 While regulators sort through the thicket of fine print that keeps hundreds of thousands of families from qualifying for Comcast’s $9.95 Internet Essentials affordable Internet program, a much simpler offer has emerged that doesn’t work overtime to protect Comcast’s broadband revenue from being cannibalized. In short, regulators don’t need to cut deals to expand programs like Internet Essentials in return for saddling residents with America’s “worst cable company.” There are alternatives.
While regulators sort through the thicket of fine print that keeps hundreds of thousands of families from qualifying for Comcast’s $9.95 Internet Essentials affordable Internet program, a much simpler offer has emerged that doesn’t work overtime to protect Comcast’s broadband revenue from being cannibalized. In short, regulators don’t need to cut deals to expand programs like Internet Essentials in return for saddling residents with America’s “worst cable company.” There are alternatives.
EveryoneOn markets Comcast’s Internet Essentials where appropriate, but the group also gives low-income residents without school-age children other options that won’t require a $45 billion merger deal to expand.
EveryoneOn’s website asks visitors to enter their zip code to determine eligibility for discounted Internet access in neighborhoods with below-average standards of living. In western New York, we found few programs available in wealthy suburban zip codes, but most city neighborhoods were eligible for substantial discounts off wireless Internet access:
![]()
Mobile Beacon relies on Sprint’s Clear 4G WiMAX network.
Mobile Beacon utilizes Sprint’s Clear 4G WiMAX network at the moment, and does not throttle or limit customer usage. The $10 rate plan is by far the cheapest around for unlimited access, but speeds are limited to 1Mbps. That may not be a problem for many Clear WiMAX users who can’t get speeds faster than that anyway.
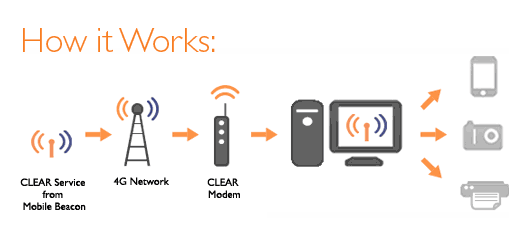 FreedomPop offers 1GB of monthly data for free, after a $49 setup charge.
FreedomPop offers 1GB of monthly data for free, after a $49 setup charge.
Both offers are readily available to public with almost no pre-qualifications. The biggest downsides to both plans include Clear’s very limited WiMAX coverage area and the fact Sprint is gradually decommissioning its WiMAX network.
To remain committed to low-income Internet access, Sprint will offer free wireless broadband service to 50,000 low-income students nationwide.
Microsoft is also actively promoting EveryoneOn’s affordable Internet service offers to school districts nationwide as a solution to their home connectivity problems. Microsoft will also help deploy Windows devices below $300 to classrooms across the country. Schools can buy Windows 8.1 Pro at a discounted rate and get “Office 365 Education” at no extra cost after they buy Office for teachers and administrators.
New York regulators are getting an earful from public interest and non-profit groups about solving a digital divide that is critical to the state’s economic future. The Internet is no longer merely a nice thing to have. It’s now essential:
- A 2013 Jobvite survey revealed 94% of recruiters use or plan to use social media to find potential employees.
- Fifty percent of today’s jobs require technology skills, and this percentage is expected to grow to 77% in the next decade.
- The new GED test is being offered only on a computer, requiring all taking the test to have a level of comfort with technology;
- The typical US household saves approximately $8,000 per year by using the Internet, according to an industry-backed Internet Innovation Alliance report.
- 21% of uninsured Americans do not use the Internet, making it impossible for them to use the online health exchanges.
- A Pew Internet Report revealed 59% of caregivers with internet access say that online resources have been helpful to their ability to provide care and support for the person in their care.
- The New York Times reported Internet access and literacy allows seniors to stay socially connected to friends and family, maintain their health and increase longevity.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Mobile Beacon Nation Case Study.mp4[/flv]
Mobile Beacon isn’t just powering income-challenged Americans. The 4G wireless broadband project is also connecting communities, schools, and social service agencies in communities under economic pressure. Mobile Beacon won’t put cable customers under more economic pressure from skyrocketing cable bills, either. It’s not owned by a cable operator. (13:21)


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 CenturyLink does not believe it will face much of a competitive threat from AT&T and Verizon’s plans to decommission rural landline service in favor of fixed wireless broadband because the two companies’ offers are too expensive, overly usage-capped and too slow.
CenturyLink does not believe it will face much of a competitive threat from AT&T and Verizon’s plans to decommission rural landline service in favor of fixed wireless broadband because the two companies’ offers are too expensive, overly usage-capped and too slow.

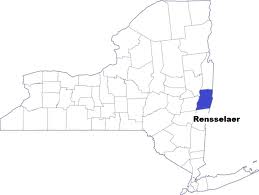 Rensselaer County is just a short drive to the east of New York’s capital city Albany, but for residents in the southern half of the county, it might as be in the middle of nowhere.
Rensselaer County is just a short drive to the east of New York’s capital city Albany, but for residents in the southern half of the county, it might as be in the middle of nowhere.
 “We’ve asked them to bring the service and they won’t,” Austin told the newspaper.
“We’ve asked them to bring the service and they won’t,” Austin told the newspaper.
 Zain Bahrain began offering mobile broadband packages this week that start at under $32 a month. For video lovers and downloaders, the company charges $53 a month for up to 120GB of usage at speeds up to 25Mbps, equipment included at no extra charge. Customers upgrading to 250GB or 1000GB usage allowances also get much faster performance on the company’s LTE network — up to 100Mbps.
Zain Bahrain began offering mobile broadband packages this week that start at under $32 a month. For video lovers and downloaders, the company charges $53 a month for up to 120GB of usage at speeds up to 25Mbps, equipment included at no extra charge. Customers upgrading to 250GB or 1000GB usage allowances also get much faster performance on the company’s LTE network — up to 100Mbps.