 Despite rosy predictions from Sprint and T-Mobile executives that the two companies joining forces will result in plentiful competition, lower prices, and more advanced service, the results of prior mergers in the wireless industry over the last 20 years delivered increasing prices, reduced innovation, and a lower customer service experience instead.
Despite rosy predictions from Sprint and T-Mobile executives that the two companies joining forces will result in plentiful competition, lower prices, and more advanced service, the results of prior mergers in the wireless industry over the last 20 years delivered increasing prices, reduced innovation, and a lower customer service experience instead.
Few markets show the stark results of consolidation more than the telecom industry. Monopoly cable rates, barely competitive wireless domination by AT&T and Verizon — both with a long history of adjusting wireless rates and plans to closely match one another (usually to the detriment of the consumer), and politicians and regulators that acquiesce to the wishes of the telecom industry have been around even before Stop the Cap! got started in 2008.
When a market disruptor begins to challenge predictable and stable marketplaces, Wall Street and investors quickly get uncomfortable. So do company executives, whose compensation packages are often dependent on their ability to keep the company’s stock price rising. That is why T-Mobile USA’s “Uncarrier” campaign, which directly challenged long-established wireless industry practices, created considerable irritation for other wireless companies, especially AT&T and Verizon.
 The two wireless industry giants initially ignored T-Mobile, suggesting CEO John Legere’s noisy and confrontational PR campaign had no material impact on AT&T and Verizon’s subscriber base and revenue. Ironically, Legere was named CEO one year after AT&T’s 2011 failed attempt to further consolidate the wireless industry with its acquisition of T-Mobile. A very generous deal breakup fee and accompanying wireless spectrum provided by AT&T after the deal collapsed gave T-Mobile some room to navigate and transform the company’s position — long the nation’s fourth largest national wireless carrier behind Sprint. It is now in third place, poaching customers from the other three, and has repeatedly forced other carriers to change their plans and pricing in response.
The two wireless industry giants initially ignored T-Mobile, suggesting CEO John Legere’s noisy and confrontational PR campaign had no material impact on AT&T and Verizon’s subscriber base and revenue. Ironically, Legere was named CEO one year after AT&T’s 2011 failed attempt to further consolidate the wireless industry with its acquisition of T-Mobile. A very generous deal breakup fee and accompanying wireless spectrum provided by AT&T after the deal collapsed gave T-Mobile some room to navigate and transform the company’s position — long the nation’s fourth largest national wireless carrier behind Sprint. It is now in third place, poaching customers from the other three, and has repeatedly forced other carriers to change their plans and pricing in response.

T-Mobile’s “Uncarrier” promotion.
T-Mobile invested in its network and delivered upgrades, but the real inroads for subscriber growth were made by throwing out the typical wireless carrier business plan. T-Mobile brought back unlimited data and made it a key feature of their wireless plans starting in 2016, a feature AT&T and Verizon had successfully banished, ended the traditional two-year contract, scrapped junk fees and surcharges that customers hated, and ran regular specials that dramatically cut family plan rates. If you lived in an area with solid T-Mobile coverage, the scrappy carrier quickly became a viable option among those contemplating ditching Verizon or AT&T. T-Mobile also benefited enormously from disaffected Sprint subscribers that spent years riding out frequent promises of an in improved network experience that frankly never matched the hype in many areas. Price conscious customers that could not afford a plan with AT&T or Verizon moved even more readily to T-Mobile’s network.
In contrast, AT&T and Verizon have spent the last 20 years consolidating the wireless industry by acquiring regional carriers that had a reputation for good service at a fair price, with the promise that the acquisition by a richer and larger competitor would accelerate network upgrades and improve service. But customers of long-gone or diminished carriers like Alltel, Leap Wireless’ Cricket, MetroPCS, and Centennial Wireless (there are others) that either no longer exist or remain alive only as a brand name on a larger company’s network, noticed higher bills and eliminated coveted features that helped them manage their data and voice plans and costs.
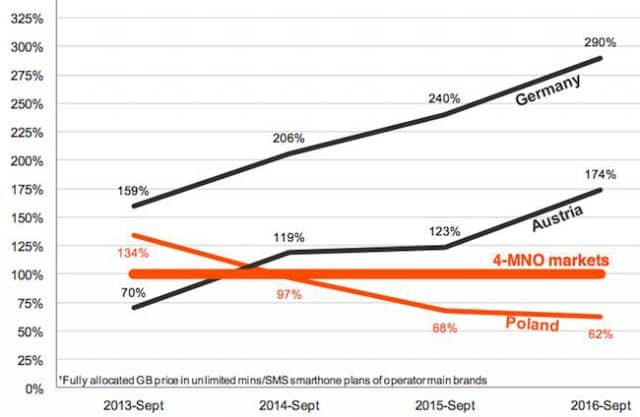
In Europe, recent industry consolidation in some countries has reduced major carriers from four to three, similar to what T-Mobile and Sprint would do in the United States. Pal Zarandy at Rewheel compared consolidated markets in Germany and Austria and discovered gigabyte data pricing where consumers had three options almost doubled in price in Germany and Austria. Austria was 30% less expensive than a control group of six neutral countries when it had three competitors. Today, with two, it is 74% more expensive than its European counterparts. In Germany, prices went from 60% more expensive to nearly triple the rates charged by control group countries.
