With video streaming now accounting for at least 64 percent of all Internet traffic, it should have come as no surprise to Australia’s ISPs that as data caps are eased and popular online video services like Netflix arrive, traffic spikes would occur on their networks as well.
With video streaming now accounting for at least 64 percent of all Internet traffic, it should have come as no surprise to Australia’s ISPs that as data caps are eased and popular online video services like Netflix arrive, traffic spikes would occur on their networks as well.
It surprised them anyway.
Telecom analyst Paul Budde told the WAToday newspaper “video streaming requires our ISPs to have robust infrastructure, and to use it in more sophisticated ways, and that largely caught Australia off guard. I think it’s fair to say everybody underestimated the effect of Netflix.”
Not everybody.
Australia’s National Broadband Network (NBN) was originally envisioned by the then Labor government as a fiber-to-the-home network capable of enormous capacity and gigabit speed. Prime Minister Kevin Rudd proposed buying out the country’s existing copper phone wire infrastructure from telecom giant Telstra to scrap it. Instead of DSL and a limited number of cable broadband providers, the national fiber to the home network would provide service to the majority of Australians, with exceptionally rural residents served by wireless and/or satellite.
Conservative critics slammed the NBN as a fiscal “white elephant” that would duplicate or overrun private investment and saddle taxpayers with the construction costs. In the run up to the federal election of 2013, critics proposed to scale back the NBN as a provider of last resort that would only offer service where others did not. Others suggested a scaled-down network would be more fiscally responsible. After the votes were counted, a Coalition government was formed, run by the conservative Liberal and National parties. Within weeks, they downsized the NBN and replaced most of its governing board.
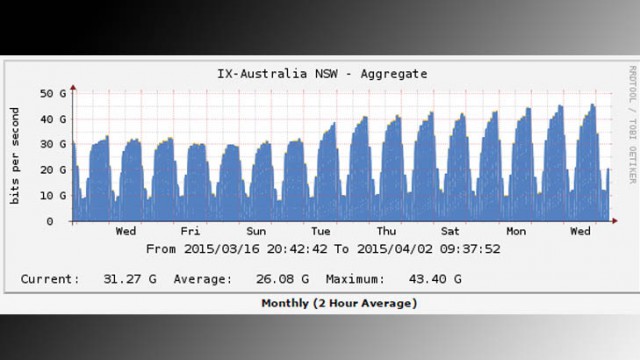
Netflix’s launch increased traffic passing through Australia’s ISPs by 50 percent, from 30 to 50Gbps in just one week, and growing.
Plans for a national fiber to the home network similar to Verizon FiOS were dropped, replaced with fiber to the neighborhood technology somewhat comparable to AT&T U-verse or Bell Fibe. Instead of gigabit fiber, Australians would rely on a motley mix of technologies including wireless broadband, DSL, VDSL, cable, and in areas where the work had begun under the earlier government, a limited amount of fiber.
In hindsight, the penny wise-pound foolish approach to broadband upgrades has begun to haunt the conservatives, who have already broken several commitments regarding the promised performance of the downsized network and are likely to break several more, forcing more costly upgrades that would have been unnecessary if the government remained focused on an all-fiber network.
Communications Minister Malcolm Turnbull has admitted the new NBN will not be able to deliver 25Mbps service to all Australians by 2016. Only 43 percent of the country will get that speed, partly because of technical compromises engineers have been forced to make to accommodate the legacy copper network that isn’t going anywhere.
Think Broadband called the fiber to the neighborhood NBN “a farce” that has led to lowest common denominator broadband. A need to co-exist with ADSL2+ technology already offered to Australians has constrained any speed benefits available from offering faster DSL variants like VDSL2. Customers qualified for VDSL2 broadband speeds will be limited to a maximum of 12Mbps to avoid interfering with existing ADSL2+ services already deployed to other customers. Only multi-dwelling units escape this limitation because those buildings typically host their own DSLAM, which provides service to each customer inside the building. In those cases, customers are limited to a maximum of 25Mbps, not exactly broadband nirvana. The NBN is predicting it will take at least a year to take the bandwidth limits off VDSL2.
 The need for further upgrades as a result of traffic growth breaks another firm commitment from the conservative government.
The need for further upgrades as a result of traffic growth breaks another firm commitment from the conservative government.
NBN executive chairman Ziggy Switkowski told reporters in 2013 that technology used in the NBN would not need to be upgraded for at least five years after construction.
“The NBN would not need to upgraded sooner than five years of construction of the first access technology,” Switkowski said. “It is economically more efficient to upgrade over time rather than build a future-proof technology in a field where fast-changing technology is the norm.”
Since Switkowski made that statement two years ago, other providers around the world have gravitated towards fiber optics, believing its capacity and upgradability makes it the best future-proof technology available to handle the kind of traffic growth also now being seen in Australia. At the start of 2015, 315,000 Australians were signed up for online video services. Today, more than two million subscribe, with Netflix adding more than a million customers in less than four months after it launched down under.
Many ISPs offer larger data caps or remove them altogether for “preferred partner” streaming services like Netflix. With usage caps in place, some customers would have used up an entire month’s allowance after just one night watching Netflix.
But the online viewing has created problems for several ISPs, especially during peak usage times. iiNet reports up to 25% of all its network traffic now comes from Netflix. As a result iiNet is accelerating network upgrades.
Customers still reliant on the NBN’s partial copper network are also reporting slowdowns, especially in the evening. The NBN will have to upgrade its backbone connection as well as the last mile connection it maintains with customers who often share access through a DSLAM. The more customers use their connections for Netflix, the greater the likelihood of congestion slowdowns until capacity upgrades are completed.

