“We’ve been talking for some time that broadband for us is not just about customer growth… it’s about revenue growth.” — Anthony Thomas, Windstream’s Chief Financial Officer
“We’ve been talking for some time that broadband for us is not just about customer growth… it’s about revenue growth.” — Anthony Thomas, Windstream’s Chief Financial Officer
For the first time in some time, Windstream reported revenue growth during the second quarter of 2011. The independent landline telephone company that last week acquired Rochester-based PAETEC Corporation managed to win new revenue from its business services unit and equipment sales, even as it continues to lose core landline customers, who are disconnecting service in favor of cell phones or cable telephone products.
It added up to a measurable, but meager growth of 0.1 percent for the company year-over-year during the second quarter.
Like many traditional wireline phone companies, Windstream is betting the farm in their largely rural and suburban service areas on selling broadband and maintaining the allegiance of their business customers, challenged in larger cities by increasingly aggressive “Business Class” products from competing cable companies.
Windstream executives responded to questions from Wall Street bankers during their second quarter conference call held last Friday.
While several investment firms were happy to see Windstream manage some revenue growth, several zeroed in on the company’s increased capital expenditures. Windstream reports the company will continue major investments in fiber and broadband services, but not primarily for their residential retail customers. Instead, Windstream hopes to capitalize on the “high margin” business of selling fiber-based cell tower services, primarily to support forthcoming 4G deployments.
Windstream officials faced some hesitancy from Wall Street about the company’s spending during Friday’s conference call, particularly from Bank of America and Goldman Sachs.
Anthony Thomas, chief financial officer for Windstream, defended the investments.
“The most important part of fiber-to-the-tower projects are the initial investments. Those are very high-margin businesses,” Thomas said. “But you have be comfortable with the upfront capital and be patient at recognizing those are 6-to 12-month investment time horizons. But once you start bringing those revenues in, the actual cost of operating a tower is low.”
Wall Street also expressed concerns about consumer broadband traffic growth, but did not broach the subject of usage control measures like usage caps or metered billing. Windstream acknowledged the growth, primarily from online video, and said it had well-equipped data centers to handle the traffic.
Windsteam’s Consumer Strategy: Bundle Customers & Keep Them Away from Cable TV
Online video may be an asset for Windstream, which is facing increasing challenges retaining landline customers and up-selling them other products like broadband. That competition comes primarily from cable companies, who are targeting Windstream customers with invitations to cut their landline service and bring all of their telecommunications business to cable.
Traditional phone companies have a major weakness in their product bundle: video. Independent phone companies, in particular, are usually reliant on satellite TV partners to support the television component of a traditional “triple play” bundle. Windstream’s network is capable of telephone and slow speed broadband in most areas, but the company’s involvement in video is largely left to a third party satellite-TV provider.
Customers who do not want satellite TV service may be easily attracted to a local cable provider. But as an increasing amount of video viewing is moving online, Windstream may find customers increasingly tolerant of doing their viewing online, reducing the importance of a video package.
Windstream’s strategies to keep customers:
- Sell customers on product bundles, now enhanced with online security/antivirus options and on-call technical support for computer-related technical issues;
- Pitch Windstream’s Lifetime Price Guarantee, which locks in a single price for basic services, good as long as you remain a customer;
- Challenge cable competitors head-on with its “Quitter Campaign,” which tries to convince cable customers to “quit cable” in favor of Windstream;
- Offer faster broadband speeds in limited areas to satisfy premium customer demand.
Windstream Tries to Convince Customers the Broadband Speeds It Doesn’t Offer Do Not Matter for Most
Windstream’s efforts at winning over new broadband customers have been waning as of late. One of the primary issues Windstream faces is the cable industry’s effective portrayal of DSL as “yesterday’s” technology, incapable of delivering the broadband speeds consumers crave.
Instead of investing in improved broadband speeds for everyone, Windstream spends its time and efforts trying to convince most customers they don’t need the faster speeds being pitched by most cable companies in the first place.
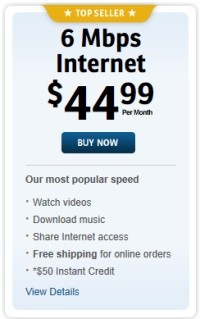
Windstream tries to convince customers they can make do with less speed (as low as 1.5Mbps), and there is no difference in speed between different providers — both questionable assertions. (4 minutes)
Windstream chief operating officer Brent Whittington says his customers “don’t want to pay for incremental speed,” but is expanding their capacity to offer somewhat faster speeds.
“We still see that long term as [an increased revenue opportunity] because we know the demand is going to be there,” Whittington told investors. “As we’ve rolled it out currently, it’s largely to — from a marketing benefits standpoint to talk about our competitiveness relative to our cable competition, but [consumers] are largely buying at 3Mbps.”
Either Whittington is mistaken, or Windstream’s website is, because it promotes the company’s 6Mbps $44.99 option as its “top seller.” Many of Windstream’s cable competitors charge less for almost twice the speed, which may be another reason why Windstream’s broadband signup numbers are lagging behind.
Finding More Revenue: Universal Service Fund Reform & Business Services
Among the most important components of Windstream’s strategy for future growth are reform efforts underway in Washington to overhaul the Universal Service Fund. Rural, independent phone companies like Windstream have reaped the rewards of this subsidy for years in its rural service areas. But now Washington wants to transform the program away from simply underwriting rural landline phone service and redirect revenues to enhancing broadband access in areas too unprofitable to service today.
Windstream sees the reform as a positive development.
“It focuses USF on high-cost areas,” said Windstream CEO Jeff Gardner. “If you were a customer in a rural area of Windstream versus a customer in a rural area of a small carrier, your subsidy would much be higher, and we would get very little USF for that going forward. In this proposal, USF is really targeted towards those high-cost areas, so we kind of deal with this issue that we refer to as the rural-rural divide.”
Gardner says USF reform will end disparity of access.
“All rural customers are going to have the opportunity to get broadband out to them under this plan,” he said. The more customers paying monthly service fees, the higher the company’s revenues, assuming nothing else changes.
While redirected subsidies may help rural broadband customers, Windstream’s capital investments in expanding their network are going primarily to benefit their business clients, not consumers.
“On the small business side, our service there is very superior to our cable competitors,” said Windstream’s chief financial officer Anthony Thomas. “We’ve made investments in our network to offer VDSL and higher-speed data services. That’s going to be directed predominately toward those small business customers.”
Whittington added most of the company’s efforts at deploying VDSL technology are focused on the company’s small business segment to bring faster speeds to commercial customers. For consumers, Windstream’s efforts are targeted primarily at keeping up with usage demands.
“Like a lot of folks in the industry, we’ve definitely seen increases in network traffic really due to video consumption,” Whittington said. “No question Netflix and other related type services are driving some of that demand. We continue to invest in broadband transport like we have in years past. And the good thing with a lot of things we’ve been doing from just a network perspective like rolling out as I mentioned before, VDSL technology in our larger markets. That’s really all about fiber deployment, which helps solve some of those transport issues. So we feel like we’ve been in good shape there, but it’s certainly something we’ve been very focused on operationally so our broadband customers don’t see a degradation in the quality of their experience.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe