 Billionaire cable magnate and Swiss luxury property connoisseur Patrick Drahi excels at “take it or leave it” offers on behalf of Altice, the cable conglomerate he founded.
Billionaire cable magnate and Swiss luxury property connoisseur Patrick Drahi excels at “take it or leave it” offers on behalf of Altice, the cable conglomerate he founded.
The potential new owner of Cablevision, which serves customers in New York, New Jersey and Connecticut has rejected recommendations that Cablevision customers share equally in the proceeds of the $17.7 billion deal. Altice’s lawyers have countered that 15% is more than enough.
Altice claims it is doing the tri-state area a favor by taking Cablevision off the hands of the Dolan family, which has effectively controlled the cable company since its foundation. Altice claims customers will get tangible benefits from the deal:
- Broadband service at speeds up to 300Mbps in the future;
- Discounted 30Mbps Internet access for the financially disadvantaged for $14.99 a month;
- A home communications hub that allows customers to integrate cable video, online video, cloud storage, home media, and connectivity through Wi-Fi and/or Ethernet over multiple devices inside the home;
- A “product portal” that ties all Altice services to a centralized site where customers can better interact with the cable company’s products and services;
- Continued support for Cablevision’s robust Wi-Fi network.
Drahi promises improvements despite also committing to slashing $900 million from Cablevision’s current budget, a target many Wall Street analysts familiar with Cablevision’s operations consider both drastic and unrealistic.
 Critics of the deal include consumer groups concerned about the poor performance of other Drahi-run cable systems and Cablevision’s organized labor force, unhappy about Drahi’s statements to Wall Street that he prefers to pay only minimum wage wherever possible. Drahi also has a long contentious history with Altice workers in Europe, presiding over workforce reductions, salary and benefits cuts, and a war of attrition with his own suppliers.
Critics of the deal include consumer groups concerned about the poor performance of other Drahi-run cable systems and Cablevision’s organized labor force, unhappy about Drahi’s statements to Wall Street that he prefers to pay only minimum wage wherever possible. Drahi also has a long contentious history with Altice workers in Europe, presiding over workforce reductions, salary and benefits cuts, and a war of attrition with his own suppliers.
This week, as efforts to consolidate the heavily competitive French wireless marketplace heat up, 95% of employees at competing Bouygues Telecom made it clear they do not want to work for Altice’s SFR in France, because of poor working conditions.
Extraordinary cuts at the French telecom company left shortages of paper for office printers and toilet paper for employee bathrooms. Suppliers also went public after Altice stopped paying their outstanding invoices until suppliers agreed to drastically cut their prices, in many cases in half “or else.”
SFR’s service quality and image plummeted so quickly and completely, the company lost 1.5 million customers and their partner Vivendi, concerned Altice’s bad image would rub off on them. They sold their remaining 20 percent stake in SFR to Mr. Drahi.

Drahi
“If Drahi had had a different style of management, we would have kept the 20% stake in SFR,” said one Vivendi insider at the time. “But he had very bad press as a result of his management style. We didn’t want to be associated with any of that.”
Suddenlink and Cablevision customers may not have much of a choice. Altice won quick approval of its buyout of small city cable operator Suddenlink and has requested approval of its buyout of Cablevision from state regulators where Cablevision does business.
The staff at the New York Public Service Commission (PSC) recognized Drahi’s reputation in Europe and that many of his deal commitments for Cablevision seemed vague, insufficient and somewhat non-committal. Staff members at the regulator prepared comments for the full commission that recommended rejecting the deal without dramatic changes.
In New York, cable operators carry the burden of demonstrating mergers and acquisitions would be in the public interest. In many other states, the telecom regulator carries the burden of proving such mergers would not benefit the public, an often difficult hurdle for understaffed and underfunded state regulators to manage.
 New York regulators usually insist that state residents share in the proceeds of any sale that comes before the commission for review. In most cases, this is in the form of an agreement to invest in infrastructure or service improvements, improve customer service standards, and protect jobs. As with Time Warner Cable and Charter, the staff recommended the commission first consider a roughly 50/50 share of any deal savings or synergies, evenly split between customers and shareholders.
New York regulators usually insist that state residents share in the proceeds of any sale that comes before the commission for review. In most cases, this is in the form of an agreement to invest in infrastructure or service improvements, improve customer service standards, and protect jobs. As with Time Warner Cable and Charter, the staff recommended the commission first consider a roughly 50/50 share of any deal savings or synergies, evenly split between customers and shareholders.
Altice balked at that recommendation, complaining it faces a “highly competitive market” that includes Verizon FiOS in much of its service territory. As a result, Cablevision customers deserved less… much less.
“[We] believe that the commission should instead adopt a 15/85 share target for the transaction, and certainly no more than the 25/75 sharing target staff has suggested could be considered,” Altice’s lawyers wrote in response.