The merger of Sprint and T-Mobile will dramatically reduce competition in several ways:
- It will end the pervasive price war for lower-income consumers on postpaid plans. Sprint and T-Mobile directly compete with each other to secure customers that skip AT&T and Verizon Wireless because of their more expensive plans and accompanying higher-standard credit check.
- Each of the four current national carriers have had to respond to aggressive price promotions for hardware (Sprint, T-Mobile), plans (T-Mobile, Sprint), and loyalty-building rewards (T-Mobile Tuesday). With a merger, those promotions can be scaled back.
- AT&T and Verizon have been forced to reintroduce unlimited data plans as a direct result of competition from Sprint and T-Mobile. Incidentally, Sprint and T-Mobile’s unlimited data features are different. T-Mobile offers zero rating of lower-resolution videos from selected websites while Sprint offers unlimited access to HD video. In fact, Sprint’s unlimited plan marketing campaign casts T-Mobile’s version in a negative light and was designed to beat T-Mobile’s plan to attract new customers.
- Since Sprint and T-Mobile are market disruptors, merging them means no new aggressive campaigns to out-disrupt each other to the consumer’s benefit. Instead, they will target the conservative plans of AT&T and Verizon, which requires less innovative marketing and less significant price cuts.
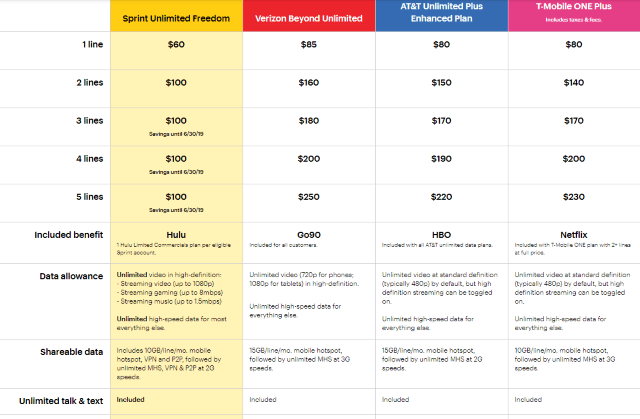
Sprint’s marketing points to differences between its plans and those from T-Mobile, Verizon, and AT&T.
In 2015, the OECD released a definitive study demonstrating the impact of consolidating telecom mergers among top industrialized countries, including the United States. The results were indisputable. If you reduce the number of national carriers to fewer than four, prices rise, service deteriorates — along with innovation and investment, and consumers are harmed. In Canada, where three national carriers dominate, the former Conservative government made finding a fourth national wireless competitor a national policy priority. While Americans gripe about their cell phone bills, many Canadians are envious because they often pay more and live with more restricted, less innovative plans.
This February, market research firm PwC published its own findings, “Commoditization in the wireless telecom industry,” showing that North America remained the most “comfortable” region in the world for wireless carriers looking for big revenue and profits, but that was starting to change because of disruptive marketplace changes by companies like T-Mobile and Sprint.
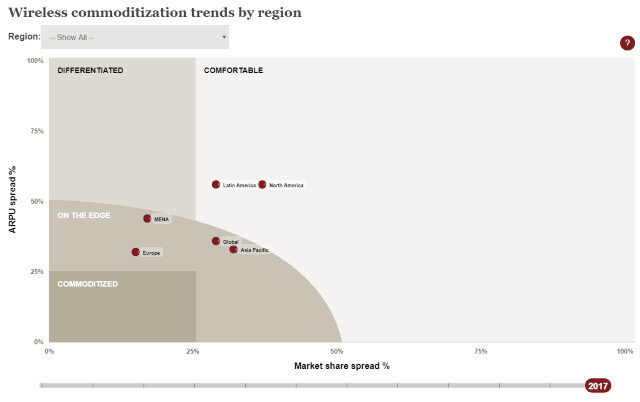
“In this zone, there is a greater than 50 percent spread in market share and ARPU between highest and lowest market players indicating that commoditization is far off,” PwC notes. For wireless carriers, “commoditization” is bad news. It means the amount of money a carrier can charge for its services is highly constrained because multiple competitors are ready to undercut another carrier’s prices or engage in all-out vicious price wars. In these areas, commoditization also means consumers treat each competitor as a viable player for their business.