Hackett
Optus worries its customers have extended Internet peak time usage by almost 90 minutes each night as they watch online streaming instead of free-to-air TV. Telstra adds it also faces a strain from “well over half” of the traffic on its network now consisting of video content.
This may explain why Internet entrepreneur and NBN co-board director Simon Hackett wishes the fiber to the neighborhood technology would disappear and be replaced by true fiber to the home service.
“It sucks,” Hackett told an audience at the Rewind/Fast Forward event in Sydney in March, referring to the fiber to the neighborhood technology. His mission is to try and make the government’s priority for cheaper broadband infrastructure “as least worse as possible.”
“Fiber-to the-[neighborhood] is the least-exciting part of the current policy, no arguments,” he added. “If I could wave a wand, it’s the bit I’d erase.”
Another cost of the Coalition government’s slimmed-down Internet expansion is already clear.
According to Netflix’s own ISP speed index, which ranks providers on the quality of streaming Netflix on their networks, Australia lags well behind the top speeds of dozens of other developed nations, including Mexico and Argentina.
But even those anemic speeds come at a high cost to ISPs, charged a connectivity virtual circuit charge (CVC) by NBN costing $12.91 per 1Mbps. The fee is designed to help recoup network construction and upgrade costs. But the fee was set before the online video wave reached Australia. iiNet boss David Buckingham worries he will have to charge customers a “Netflix tax” of $19.18 a month for moderate Netflix viewing to recoup enough money to pay the CVC fees. If a viewer wants to watch a 4K video stream, Buckingham predicts ISPs will have to place a surcharge of $44.26 a month on occasional 4K viewing, if customers can even sustain such a video on NBN’s often anemic broadband connections.
Some experts fear costs will continue to rise as the government eventually recognizes its budget-priced NBN is saddled with obsolete technology that will need expensive upgrades sooner than most think.
Instead of staying focused on fiber optics, technology the former Rudd government suggested would offer Australians gigabit speeds almost immediately and would have plenty of capacity for traffic, the conservative, constrained, “more affordable” NBN is leaving many customers with no better than 12Mbps with a future promise to deliver 50Mbps some day. There is little value for money from that.


 Subscribe
Subscribe A plan to place a 15GB monthly usage cap on Eastlink broadband service in rural Nova Scotia has led to calls to ban data caps, with a NDP Member of the Legislative Assembly of Nova Scotia leading the charge.
A plan to place a 15GB monthly usage cap on Eastlink broadband service in rural Nova Scotia has led to calls to ban data caps, with a NDP Member of the Legislative Assembly of Nova Scotia leading the charge.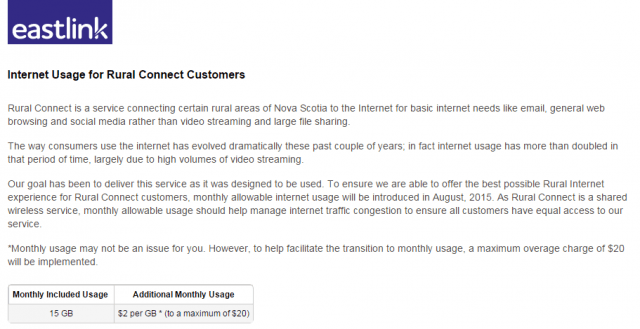

 Fournier suspects Eastlink has not invested enough to keep up with a growing Internet because the service originally advertised itself as a way to listen to online music and watch video. But he also wonders if the data cap is an attempt to force the government to fund additional upgrades to get Eastlink to back down.
Fournier suspects Eastlink has not invested enough to keep up with a growing Internet because the service originally advertised itself as a way to listen to online music and watch video. But he also wonders if the data cap is an attempt to force the government to fund additional upgrades to get Eastlink to back down. Sprint’s all-new “All-In” wireless plan was supposed to simplify wireless pricing for consumers by bundling a leased phone, unlimited voice, data, and texting for a flat $80 a month, but customers slogging through the fine print discovered speed throttling and roaming punishments were silent passengers along for the ride:
Sprint’s all-new “All-In” wireless plan was supposed to simplify wireless pricing for consumers by bundling a leased phone, unlimited voice, data, and texting for a flat $80 a month, but customers slogging through the fine print discovered speed throttling and roaming punishments were silent passengers along for the ride:
 With AT&T’s arrival in the Mexican wireless marketplace with its purchase of Iusacell and Nextel, América Móvil is responding with
With AT&T’s arrival in the Mexican wireless marketplace with its purchase of Iusacell and Nextel, América Móvil is responding with