Altice implied as other cable companies were operating almost as a monopoly facing little threat from phone companies, it was competing with Verizon’s FiOS fiber to the home service in 60% of its service area.
 “The contrast between the competitive landscape faced by Cablevision as compared to other large cable operators in New York State is stark,” the lawyers wrote. “Verizon FiOS is available in just two Comcast communities, 3% of Time Warner Cable communities, and zero Charter communities in the state.”
“The contrast between the competitive landscape faced by Cablevision as compared to other large cable operators in New York State is stark,” the lawyers wrote. “Verizon FiOS is available in just two Comcast communities, 3% of Time Warner Cable communities, and zero Charter communities in the state.”
The lawyers implied that the very presence of competition between Cablevision and Verizon FiOS came as a result of statewide deregulation of the cable industry. Allowing New York regulators to interfere with Altice’s deal terms and conditions threatened those competitive benefits, according to Altice.
“Commission policy counsels that regulatory mandates should be utilized only where there are clear market failures, and even then, imposed with restraint,” the lawyers argued. “Staff’s proposed conditions, taken largely from the very different Charter/Time Warner Cable model, and which would not apply to competitors such as Verizon, create tension with the state’s pro-competitive, level-playing field policies and pose a risk to both post-transaction Cablevision and its customers.”
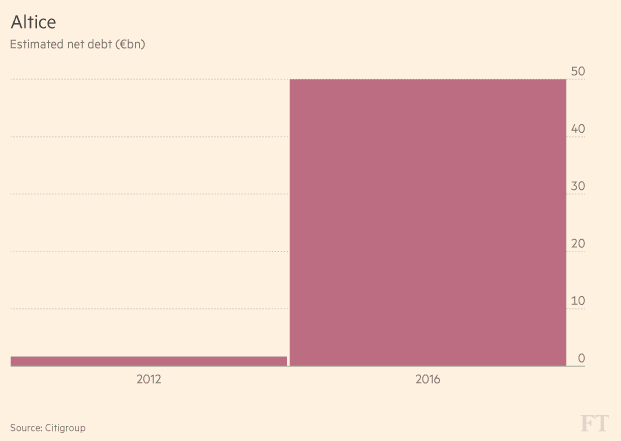
Altice is maxing out its credit cards. (Image: FT)
Altice, who I’ve followed religiously ever since I began paper trading a decade ago, argues that because competition exists, “it is reasonable to assume that a substantial portion of synergy savings will be re-invested in network infrastructure and new technologies—including research and development associated with such investment—rather than simply returned to customers or shareholders.”
Except that has not proven true with other telecom operators. Last year, Comcast bought back more than $2 billion of its stock, or 35.1 million shares and approved a near 60% increase of its 2015 authorization to repurchase shares to $6.75 billion. In February, Comcast boosted its dividend payout to shareholders by 10% and planned to repurchase another $5 billion of its own stock during 2016. Last year, Verizon announced it was returning capital to its shareholders through a $5 billion accelerated share-repurchase program and raised its dividend payout to the highest level (56.5¢ per share) since at least 2000. From 2012-2014, AT&T paid out nearly $27 billion to investors through its own share repurchase program. This quarter, it announced a 48¢ share dividend payout, also the highest amount since at least 2000.
Altice also argued New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut customers did not deserve a bigger share of Cablevision’s synergy savings because Altice also has to contend with its purchase of Suddenlink.
“The Commission should instead take into consideration Suddenlink’s operations, which Altice acquired at the end of 2015, just as it took into account all of the U.S. entities comprising New Charter post-closing,” Altice’s lawyers argued. The hole in that argument, deal critics claim, is that Altice doesn’t extend the synergy savings from its deal with Suddenlink to anyone except itself.
Altice also pushed back on other PSC staff recommendations:
- Altice does not want to provide standalone telephone and/or Lifeline service to Cablevision customers;
- Altice objects to providing battery backup power for telephone services, but will allow customers to buy their own;
- Altice protested recommendations from the PSC staff to ban usage caps/usage based billing as a condition of sale. Altice claims usage caps may benefit customers and objects to a rulemaking that prohibits Cablevision from imposing them while leaving their competitors free to cap at will. “Cablevision’s competitors are launching aggressive service offers that Cablevision will have to match or beat—and if the company is subject to regulatory restrictions its competitors do not face, it will be handicapped in keeping up with market demands,” Altice argued.
- New York City should have no say whether this sale is approved or not, claiming the sale does not trigger the city’s right of review.
If the PSC is unimpressed with Altice’s arguments, the cable operator has one other: federal and state law prohibits the commission from imposing most of the terms and conditions its staff recommended. The presentation is unlikely to win much favor at the PSC, particularly because Altice concedes almost nothing and objects to nearly everything on the staff’s menu of deal conditions.