In France, four national providers — Orange, SFR, Bouygues Telecom and Free, have been in a price war for years, keeping France’s wireless prices shockingly low in comparison to North America. The price war in the United States is just beginning. PwC notes as the U.S. market becomes saturated — meaning everyone who wants a cellphone already has one — companies will have to compete more on price and service. T-Mobile and Sprint have been the most aggressive, and the effect is “meaningful competition.” In Canada, where three national carriers exist, competition is constrained by the domination of three large national companies and some regional players. Instead of cutting prices and expanding plan features, many Canadian providers are now trying to bundle their cable, phone, and wireless customers into a single package to “protect [market] share and increase stickiness.” In other words, Canadian wireless carriers are designing plans to hold the line on pricing while keeping customers loyal at the same time.
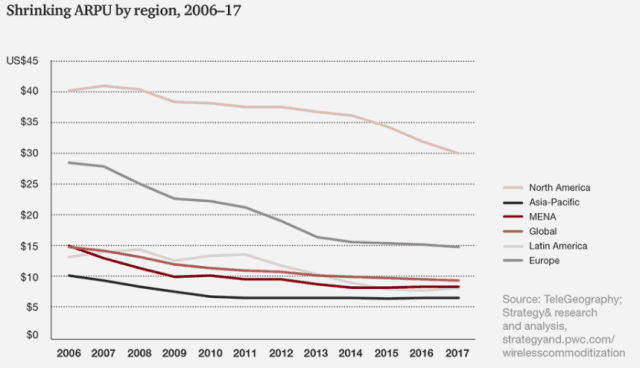
While average revenue per customer is now around $30 a month in North America, it is less than half that amount in virtually every other region in the world. PwC shows the direct impact of competition starting around 2014, when T-Mobile and Sprint got particularly aggressive about pricing. Wireless carrier ARPU was no longer a nearly flat line from 2009-2013. Now it is dropping faster than every other region in the world as AT&T and Verizon have to change their pricing to respond to competition pressures.

Sprint and T-Mobile’s CEOs launch their PR blitz. (Image: Cheddar)
While reports are likely to surface arguing the alleged pro-consumer benefits of the Sprint/T-Mobile merger, it will be critical to determine who or what entities funded that research. We expect a full-scale PR campaign to sell this merger, using industry-funded astroturf groups, industry-sponsored research, and industry-connected analysis and cheerleading.
In 2011, the Justice Department definitively crushed the proposed merger of AT&T and T-Mobile. It cited strong and convincing evidence that removing a competitor from the wireless market will lead to consumer harm from reduced competition and higher prices. If one substitutes Sprint for AT&T, the evidence still shows Sprint’s own aggressive marketing and promotions (and its competitors’ willingness to match or beat them) will be missing from a marketplace where Sprint no longer exists. That cannot and should not be allowed to happen.
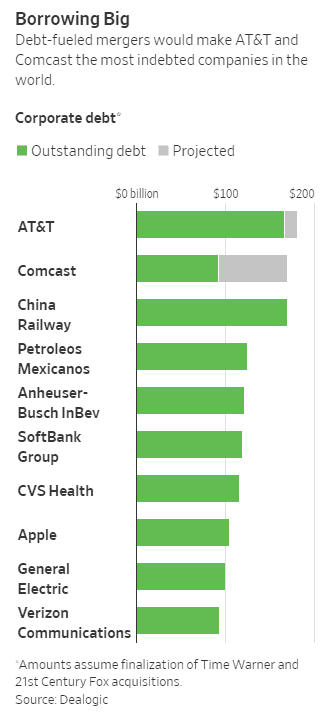 If Comcast’s $65 billion all-cash offer for 21st Century Fox is accepted, America’s largest cable operator will also be among the world’s largest corporate debtors, owing $170 billion in all.
If Comcast’s $65 billion all-cash offer for 21st Century Fox is accepted, America’s largest cable operator will also be among the world’s largest corporate debtors, owing $170 billion in all. AT&T and Comcast officials told the Journal any fears are unwarranted; they are different from most companies because their respective debts are expected to be repaid quickly with higher levels of cash generated by their businesses. AT&T claims it could apply the $8-10 billion of its anticipated free cash flow from the merger with Time Warner to reduce debts, although that could threaten shareholder perks like dividend payouts and share buybacks, as well as customer-focused network upgrades.
AT&T and Comcast officials told the Journal any fears are unwarranted; they are different from most companies because their respective debts are expected to be repaid quickly with higher levels of cash generated by their businesses. AT&T claims it could apply the $8-10 billion of its anticipated free cash flow from the merger with Time Warner to reduce debts, although that could threaten shareholder perks like dividend payouts and share buybacks, as well as customer-focused network upgrades.

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 The article in Light Reading
The article in Light Reading  The more debt (and debt payments) that pile up at the two companies, the less money will be available to spend on fiber upgrades. In fact, there is evidence these companies are hoping to further cut costs in their core landline network operations. Some regulators have noticed. Verizon was forced to make a deal with New York regulators requiring the company to spend millions replacing failing copper-based facilities and upgrade them to fiber and remove or replace tens of thousands of deteriorated utility poles. Verizon faced similar action in Pennsylvania.
The more debt (and debt payments) that pile up at the two companies, the less money will be available to spend on fiber upgrades. In fact, there is evidence these companies are hoping to further cut costs in their core landline network operations. Some regulators have noticed. Verizon was forced to make a deal with New York regulators requiring the company to spend millions replacing failing copper-based facilities and upgrade them to fiber and remove or replace tens of thousands of deteriorated utility poles. Verizon faced similar action in Pennsylvania.
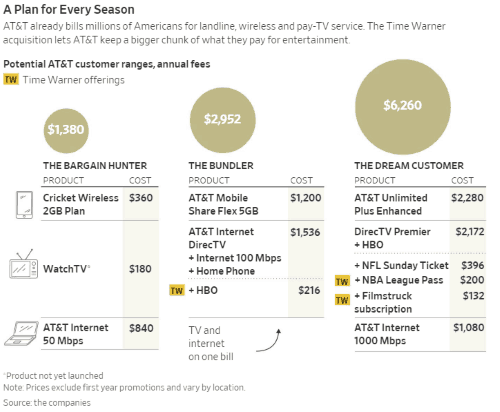
 With Comcast on the verge of picking up much of 21st Century Fox’s content library and studio, Comcast will be able to defend its own turf creating similar giant bundles of content to keep its customers happy. Wall Street is already putting pressure on Verizon to respond with an acquisition of its own to protect its base of FiOS and Verizon Wireless customers.
With Comcast on the verge of picking up much of 21st Century Fox’s content library and studio, Comcast will be able to defend its own turf creating similar giant bundles of content to keep its customers happy. Wall Street is already putting pressure on Verizon to respond with an acquisition of its own to protect its base of FiOS and Verizon Wireless customers. AT&T has won its $85 billion bid to acquire Time Warner, Inc., overturning Justice Department opposition in a court case and completely rejecting allegations the merger was anti-consumer and would raise prices by suppressing competition. The favorable decision is expected to signal the business community the time is right for several more multi-billion dollar media mergers.
AT&T has won its $85 billion bid to acquire Time Warner, Inc., overturning Justice Department opposition in a court case and completely rejecting allegations the merger was anti-consumer and would raise prices by suppressing competition. The favorable decision is expected to signal the business community the time is right for several more multi-billion dollar media mergers. Despite rosy predictions from Sprint and T-Mobile executives that the two companies joining forces will result in plentiful competition, lower prices, and more advanced service, the results of prior mergers in the wireless industry over the last 20 years delivered increasing prices, reduced innovation, and a lower customer service experience instead.
Despite rosy predictions from Sprint and T-Mobile executives that the two companies joining forces will result in plentiful competition, lower prices, and more advanced service, the results of prior mergers in the wireless industry over the last 20 years delivered increasing prices, reduced innovation, and a lower customer service experience instead. The two wireless industry giants initially ignored T-Mobile, suggesting CEO John Legere’s noisy and confrontational PR campaign had no material impact on AT&T and Verizon’s subscriber base and revenue. Ironically, Legere was named CEO one year after AT&T’s 2011 failed attempt to further consolidate the wireless industry with its acquisition of T-Mobile. A very generous deal breakup fee and accompanying wireless spectrum provided by AT&T after the deal collapsed gave T-Mobile some room to navigate and transform the company’s position — long the nation’s fourth largest national wireless carrier behind Sprint. It is now in third place, poaching customers from the other three, and has repeatedly forced other carriers to change their plans and pricing in response.
The two wireless industry giants initially ignored T-Mobile, suggesting CEO John Legere’s noisy and confrontational PR campaign had no material impact on AT&T and Verizon’s subscriber base and revenue. Ironically, Legere was named CEO one year after AT&T’s 2011 failed attempt to further consolidate the wireless industry with its acquisition of T-Mobile. A very generous deal breakup fee and accompanying wireless spectrum provided by AT&T after the deal collapsed gave T-Mobile some room to navigate and transform the company’s position — long the nation’s fourth largest national wireless carrier behind Sprint. It is now in third place, poaching customers from the other three, and has repeatedly forced other carriers to change their plans and pricing in response.





