 New York State Attorney General Eric Schneiderman is convinced Verizon Communications is abandoning quality landline service for millions of New Yorkers while diverting money and resources to its more profitable cell service Verizon Wireless.
New York State Attorney General Eric Schneiderman is convinced Verizon Communications is abandoning quality landline service for millions of New Yorkers while diverting money and resources to its more profitable cell service Verizon Wireless.
Last week, Schneiderman blasted the state’s largest landline provider for mounting complaints about poor service that now impact 92 percent of its customers, calling deregulation a failure for consumers and businesses in New York.
“Verizon customers deserve the high-quality service they’ve been promised,” Schneiderman told The Associated Press.
 The attorney general reports that the number of customers enduring service outages for more than 24 hours has increased, while landline infrastructure — particularly wiring — is allowed to deteriorate.
The attorney general reports that the number of customers enduring service outages for more than 24 hours has increased, while landline infrastructure — particularly wiring — is allowed to deteriorate.
Schneiderman suspects Verizon is shortchanging landline service as an increasing number of wired phone customers disconnect service, often in favor of Verizon’s more lucrative cell phone service. The state Public Service Commission (PSC) fined Verizon $400,000 in March for similar concerns, pointing to the company’s intentional workforce reductions lengthening repair windows and creating repair backlogs in some regions.
Schneiderman’s office filed comments with the PSC requesting changes to Verizon’s Service Quality Improvement Plan, which was originally launched in 2010:
At best, New York’s telephone service market is a duopoly, and contrary to theoretical expectations of market controls, the presence of a single competitor has not in fact prevented Verizon from allowing customer service to continue to degrade. Rather than meet its obligations to provide wireline telephone customers with minimally adequate telephone service, Verizon is continuing to drastically reduce its workforce with the result that the company cannot meet its customers’ repair needs in a timely manner.
Verizon’s management has demonstrated that it is unwilling to compete to retain its wireline customer base, and instead is entirely focused on expanding its wireless business affiliate. It is incumbent on the Commission to take appropriate regulatory action to ensure that customers receive reliable telephone service with adequate repair performance. Therefore, the Commission should modify Verizon’s service plan to ensure customers receive adequate service quality in the future.
Verizon defended its service in New York pointing out the company has invested $1.5 billion in the state for infrastructure, including its FiOS fiber to the home network. Verizon spokesman John Bonomo questioned Schneiderman’s claim that 92 percent of Verizon New York customers had poor service, noting 98 percent of its landline customers don’t have service problems.
Schneiderman’s highlighting of a $400,000 service fine imposed by the PSC did not account for unprecedented damage from both Hurricane Irene and Tropical Storm Lee late last summer, Bonomo added.
But the state’s attorney general notes Verizon’s service problems in New York have been ongoing well before last summer.
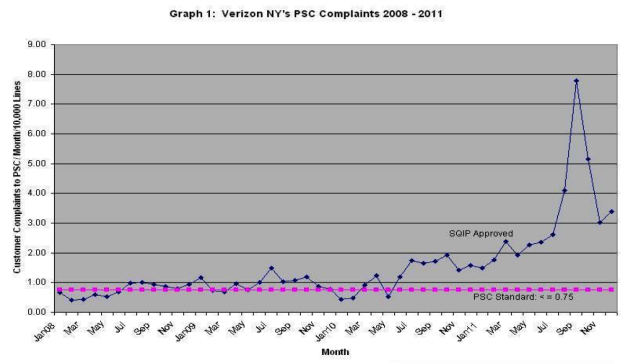
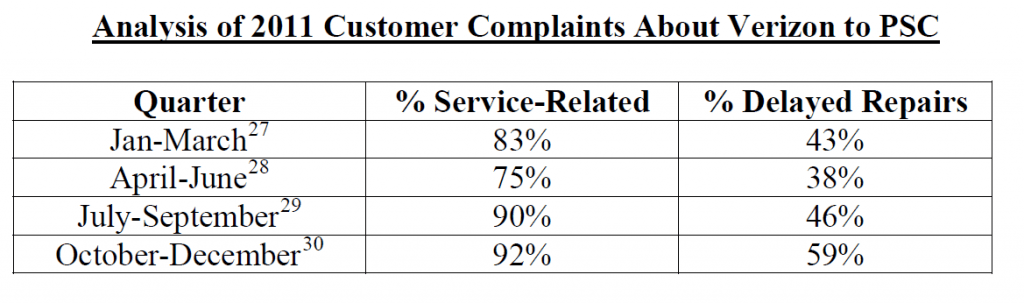
Service complaints, charted here from 2008-2011, show a major spike last summer and fall and remain higher than normal.