The Communications Workers of America has also attacked the deal, arguing much of Altice’s presentation to the PSC is less than meets the eye. The CWA notes Altice intends to erect a money silo around Cablevision, purporting to protect its finances and operations from the rest of Altice’s telecom empire. But that also means Altice will invest none of its own money in Cablevision upgrades and service improvements, relying on Cablevision’s existing resources, credit lines, and debt obligations to cover the costs. Considering Drahi’s management style, that is likely to drive up debt.
The Financial Times reports Altice has already run up debt, ballooning over the past two years from €1.7 billion in 2012 to just over €50 billion by the end of this year, assuming its acquisition of Cablevision goes through. The warning signs of high leverage are already clear to some investors: With Cablevision’s acquisition, Altice would have net debt at about seven times earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA) — compared with about four times for its European units.
With jitters over European banks, interest rates, oil and gas, and the general state of the stock market, investors are expressing concern.
“From a general valuation perspective, companies with high leverage start becoming a source of fear,” one Altice investor told the Financial Times.
The PSC will likely adopt many of the staff recommendations regardless of Altice’s objections if it approves the sale. Some of those conditions are likely to include broadband service improvements, a low-income discounted Internet access program, and coverage area expansion into currently unserved areas.



 Subscribe
Subscribe Billionaire cable magnate and
Billionaire cable magnate and  Critics of the deal include consumer groups concerned about the poor performance of other Drahi-run cable systems and Cablevision’s organized labor force, unhappy about Drahi’s statements to Wall Street that he prefers to pay only minimum wage wherever possible. Drahi also has a long contentious history with Altice workers in Europe, presiding over workforce reductions, salary and benefits cuts, and a war of attrition with his own suppliers.
Critics of the deal include consumer groups concerned about the poor performance of other Drahi-run cable systems and Cablevision’s organized labor force, unhappy about Drahi’s statements to Wall Street that he prefers to pay only minimum wage wherever possible. Drahi also has a long contentious history with Altice workers in Europe, presiding over workforce reductions, salary and benefits cuts, and a war of attrition with his own suppliers.
 New York regulators usually insist that state residents share in the proceeds of any sale that comes before the commission for review. In most cases, this is in the form of an agreement to invest in infrastructure or service improvements, improve customer service standards, and protect jobs. As with Time Warner Cable and Charter, the staff recommended the commission first consider a roughly 50/50 share of any deal savings or synergies, evenly split between customers and shareholders.
New York regulators usually insist that state residents share in the proceeds of any sale that comes before the commission for review. In most cases, this is in the form of an agreement to invest in infrastructure or service improvements, improve customer service standards, and protect jobs. As with Time Warner Cable and Charter, the staff recommended the commission first consider a roughly 50/50 share of any deal savings or synergies, evenly split between customers and shareholders. “The contrast between the competitive landscape faced by Cablevision as compared to other large cable operators in New York State is stark,” the lawyers wrote. “Verizon FiOS is available in just two Comcast communities, 3% of Time Warner Cable communities, and zero Charter communities in the state.”
“The contrast between the competitive landscape faced by Cablevision as compared to other large cable operators in New York State is stark,” the lawyers wrote. “Verizon FiOS is available in just two Comcast communities, 3% of Time Warner Cable communities, and zero Charter communities in the state.”



 CenturyLink is planning to trial usage caps on its broadband service later this year, not to reduce congestion or to bank the extra money for service upgrades, but to boost revenue and profits.
CenturyLink is planning to trial usage caps on its broadband service later this year, not to reduce congestion or to bank the extra money for service upgrades, but to boost revenue and profits.
 CenturyLink now has 940,000 households connected to its Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON), many for its Prism TV service. Another 490,000 businesses also have access to CenturyLink’s GPON network, primarily for broadband. Post claims more than 30% of the company’s service area is now served with broadband speeds of 40Mbps or greater.
CenturyLink now has 940,000 households connected to its Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON), many for its Prism TV service. Another 490,000 businesses also have access to CenturyLink’s GPON network, primarily for broadband. Post claims more than 30% of the company’s service area is now served with broadband speeds of 40Mbps or greater. Sprint customers will once again have to endure service interruptions and disruptions and the possibility of degraded service after the cellular company quietly announced it was terminating leases with Crown Castle and American Tower — two of the largest owners of shared communications towers in the country, and relocating Sprint cell sites to government-owned property.
Sprint customers will once again have to endure service interruptions and disruptions and the possibility of degraded service after the cellular company quietly announced it was terminating leases with Crown Castle and American Tower — two of the largest owners of shared communications towers in the country, and relocating Sprint cell sites to government-owned property. A behind the scenes struggle between DISH Networks and Charter Communications over DISH’s online video service Sling TV has led to an admission by a Wall Street analyst that “usage-based billing” is an important tool for stifling over-the-top online video competition.
A behind the scenes struggle between DISH Networks and Charter Communications over DISH’s online video service Sling TV has led to an admission by a Wall Street analyst that “usage-based billing” is an important tool for stifling over-the-top online video competition.
