“Verizon’s treatment of the news is a testament to the need for strong Net Neutrality protections.”

Sugarstring’s logo is as twisty as its editorial policies.
Verizon Wireless’ launch of Sugarstring, a high-budget tech news website targeting millennial 20-somethings with tech and lifestyle news they can use seemed innocent enough until its editor revealed in a private e-mail Verizon considers reporting on electronic spying and Net Neutrality issues “verboten.”
Verizon is deeply embroiled in both issues and evidently has no interest spending money enlightening the masses, so it has told its staff (but not you) both topics are forbidden.
The Daily Dot reported the revelation straight from Cole Stryker, Sugarstring’s editor.
“I’ve been hired to edit SugarString.com,” writes Stryker in a recruiting email to Daily Dot’s Patrick Howell O’Neill. “Downside is there are two verboten topics (spying and net neutrality), but I’ve been given wide berth to cover pretty much all other topics that touch tech in some way.”
Verizon’s cavalier censorship policies say a lot about the company’s interest in controlling the messages that people see and read online. The news site is intended to be a high-profile destination for Verizon Wireless’ mobile customers and will logically get significant exposure from the company bankrolling it.
Verizon might argue that since it pays the bills, it has a right to decide what information should pass through its websites. It is hardly a big stretch for them to argue that if they own the wires over which you receive Internet service, they should have a say in what travels across those as well.
Censorship need not be crude and obvious as it often was on foreign propaganda broadcasts during the Cold War. Today’s “news management” is much more subtle and more insidious.
Take RT (formerly Russia Today), the Moscow-based 24/7 English-language news network. Although dropped by many major cable systems including Time Warner Cable after Russian troops invaded eastern Ukraine, the network is still growing and finding more places on the air around the world.

Radio Moscow during the Cold War represented a more overt form of propaganda. Corporations like Verizon have learned to be more subtle.
RT is nothing like what shortwave listeners used to endure from English-language Radio Moscow World Service during the Communist years. You couldn’t miss that station. Broadcasting on up to 47 frequencies simultaneously, 24 hours a day, it was easily the most commonly encountered signal on the shortwave dial. Plodding features like, “On the Occasion of the 45th Anniversary of the Stunning Achievements of World Socialism,” or “The Voices of Soviet Public Opinion Demand Peace and Progress for the Non-Aligned World” (Part 36) were everything you might expect and less.
Radio Moscow boldly told listeners in its series, “The History of the Soviet Union, the Socialist Revolution, and Its Aims and Results,” that elections in the USSR were superior to those in other countries because the government took the money out of politics. Only by putting national infrastructure entirely in the hands of the people, along with public ownership of the means of production, can a nation achieve true democracy. They didn’t bother to mention the USSR was a one-party state, which made elections pro-forma, or that the entire Soviet economy was a basket case since the days of Leonid Brezhnev. (10:01) You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
Radio Moscow has been replaced by RT Television, which in the post-Soviet era now exists primarily to boost all-things Putin. The propaganda has been sharpened up by employing U.S. reporters and moving to the far more subtle practice of “self-censorship.” A former RT reporter fed up with increasingly strident propaganda over the matter of Russia, Crimea and the Ukraine quit live on the air. In a later interview on CNN, Liz Wahl told Anderson Cooper that RT’s staff was made up mostly of impressionable young people eager to win favor from RT’s management. They quickly learned and accepted that certain points of view or story subjects were either frowned upon or outright verboten. Instead of being sent to a gulag for disobedience, those straying from Putin’s party line were taken off stories, reassigned to menial work, or shunned. Who wants that?
Avoiding certain topics or points of view at the behest of corporate management (or the state) is just as insidious as directly slanting the news to one’s favor. Few real journalists would accept a job (or stay) at a news organization that was compromised by coverage limits or editorial interference that came from conflict with a corporate or political agenda.
That Verizon chooses to ban stories that embarrass Verizon, such as Edward Snowden’s revelations that Verizon voluntarily provided the National Security Agency (NSA) the phone records of all of its customers and is still actively engaged in tracking its customers’ web activities, does not mean it is going to block you from visiting CNN.com tomorrow. That Verizon doesn’t want to fuel the public consciousness of Net Neutrality is understanding considering the company has paid its lawyers plenty to fight the principle in court, openly admitting it favors paid fast lanes for traffic. But Verizon is clearly on a road that, if unchecked, eventually leads to content and traffic manipulation.
Verizon steps far over the line of jounalistic integrity informing editors to avoid both issues while saying nothing to readers and it isn’t the first time Verizon has crossed the line.
 Tim Karr from Free Press reminds us Verizon has a very different view about the First Amendment that the rest of us:
Tim Karr from Free Press reminds us Verizon has a very different view about the First Amendment that the rest of us:
In a 2012 legal brief to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit, Verizon mangled the intent of the First Amendment to claim that the Constitution gives the phone company the right to control everyone’s online information. In the brief, which was part of the company’s successful bid to overturn the FCC’s Open Internet Order — Verizon argued that the First Amendment gives it the right to serve as the Internet’s editor-in-chief. The company’s attorneys claimed that “broadband providers possess ‘editorial discretion.'” even when they are “transmitting the speech of others.”
Verizon continued in this vein, asserting that “Just as a newspaper is entitled to decide which content to publish and where, broadband providers may feature some content over others.” And that means that Verizon could privilege its SugarString version of the news over the content of real news sites, because the company believes it should be able to “give differential pricing or priority access” to its own content.
What Verizon cannot “manage,” it wants the right to censor:
When it comes to a question of customer freedom vs. profits, Verizon follows the money every time:
In 2011, Free Press and others caught Verizon Wireless blocking people from using tethering applications on their phones. Verizon had asked Google to remove 11 free tethering applications from the Android marketplace. These applications allowed users to circumvent Verizon’s $20 tethering fee and turn their smartphones into Wi-Fi hotspots on their own. By blocking those applications, Verizon violated a Net Neutrality pledge it made to the FCC as a condition of the 2008 airwaves auction.
All of these examples challenge Verizon’s ongoing assertion it has no incentive to censor, block, or interfere with online content, making Net Neutrality unnecessary. You have just seen another example of why Net Neutrality is urgently needed. Verizon has demonstrated repeatedly it puts its own interests above its customers, so regulators should respond with a clear, unambiguous, and robustly enforced policy of Net Neutrality that protects the interests of you and I.


