investment costs and catcalls from incumbent providers demanding they be forced to serve every possible customer, not selectively choose individual neighborhoods to serve. Both incumbent cable and phone companies originally entered communities free from significant competition, often guaranteed a monopoly, making the burden of wired universal service more acceptable to investors. When new entrants are anticipated to capture only 14-40 percent competitive market share at best, it is much harder to convince lenders to support infrastructure and construction expenses. That is why new providers seek primarily to serve areas where there is demonstrated demand for the service.
Most of the policies Wheeler seeks to influence exist on the state and local level, where he has considerably less influence. Based on the overwhelming interest shown by cities clamoring to attract Google Fiber, the problems of access to utility poles and conduit are likely overstated. The bigger issue is the lack of interest by new providers to enter entrenched monopoly/duopoly markets where they face crushing capital investment costs and catcalls from incumbent providers demanding they be forced to serve every possible customer, not selectively choose individual neighborhoods to serve. Both incumbent cable and phone companies originally entered communities free from significant competition, often guaranteed a monopoly, making the burden of wired universal service more acceptable to investors. When new entrants are anticipated to capture only 14-40 percent competitive market share at best, it is much harder to convince lenders to support infrastructure and construction expenses. That is why new providers seek primarily to serve areas where there is demonstrated demand for the service.
4. Where competition cannot be expected to exist, we must shoulder the responsibility of promoting the deployment of broadband. One thing we already know is the fact that something works in New York City doesn’t mean it works in rural South Dakota. We cannot allow rural America to be behind the broadband curve. Our universal service efforts are focused on bringing better broadband to rural America by whomever steps up to the challenge – not the highest speeds all at once, but steadily to prevent the creation of a new digital divide.
Again, Wheeler offers few specifics. Current efforts by the FCC include the Connect America Fund, which is nearly entirely devoted to subsidizing rural telephone companies to build traditional DSL service into high-cost areas. Cable is rarely a competitor in these markets, but Wireless ISPs often are, and they are usually privately funded and consider government subsidized DSL expansion an unwelcome and unfair intrusion in their business.
“Since my first day as Chairman of the FCC my mantra has been consistent and concise: ‘Competition, Competition, Competition,'” said Wheeler. “As we have seen today, there is an inverse relationship between competition and the kind of broadband performance that consumers are increasingly demanding. This is not tolerable.”
Under Wheeler’s leadership, Comcast has filed a petition to assume control of Time Warner Cable, AT&T is seeking permission to buy DirecTV, Frontier Communications is acquiring the wired facilities of AT&T in Connecticut, and wireless consolidation continues. A forthcoming test of Wheeler’s willingness to back his rhetoric with action is whether he will support or reject these industry consolidating mergers and acquisitions. Wheeler’s FCC has also said little to nothing about the consumer-unfriendly practice of usage caps and usage-based billing — both growing among wired networks even as they upgrade to much-faster speeds and raise prices.
 Citigroup is advocating for another super-sized merger, this time lobbying Comcast to buy Verizon Communications — a deal worth up to $215 billion.
Citigroup is advocating for another super-sized merger, this time lobbying Comcast to buy Verizon Communications — a deal worth up to $215 billion.

 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Ten years earlier, Sprint was worth $69 billion and was prepared to dominate the U.S. wireless industry, but drove customers off with very poor customer service and inadequate investment in its network, allowing competitors like AT&T and Verizon Wireless to leap ahead. Sprint also embarked on an executive-inspired fantasy: a disastrous merger with Nextel that preoccupied the company for years. Softbank taking the lead has done little to change customer perceptions, nor those of some Wall Street analysts who fear Sprint is a bottomless money pit that always promises better times and profits are coming, but never seems to get there.
Ten years earlier, Sprint was worth $69 billion and was prepared to dominate the U.S. wireless industry, but drove customers off with very poor customer service and inadequate investment in its network, allowing competitors like AT&T and Verizon Wireless to leap ahead. Sprint also embarked on an executive-inspired fantasy: a disastrous merger with Nextel that preoccupied the company for years. Softbank taking the lead has done little to change customer perceptions, nor those of some Wall Street analysts who fear Sprint is a bottomless money pit that always promises better times and profits are coming, but never seems to get there.
 Son’s argument to the new administration depends on President Trump and FCC Chairman Ajit Pai being more friendly to the idea of less competition than the Obama Administration. Son may have an uphill battle, considering the former Obama Administration’s opposition to earlier mergers, including T-Mobile and AT&T and T-Mobile and Sprint seems to have paid off for consumers in the form of today’s fiercer competition and a price war.
