
Verizon “redacted” hundreds of pages of information about its controversial Voice Link project, including its User’s Guide.
Verizon today lost its appeal to keep company documents about its controversial Voice Link wireless landline replacement away from company critics that allege the company is intentionally undercutting its landline network and redirecting investment towards its more profitable wireless service.
In a 20-page decision published this afternoon, Kathleen Burgess blamed Verizon for hurting its own case with excessive secrecy.
“But for Verizon’s failure to submit documents with fewer redactions, as directed by the Records Access Officer (RAO), it might have satisfied its burden of proof,” that the company would suffer harm if it released proprietary information that could be accessed by competing providers, ruled Burgess.
Burgess took a dim view of Verizon’s attempt to claim blanket confidentiality for its Voice Link project, even including a redaction of Voice Link’s User’s Manual — the same one given to customers subscribing to the service. Burgess noted in response to a Freedom of Information Law (FOIL) request from consumer groups, Verizon responded with “13 documents – 330 pages – with blanket redactions except for the page headings and page numbers.”
Verizon needed to meet its burden of proof by “presenting specific, persuasive evidence that disclosure will likely cause it, or another affected enterprise, to suffer a competitive injury.”
“Verizon apparently believes that it is possible to meet the burden of protecting information under FOIL by providing a cogent and persuasive explanation of how a competitor could use the information and why it is likely to lead to harm,” Burgess observed (emphasis ours). “As an initial matter, [Verizon] has not parsed out each of the 13 documents and demonstrated how each, if disclosed, would competitively injure it. Instead, Verizon is attempting to obtain a blanket exemption for all 13 documents by summarily stating that disclosure would enable competitors to obtain, for free, information on processes that the company developed at considerable expense and effort. Verizon has, however, failed to demonstrate, in adequate detail, how the complete disclosure of all 13 documents would result in substantial competitive injury.”
Verizon hurt its own case by “co-mingling” detailed cost information that might otherwise win confidentiality with the Public Service Commission with less proprietary marketing information and even publicly available documents and then redacted all of them, according to Burgess.
 As a result, Verizon lost its case:
As a result, Verizon lost its case:
The Commission recognizes that limiting competitor access to proprietary material is an important policy. Exemptions are to be narrowly construed, however. The entity resisting disclosure bears the burden of proof and, therefore, must demonstrate a particularized and specific justification for denying access to the subject documents. Absent such a showing of competitive injury covering each document that comprises the response, the speculative concerns articulated by Verizon are not enough to sustain the company’s burden of proving that the information should remain protected as trade secret materials.
[…] Under FOIL case law, the burden is on Verizon to demonstrate a particularized and specific justification, supported by evidence, for denying access to the documents at issue and, inasmuch as Verizon has failed to meet its burden, I uphold the RAO’s November 4, 2013 Determination.
Absent a court order or later ruling, full versions of the blacked-out documents may become public two weeks from today.


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T this month signed up their 10 millionth customer to U-verse High Speed Internet service, surpassing Verizon FiOS as the nation’s biggest telephone company supplier of broadband, television, and telephone service. Coinciding with that success, AT&T is raising prices for U-verse, despite AT&T’s record earnings from the fiber to the neighborhood service, now accounting for $1 billion a month in revenue.
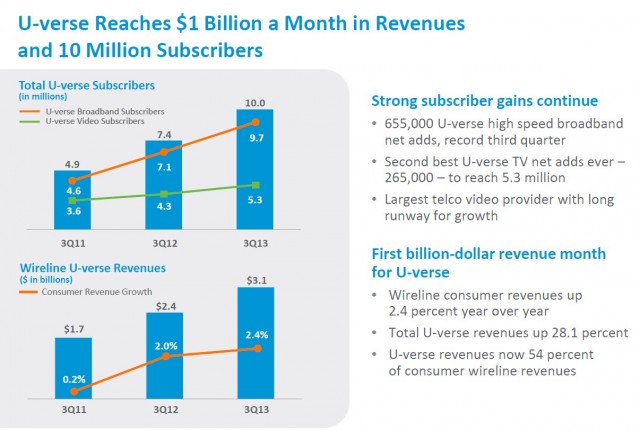
AT&T this month signed up their 10 millionth customer to U-verse High Speed Internet service, surpassing Verizon FiOS as the nation’s biggest telephone company supplier of broadband, television, and telephone service. Coinciding with that success, AT&T is raising prices for U-verse, despite AT&T’s record earnings from the fiber to the neighborhood service, now accounting for $1 billion a month in revenue.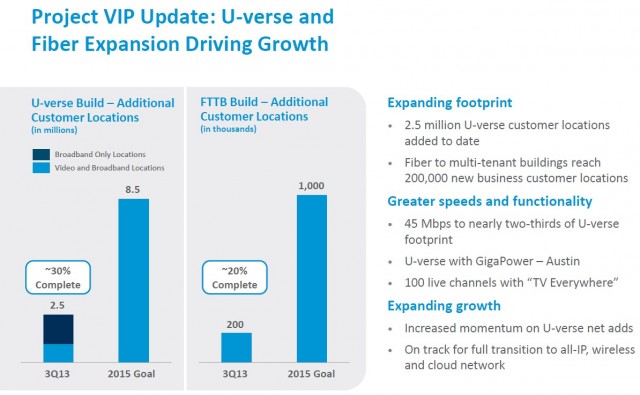

 “Use it or lose it” is the policy under which the Federal Communications Commission licenses scarce, publicly owned airwaves, but in practice companies warehousing unused spectrum can sell it off and make a handsome profit.
“Use it or lose it” is the policy under which the Federal Communications Commission licenses scarce, publicly owned airwaves, but in practice companies warehousing unused spectrum can sell it off and make a handsome profit.


