 What do an emergency operations center in Cochise County, Ariz., Colorado hospitals, the Idaho Bureau of Corrections, and many 911 call centers across Massachusetts have in common? They were all brought down by a two-day nationwide CenturyLink outage from Dec. 27-28 that also resulted in internet outages for tens of thousands of CenturyLink’s residential customers. The cause? CenturyLink blamed a single, faulty third-party network management card in Denver for disrupting services for CenturyLink and other phone companies, notably Verizon, from Alaska to Florida.
What do an emergency operations center in Cochise County, Ariz., Colorado hospitals, the Idaho Bureau of Corrections, and many 911 call centers across Massachusetts have in common? They were all brought down by a two-day nationwide CenturyLink outage from Dec. 27-28 that also resulted in internet outages for tens of thousands of CenturyLink’s residential customers. The cause? CenturyLink blamed a single, faulty third-party network management card in Denver for disrupting services for CenturyLink and other phone companies, notably Verizon, from Alaska to Florida.
Hours after outage began, two days after Christmas, CenturyLink issued a general statement:
“CenturyLink experienced a network event on one of our six transport networks beginning on December 27 that impacted voice, IP, and transport services for some of our customers. The event also impacted CenturyLink’s visibility into our network management system, impairing our ability to troubleshoot and prolonging the duration of the outage.”
That “network event” caused serious disruptions to critical services in 37 states, including 911, according to Brian Kyes, president of the Massachusetts Major City Chiefs of Police Association.
“This is affecting 911 (wireline & wireless) delivery to most of Massachusetts,” Kyes said in a statement during the outage to the Boston Herald. “We have heard from MEMA that this issue may also affect some landlines but I have not heard of any specific situations or communities that have been impacted. We are advising all police and fire chiefs to test their local 911 systems and notify their residents of potential issues by reverse 911, social media or any other means that they have at their disposal. The interruption in service may depend on a particular phone carrier and the information that we have is that it may be intermittent.”
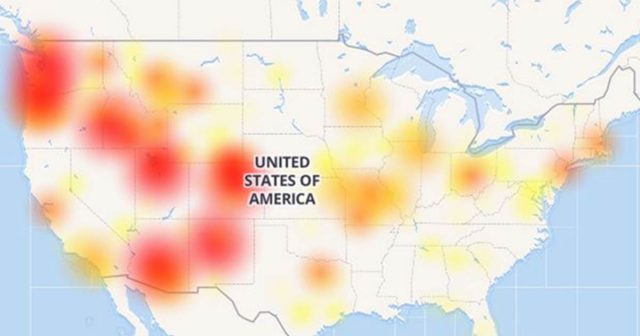
CenturyLink outages on Dec. 27, 2018. (Image: Downdetector.com)
The disruptions affected much of Massachusetts — a state served primarily by Verizon Communications, because CenturyLink is a major commercial services vendor inside and outside of its local landline service areas and supplies some connectivity services to Verizon, mostly for wireless customers.
ATM networks also went down in certain parts of the country. CenturyLink is one of many vendors providing data connectivity between the cashpoint machines and several banking institutions.
Also impacted, the Idaho Department of Corrections, including inmate phone systems, and the Idaho Department of Education, which lost the ability to make or receive calls.
Consumers also noticed their internet connections were often down or sporadic in some locations, primarily because CenturyLink’s backbone network became saturated with rogue packets.
The Denver Post presented a more detailed technical explanation about the outage:
CenturyLink said the [defective] card was propagating “invalid frame packets” that were sent out over its secondary network, which controlled the flow of data traffic.
“Once on the secondary communication channel, the invalid frame packets multiplied, forming loops and replicating high volumes of traffic across the network, which congested controller card CPUs (central processing unit) network-wide, causing functionality issues and rendering many nodes unreachable,” the company said in a statement.
Once the syndrome gets going, it can be difficult to trace back to its original source and to stop, a big reason networks are designed to isolate failures early and contain them.
“We have learned through experience about these different types of failure modes. We build our systems to try and localize those failures,” said Craig Partridge, chair of the computer science department at Colorado State University in Fort Collins and a member of the Internet Hall of Fame. “I would hope that what is going on is that CenturyLink is trying to understand why a relatively well-known failure mode has bit them.”
The Federal Communications Commission also expects answers to some questions, opening another investigation of the phone company. In 2015, CenturyLink agreed to pay a $16 million settlement to the federal agency after a seven-state outage in April 2014.

