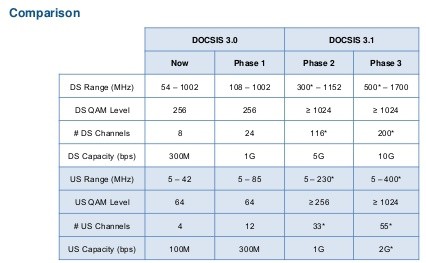
Next year’s upgrade to DOCSIS 3.1 will support cable broadband speeds up to one gigabit shortly after introduction.
Telephone companies relying on traditional ADSL service to power their broadband offering will likely face a renewed competitive assault in 2016 that will further reduce their already-challenged market share in areas where cable companies compete.
Cable operators are hungry for profitable broadband customers and the best place to find new prospects is at the phone company, where DSL is still a common technology to deliver Internet access. But while cable Internet speeds have risen, significant DSL speed hikes have proven more modest in the residential market.
In 2016, the cable industry intends to poach some of the remaining price-sensitive holdouts still clinging to DSL with revised broadband offers promising more speed for the dollar.
Cable broadband has already proven itself a runaway success when matched against telephone company DSL service. Over the last year, Strategy Analytics found Comcast and Time Warner Cable alone signed up a combined 71 percent of the three million new broadband customers in the U.S.
“Cable operators continue to increase market share in U.S. broadband,” said Jason Blackwell, a director at Strategy Analytics. “Over the past twelve months, Comcast has accounted for 42 percent of new subscribers among the operators that we track. Fiber growth is still strong, but the telco operators haven’t been able to shake off the losses of DSL subscribers. In 2016, we expect to see a real battle in broadband, as cable operators begin to roll out DOCSIS 3.1 for even higher speed offers, placing additional pressure on telcos.”
That battle will come in the form of upgraded economy broadband plans, many arriving shortly after providers upgrade to the DOCSIS 3.1 cable broadband platform. Currently those plans offer speeds ranging from 2-6Mbps. Starting next year, customers can expect economy plan prices to stay generally comparable to DSL, with promises of faster and more consistent speeds. A source tells Stop the Cap! at least two significant cable operators are considering 10Mbps to be an appropriate entry-level broadband speed for 2016, in keeping with FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler’s dislike of Internet speeds below 10Mbps.
 Just a few years earlier, most providers wouldn’t think of offering discounted 10Mbps service, fearing it would cannibalize revenue as customers downgraded to get lower priced service. Increasing demands on bandwidth from online video and multiple in-home users have gradually raised consumer expectations, and their need for speed.
Just a few years earlier, most providers wouldn’t think of offering discounted 10Mbps service, fearing it would cannibalize revenue as customers downgraded to get lower priced service. Increasing demands on bandwidth from online video and multiple in-home users have gradually raised consumer expectations, and their need for speed.
Unfortunately for many phone companies that have neglected significant investment in their aging wireline networks, the costs to keep up with cable will become unmanageable unless investors are willing to tolerate significant growth in capital expenses to pay for network upgrades. Frontier Communications still claims most of their customers are satisfied with 6Mbps DSL, neglecting to mention many of those customers live in areas where cable competition (or faster service from Frontier) is not available.
Where competition does exist, it’s especially bad news for phone companies that still rely on DSL. Earlier this year, Frontier’s former CEO Maggie Wilderotter admitted Frontier’s share of the residential broadband market had dropped to less than 25% in 26 of the 27 states where it provides service. In Connecticut, the one state where Frontier was doing better, its acquired AT&T U-verse system has enabled the phone company to deliver broadband speeds up to 100Mbps. But even those speeds do not satisfy state officials who are seeking proposals from providers to build a gigabit fiber network in a public-private partnership.
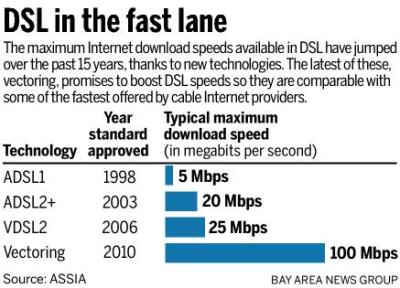
DSL speed upgrades have been spotty and more modest.
Frontier’s recent experiments with fiber to the home service in a small part of Durham, N.C., and the unintentional revelation of a gigabit broadband inquiry page on Frontier’s website suggests the company may be exploring at least a limited rollout of gigabit fiber service in the state. But company officials have also repeatedly stressed in quarterly results conference calls there were no significant plans to embark on a major spending program to deliver major upgrades across their service areas.
Some phone companies may have little choice except to offer upgrades where cable operators are continuing to rob them of customers. In the northeast, where Frontier has a substantial presence, cable operators including Charter, Comcast and Time Warner Cable are committing to additional speed upgrades. Time Warner Cable’s current standard speed of 15Mbps will rise to 50-60Mbps in 2016, up to ten times faster than Frontier’s most popular “up to” 6Mbps DSL plan.
Most of the broadband customer gains won by Comcast and Time Warner Cable come as a result of DSL disconnects. AT&T said goodbye to 106,000 customers during the third quarter. Verizon managed to pick up 2,000 new subscribers overall, almost all signing up for FiOS fiber to the home service. No cable operator lost broadband market share, reported analyst firm Evercore. Leichtman Research offered additional insight, finding AT&T and Verizon were successful adding 305,000 U-verse and FiOS broadband customers, while losing 432,000 DSL customers during the same quarter.
The message to phone companies couldn’t be clearer: upgrade your networks or else.


 Subscribe
Subscribe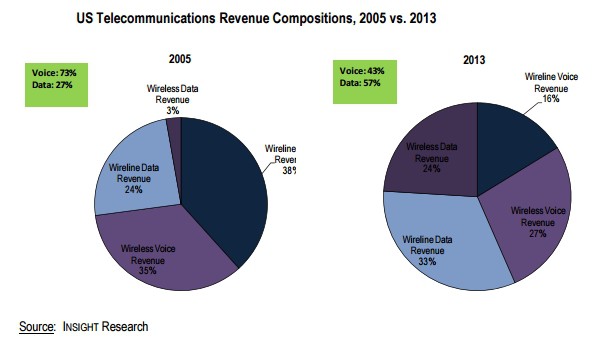 The year 2013 marked a significant turning point for phone companies that have handled voice telephone calls for over 100 years. For the first time,
The year 2013 marked a significant turning point for phone companies that have handled voice telephone calls for over 100 years. For the first time,  Starting in 2008, wireless industry executives noticed something peculiar. While revenue from texting add-on plans was surging, the growth in calling began to level off. Wireless voice usage per subscriber peaked at an average of 769 minutes in 2007 and began falling after that year. By 2011, the average customer was making 615 minutes of calls a month. As customers began downgrading calling plans, wireless carriers shifted their quest for revenue towards text messaging.
Starting in 2008, wireless industry executives noticed something peculiar. While revenue from texting add-on plans was surging, the growth in calling began to level off. Wireless voice usage per subscriber peaked at an average of 769 minutes in 2007 and began falling after that year. By 2011, the average customer was making 615 minutes of calls a month. As customers began downgrading calling plans, wireless carriers shifted their quest for revenue towards text messaging.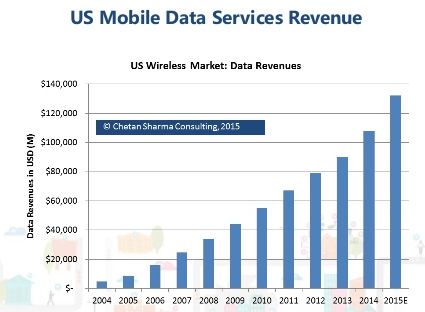 The industry’s demand for profit eventually threatened to kill the goose that laid the golden egg. At the same time wireless carriers were raising prices on text messages and forcing customers into expensive texting add-on plans, free third-party messaging apps began eating into texting volume. By 2012, the use of SMS declined for the first time, with 2.19 trillion text messages sent and received, down 4.9 percent from a year earlier.
The industry’s demand for profit eventually threatened to kill the goose that laid the golden egg. At the same time wireless carriers were raising prices on text messages and forcing customers into expensive texting add-on plans, free third-party messaging apps began eating into texting volume. By 2012, the use of SMS declined for the first time, with 2.19 trillion text messages sent and received, down 4.9 percent from a year earlier. Some even expect carriers to eventually
Some even expect carriers to eventually 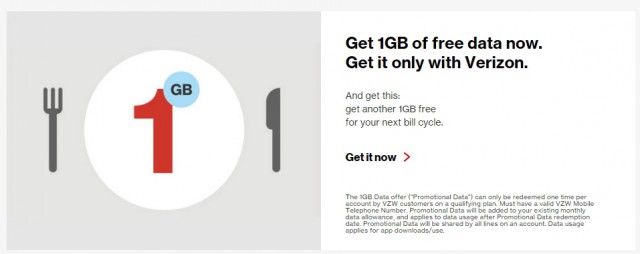 Since Verizon Wireless stopped selling unlimited data plans and turned data into a precious commodity usually worth about $10 per gigabyte, the company can afford to give some of it away to their loyal customers.
Since Verizon Wireless stopped selling unlimited data plans and turned data into a precious commodity usually worth about $10 per gigabyte, the company can afford to give some of it away to their loyal customers. Verizon Wireless has informed employees Wednesday that its national operation will be reorganized resulting in significant job cuts.
Verizon Wireless has informed employees Wednesday that its national operation will be reorganized resulting in significant job cuts. Google Fiber today
Google Fiber today