“Since at least 2008, Verizon has frequently failed to meet these PSC telephone service standards essential to safe and reliable telephone service,” Schneiderman says. “Even as the number of telephone lines needing to be maintained has dwindled to half those of a decade ago (as customers choose to rely instead on wireless and/or cable telephony), Verizon’s continues to fail to meet the PSC’s service standard.”
Customers on the upper west side of New York City don’t need to be reminded of Verizon’s service failures. Hundreds of Verizon landline customers in New York’s largest city were left without basic phone service for more than a week, only made worse by the fact Verizon told many of them they’d be without service for at least one additional week while the company worked on repairs.
Phone and Internet service went dead in multiple buildings along Central Park West April 10, but customers wanted to kill when they learned the phone company wanted more than two weeks to get service restored.
“I was like, excuse me, are you serious? Two weeks?” Iram Rivera, a concierge at 262 Central Park West, told DNAinfo. His building was hard hit by the service outage — 80 percent of the building’s 80 apartments were affected.
“I just don’t get the feeling that there’s much of an appreciation on Verizon’s part that this is a hardship for people,” said Ken Coughlin, who lives on West 87th Street and Central Park West. “There’s no communication, there’s no updates, it’s infuriating.”
The outage only affected traditional landline service and DSL broadband over copper phone wiring. The more modern fiber-optic FiOS network that provides TV, Internet and voice service wasn’t affected, Bonomo said.
Schneiderman notes landline outages have an especially hard impact on small businesses:
In the current recession, the fragile economic condition of many small businesses puts them at risk of financial disaster if they suddenly lose telephone service, and their provider is unable to restore service promptly. Each day that these businesses are without service they lose significant revenues that many simply cannot survive without.
Small businesses depend on functional telephone service to meet the needs of their customers in numerous ways. When customers are unable to reach a business by telephone, they may assume the business is closed and purchase the goods or services they want elsewhere. Restaurants are prevented from giving reservations to prospective customers who call. Many types of businesses depend on working telephone lines for processing credit card charges, and may lose substantial sales by limiting transactions to cash or checks. Professional offices can be prevented from providing medical, legal or accounting services to their clients without working telephone service.
In Schneiderman’s view, the deregulation policies now in place in New York have failed consumers, leaving them with a duopoly of phone providers with insufficient oversight.
For competition to benefit customers with improved service, lower prices, and more innovation, there has to first be a willingness to compete, which is significantly absent from Verizon-New York’s policies and practices.
Rather than robust competition, New York’s telephone market is at best a duopoly, with as many indicators of cooperation between the two providers as robust contest for customers. Furthermore, the actual behavior of consumers in the real world is markedly different from the PSC’s theoretical assumptions about the telephone market.
When a Verizon customer experiences a prolonged service outage or installation delay, the option to switch carriers to a cable provider is of no immediate use. Finally, even if consumers wanted to compare Verizon’s service performance with cable provider alternatives, the lack of available information prevents consumers from making educated choices.
In New York, most customers are served by Verizon Communications, Time Warner Cable, or Cablevision. Time Warner Cable and Verizon recently agreed to cross-market the other’s products and services as part of a wireless spectrum transfer.


 Subscribe
Subscribe