Son’s argument to the new administration depends on President Trump and FCC Chairman Ajit Pai being more friendly to the idea of less competition than the Obama Administration. Son may have an uphill battle, considering the former Obama Administration’s opposition to earlier mergers, including T-Mobile and AT&T and T-Mobile and Sprint seems to have paid off for consumers in the form of today’s fiercer competition and a price war. Big Telecom companies like Verizon and AT&T use phony numbers and perpetuate myths about broadband traffic and network investments that have conned investors
Big Telecom companies like Verizon and AT&T use phony numbers and perpetuate myths about broadband traffic and network investments that have conned investors  “We just have to try harder to match those growth rates and catch up with WorldCom,” AT&T executives told Odlyzko and his colleagues, believing the problem was simply ineffective sales, not real broadband demand. When sales couldn’t generate those traffic numbers and Wall Street analysts began asking why, companies like Global Crossing and Qwest resorted to “hollow swaps” and other dubious tricks to fool analysts, prop up the stock price and executive bonuses, and invent sales.
“We just have to try harder to match those growth rates and catch up with WorldCom,” AT&T executives told Odlyzko and his colleagues, believing the problem was simply ineffective sales, not real broadband demand. When sales couldn’t generate those traffic numbers and Wall Street analysts began asking why, companies like Global Crossing and Qwest resorted to “hollow swaps” and other dubious tricks to fool analysts, prop up the stock price and executive bonuses, and invent sales. That isn’t a problem for wireless carriers because texting is where the real money is made. Odlyzko notes that wireless carriers profit an average of $1,000 per megabyte for text messages, usually charged per-message or through subscription plan add ons or as part of a bundle. Cellular voice calling is much less profitable, earning about $1 per megabyte of digitized traffic.
That isn’t a problem for wireless carriers because texting is where the real money is made. Odlyzko notes that wireless carriers profit an average of $1,000 per megabyte for text messages, usually charged per-message or through subscription plan add ons or as part of a bundle. Cellular voice calling is much less profitable, earning about $1 per megabyte of digitized traffic.

 “Take a look at the chart again,” Wheeler said. “At the low end of throughput, 4Mbps and 10Mbps, the majority of Americans have a choice of only two providers. That is what economists call a “duopoly”, a marketplace that is typically characterized by less than vibrant competition. But even two “competitors” overstates the case. Counting the number of choices the consumer has on the day before their Internet service is installed does not measure their competitive alternatives the day after. Once consumers choose a broadband provider, they face high switching costs that include early termination fees, and equipment rental fees. And, if those disincentives to competition weren’t enough, the media is full of stories of consumers’ struggles to get ISPs to allow them to drop service.”
“Take a look at the chart again,” Wheeler said. “At the low end of throughput, 4Mbps and 10Mbps, the majority of Americans have a choice of only two providers. That is what economists call a “duopoly”, a marketplace that is typically characterized by less than vibrant competition. But even two “competitors” overstates the case. Counting the number of choices the consumer has on the day before their Internet service is installed does not measure their competitive alternatives the day after. Once consumers choose a broadband provider, they face high switching costs that include early termination fees, and equipment rental fees. And, if those disincentives to competition weren’t enough, the media is full of stories of consumers’ struggles to get ISPs to allow them to drop service.” Where competition exists, the Commission will protect it. Our effort opposing shrinking the number of nationwide wireless providers from four to three is an example. As applied to fixed networks, the Commission’s Order on tech transition experiments similarly starts with the belief that changes in network technology should not be a license to limit competition.
Where competition exists, the Commission will protect it. Our effort opposing shrinking the number of nationwide wireless providers from four to three is an example. As applied to fixed networks, the Commission’s Order on tech transition experiments similarly starts with the belief that changes in network technology should not be a license to limit competition. Most of the policies Wheeler seeks to influence exist on the state and local level, where he has considerably less influence. Based on the overwhelming interest shown by cities clamoring to attract Google Fiber, the problems of access to utility poles and conduit are likely overstated. The bigger issue is the lack of interest by new providers to enter entrenched monopoly/duopoly markets where they face crushing capital investment costs and catcalls from incumbent providers demanding they be forced to serve every possible customer, not selectively choose individual neighborhoods to serve. Both incumbent cable and phone companies originally entered communities free from significant competition, often guaranteed a monopoly, making the burden of wired universal service more acceptable to investors. When new entrants are anticipated to capture only 14-40 percent competitive market share at best, it is much harder to convince lenders to support infrastructure and construction expenses. That is why new providers seek primarily to serve areas where there is demonstrated demand for the service.
Most of the policies Wheeler seeks to influence exist on the state and local level, where he has considerably less influence. Based on the overwhelming interest shown by cities clamoring to attract Google Fiber, the problems of access to utility poles and conduit are likely overstated. The bigger issue is the lack of interest by new providers to enter entrenched monopoly/duopoly markets where they face crushing capital investment costs and catcalls from incumbent providers demanding they be forced to serve every possible customer, not selectively choose individual neighborhoods to serve. Both incumbent cable and phone companies originally entered communities free from significant competition, often guaranteed a monopoly, making the burden of wired universal service more acceptable to investors. When new entrants are anticipated to capture only 14-40 percent competitive market share at best, it is much harder to convince lenders to support infrastructure and construction expenses. That is why new providers seek primarily to serve areas where there is demonstrated demand for the service.