 Subscribe
Subscribe The Federal Communications Commission announced Friday it will
The Federal Communications Commission announced Friday it will 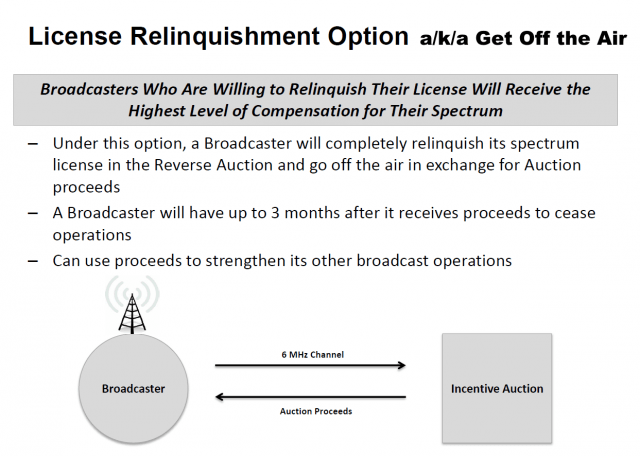 There is so much money to be made buying and selling the public airwaves — at least twice as much as broadcasters originally anticipated– spectrum speculators have also jumped on board, snapping up low power television station construction permits and existing stations with hopes of selling them off the air in return for millions in compensation. Wireless customers are effectively footing the bill for the auction as wireless companies bid for the additional spectrum. Television stations will receive 85% of the proceeds, the FCC will keep 15%.
There is so much money to be made buying and selling the public airwaves — at least twice as much as broadcasters originally anticipated– spectrum speculators have also jumped on board, snapping up low power television station construction permits and existing stations with hopes of selling them off the air in return for millions in compensation. Wireless customers are effectively footing the bill for the auction as wireless companies bid for the additional spectrum. Television stations will receive 85% of the proceeds, the FCC will keep 15%. Major network-affiliated or owned stations in major cities are unlikely to take the deal. But in medium and smaller-sized markets where conglomerates own and operate most television stations, there is a greater chance some will be closed down, moved to a lower channel, or transferred to a digital sub-channel of a co-owned-and-operated station in the same city. The most likely targets for shutdown will be independent, CW and MyNetworkTV affiliates. In smaller cities, multiple network affiliates owned by one company could be combined, relinquishing one or more channels in return for tens of millions in cash compensation.
Major network-affiliated or owned stations in major cities are unlikely to take the deal. But in medium and smaller-sized markets where conglomerates own and operate most television stations, there is a greater chance some will be closed down, moved to a lower channel, or transferred to a digital sub-channel of a co-owned-and-operated station in the same city. The most likely targets for shutdown will be independent, CW and MyNetworkTV affiliates. In smaller cities, multiple network affiliates owned by one company could be combined, relinquishing one or more channels in return for tens of millions in cash compensation. T-Mobile has asked the Federal Communications Commission to investigate AT&T’s “artificially high roaming rates” charged when its customers travel outside of T-Mobile’s home service area.
T-Mobile has asked the Federal Communications Commission to investigate AT&T’s “artificially high roaming rates” charged when its customers travel outside of T-Mobile’s home service area. Because of AT&T’s artificially high roaming rates, T-Mobile wireless customers roaming in South Africa have a better user experience than customers roaming on AT&T’s network in South Dakota, argues T-Mobile. Their speed is twice as fast, and their data usage is unlimited.
Because of AT&T’s artificially high roaming rates, T-Mobile wireless customers roaming in South Africa have a better user experience than customers roaming on AT&T’s network in South Dakota, argues T-Mobile. Their speed is twice as fast, and their data usage is unlimited.



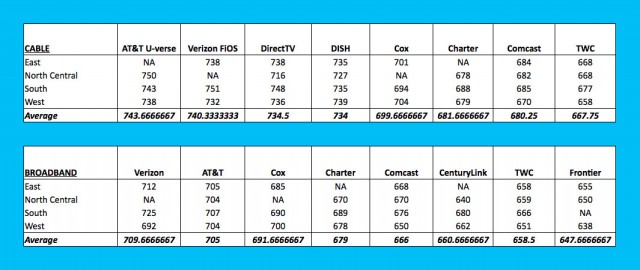
 Love can be a fickle thing.
Love can be a fickle thing. The highest rating across television and broadband categories achieved by either cable company was ‘Meh.’ J.D. Power diplomatically scored both cable companies on a scale that started with “among the best” as simply “the rest.” Customers in the west were the most charitable, those in the south and eastern U.S. indicated they were worked to their last nerve.
The highest rating across television and broadband categories achieved by either cable company was ‘Meh.’ J.D. Power diplomatically scored both cable companies on a scale that started with “among the best” as simply “the rest.” Customers in the west were the most charitable, those in the south and eastern U.S. indicated they were worked to their last nerve.