Pai
FCC Chairman Ajit Pai said the agency would once again take a look at CenturyLink, focusing on disruptions to emergency services.
“When an emergency strikes, it’s critical that Americans are able to use 911 to reach those who can help,” Pai said in a statement. “This inquiry will include an examination of the effect that CenturyLink’s outage appears to have had on other providers’ 911 services.”
A retired manager at Qwest, a former Baby Bell now owned by CenturyLink, strongly criticized CenturyLink’s lack of communications with customers and an apparent lack of network redundancy.
“For a company in the communication business, they sure failed on this,” said Albuquerque resident Sam Martin. “I participated on the Qwest Disaster Recovery teams, and I do not recall ever having the network down for this kind of time and certainly never the 911 network. The 911 network should never have been down. The lack of this network can contribute to delays in rescue and fire saving lives.”
Martin is dubious about CenturyLink’s explanation for the network outage, suggesting a defective network card may be only a part of the problem.
“The explanations given so far are not valid,” Martin said. “The public may not be aware of it, but the communication network has redundancy and for essential services like inter-office trunking and 911 calls, there are duplicate fiber optic feeds – “rings” that duplicate the main circuit in another path – and switching equipment to these locations so that they may be switched electronically and automatically upon failure to a back-up network ring. When these systems are operating properly, the customer is unaware a failure occurred. If the automatic switching does not take place, employees involved with disaster recovery can intervene and manually switch the affected network to another fiber ring or electronic hub and service is restored until the actual damage is fixed.”
None of those things appeared to happen in this case, and the outage persisted for 48 hours before all services were restored.
“CenturyLink has to have a disaster recovery plan with redundancies in place for electrical, inbound and outbound local and toll-free carriers, as well as network and hardware component redundancies. CenturyLink should be able to switch between multiple fiber optic rings or central offices in case entire networks of phones go down. They would then locate and repair, or replace, defective telecommunication components without the customer ever knowing. The fact that this did not happen is discouraging and scary for the consumer. The fact that it happened nationwide is even more surprising and disturbing. Hopefully the truth will come out soon.”
A critical editorial in the Albuquerque Journal added:
We need answers from CenturyLink beyond the cryptic “a network element” caused the outage. We need to know how many CenturyLink and Verizon customers were affected. And we need to know what they – and other internet and phone providers – are doing to prevent similar outages or worse from happening in the future. Because if the outage showed nothing else, it’s that like an old-time string of Christmas lights, we are living in an interconnected world.
And when one light goes out, they can all go out.
KTVB in Boise, Idaho reported on CenturyLink’s massive outage on Dec. 27-28 and how it impacted local businesses and government services. (3:09)


 Subscribe
Subscribe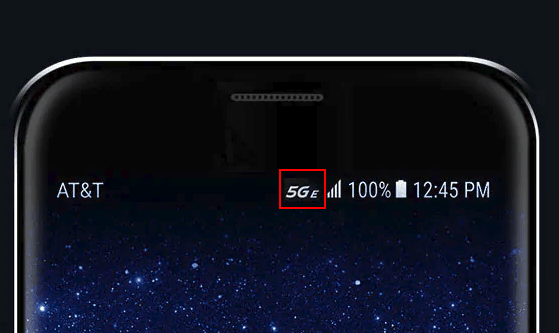 AT&T customers with Samsung Galaxy 8 Active or LG’s V30 or V40 smartphones began noticing a new icon on their phones starting last weekend: an italicized 5G
AT&T customers with Samsung Galaxy 8 Active or LG’s V30 or V40 smartphones began noticing a new icon on their phones starting last weekend: an italicized 5G Walter Piecyk, an analyst at BTIG Research,
Walter Piecyk, an analyst at BTIG Research, 

 Phone vendors are planning to tamp down customer expectations for their first 5G smartphones, claiming real world speeds will be at or slightly better than 4G LTE speeds in many markets and no better than a few hundred megabits from a barely used cell tower. The 5G technology being deployed to work with smartphones is different from the fixed 5G wireless experience some Verizon customers are getting with its wireless home broadband service.
Phone vendors are planning to tamp down customer expectations for their first 5G smartphones, claiming real world speeds will be at or slightly better than 4G LTE speeds in many markets and no better than a few hundred megabits from a barely used cell tower. The 5G technology being deployed to work with smartphones is different from the fixed 5G wireless experience some Verizon customers are getting with its wireless home broadband service. The latest findings
The latest findings  Vermont residents want better internet service and protection for universal access to phone service, even if customers have to pay a surcharge on their bill to make sure the traditional landline is still available in 100% of the state.
Vermont residents want better internet service and protection for universal access to phone service, even if customers have to pay a surcharge on their bill to make sure the traditional landline is still available in 100% of the state. The majority of residents own cell phones, with Verizon (47.5%) and AT&T (31.8%) dominating market share. Sprint has 0.6% of the market; T-Mobile has a 1.2% share, both largely due to coverage issues. But even with Verizon and AT&T, 40% of respondents said cell phone companies cannot deliver a signal in their homes. As a result, many residents are hanging on to landline service, which is considered more reliable than cell service. Some 40% of those relying on cell phones said they would consider going back to a landline for various reasons.
The majority of residents own cell phones, with Verizon (47.5%) and AT&T (31.8%) dominating market share. Sprint has 0.6% of the market; T-Mobile has a 1.2% share, both largely due to coverage issues. But even with Verizon and AT&T, 40% of respondents said cell phone companies cannot deliver a signal in their homes. As a result, many residents are hanging on to landline service, which is considered more reliable than cell service. Some 40% of those relying on cell phones said they would consider going back to a landline for various reasons.

 Despite a strong economy, Verizon Communications will shed 10,400 employees and cut $10 billion in costs as part of a transformation initiative promoted by the company’s newest top executive.
Despite a strong economy, Verizon Communications will shed 10,400 employees and cut $10 billion in costs as part of a transformation initiative promoted by the company’s newest top executive.