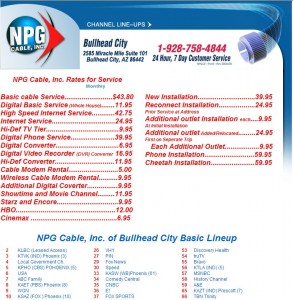
All-you-can-eat buffets, steak dinner vs. salad check splitting, electric and water service meters, toll highways with trucks vs. Mini-Coopers…. The justifications for Internet Overcharging representing “fairness” in broadband pricing have involved just about every analogy the broadband industry can come up with, all designed to make you think sticking a bigger bill to someone else down the street will somehow make your broadband bill smaller.
To convince sucker people into “billing fairness” that doesn’t actually reduce your pricing but could dramatically increase it is a tricky proposition. To make it work, they have to convince you of a broadband boogeyman up the street who is using up all your Internet and making you pay for it.
As the Re-Education effort continues among the astroturfer and industry PR crowd, the one service broadband providers strenuously avoid comparing themselves to is your local telephone or cell phone provider. That’s ironic, considering telephone companies move your calls around much the same way Internet traffic moves from point to point. It’s the closest comparative service around, but your Internet provider doesn’t dare use it in their analogies, because the entire argument for Internet Overcharging schemes falls apart when they do.
While some in the broadband industry want to take your flat rate pricing away, the telephone and cell phone industry is working harder and harder to move to flat rate pricing. Many traditional phone companies now peddle their own unlimited nationwide calling phone plan for $20-40 a month. Even some of the same broadband providers that want to take away your unlimited broadband service continue to mail blizzards of postcards and saturate the airwaves with marketing for their “talk all you want” unlimited phone plans.
In the mobile phone industry, an all-out price and feature war has erupted, as providers offer practically unlimited local and long distance calling. No more buckets of minutes to count, no more overage penalties, no more worries about putting off calling until the evening or weekends to protect your minute allowance.
In the past week, major providers have fallen all over themselves with new unlimited calling plans. Let’s take a look at today’s mobile calling landscape:
![]() AT&T: Last Wednesday, AT&T launched A-List, primarily in response to Sprint’s new Any Mobile, Anytime (see below). A-List lets customers add up to five numbers on an individual plan or up to 10 shared numbers on a FamilyTalk plan for unlimited calling to and from any phone number in the United States. The new feature begins September 20, and customers can change their A-List members at any time. Since customers often make the vast majority of their calls to a select group of people, it’s easy to get virtually unlimited calling that doesn’t exhaust your minute allowance.
AT&T: Last Wednesday, AT&T launched A-List, primarily in response to Sprint’s new Any Mobile, Anytime (see below). A-List lets customers add up to five numbers on an individual plan or up to 10 shared numbers on a FamilyTalk plan for unlimited calling to and from any phone number in the United States. The new feature begins September 20, and customers can change their A-List members at any time. Since customers often make the vast majority of their calls to a select group of people, it’s easy to get virtually unlimited calling that doesn’t exhaust your minute allowance.
![]() Boost Mobile: Back in January, Boost Mobile, the prepaid mobile phone service using the Nextel system (certain areas also provide Boost on Sprint’s network), launched a $50 unlimited calling plan that also includes unlimited handset data use, unlimited text messaging, unlimited walkie-talkie use, no roaming, no hidden fees, no contract and no credit check.
Boost Mobile: Back in January, Boost Mobile, the prepaid mobile phone service using the Nextel system (certain areas also provide Boost on Sprint’s network), launched a $50 unlimited calling plan that also includes unlimited handset data use, unlimited text messaging, unlimited walkie-talkie use, no roaming, no hidden fees, no contract and no credit check.
![]() Cricket: Cricket has always had a business plan catering to the prepaid user looking for generous or unlimited calling. The company heavily emphasizes its package bundles, such as their $45 monthly plan that offers unlimited calling, unlimited text, video and picture messaging, unlimited mobile web browsing, and free 411 service. The downside is their more limited coverage area, operating primarily for customers in urban and adjacent suburban areas, and providing almost no rural coverage at all.
Cricket: Cricket has always had a business plan catering to the prepaid user looking for generous or unlimited calling. The company heavily emphasizes its package bundles, such as their $45 monthly plan that offers unlimited calling, unlimited text, video and picture messaging, unlimited mobile web browsing, and free 411 service. The downside is their more limited coverage area, operating primarily for customers in urban and adjacent suburban areas, and providing almost no rural coverage at all.
![]() MetroPCS: Similar to Cricket, MetroPCS aggressively prices unlimited calling plans and bundles in its more limited service areas. For $40 a month, customers enjoy unlimited long distance calling, unlimited text and picture messaging, and web access. That pricing is comparable to many wired phone lines with a package of phone features without unlimited long distance. MetroPCS operates with a similar approach to Cricket – provide good coverage in the urban and suburban areas they focus service on, but usually ignores rural or more distant suburban areas.
MetroPCS: Similar to Cricket, MetroPCS aggressively prices unlimited calling plans and bundles in its more limited service areas. For $40 a month, customers enjoy unlimited long distance calling, unlimited text and picture messaging, and web access. That pricing is comparable to many wired phone lines with a package of phone features without unlimited long distance. MetroPCS operates with a similar approach to Cricket – provide good coverage in the urban and suburban areas they focus service on, but usually ignores rural or more distant suburban areas.
![]() PlatinumTel: Operating on the Sprint network, PlatinumTel is another prepaid provider offering unlimited calling, but with some important differences. For $50 a month, customers enjoy unlimited calling to any domestic phone numbers, unlimited text messaging, etc. But the service also provides unlimited roaming off their network, so if you get outside of Sprint’s coverage area, but are able to get a signal from another provider, you can still make and receive calls without incurring huge roaming fees. You also get 100MB of included data (a small additional fee adds more data).
PlatinumTel: Operating on the Sprint network, PlatinumTel is another prepaid provider offering unlimited calling, but with some important differences. For $50 a month, customers enjoy unlimited calling to any domestic phone numbers, unlimited text messaging, etc. But the service also provides unlimited roaming off their network, so if you get outside of Sprint’s coverage area, but are able to get a signal from another provider, you can still make and receive calls without incurring huge roaming fees. You also get 100MB of included data (a small additional fee adds more data).
 Straight Talk (from TracFone): If you’ve been to Walmart, you have probably seen TracFone phones and prepaid top-up cards at their stores. TracFone is another provider that operates on someone else’s cellular network. Their Straight Talk service operates on the robust Verizon Wireless network, providing excellent coverage in most areas except most of Kansas, Nebraska, Nevada, Mississippi and western Texas. A $45 monthly fee brings unlimited minutes and text messages, but only 30 megabytes of data for data-enabled phones.
Straight Talk (from TracFone): If you’ve been to Walmart, you have probably seen TracFone phones and prepaid top-up cards at their stores. TracFone is another provider that operates on someone else’s cellular network. Their Straight Talk service operates on the robust Verizon Wireless network, providing excellent coverage in most areas except most of Kansas, Nebraska, Nevada, Mississippi and western Texas. A $45 monthly fee brings unlimited minutes and text messages, but only 30 megabytes of data for data-enabled phones.
 Sprint Nextel: Already offering unlimited calling to other Sprint mobile customers, the third largest national mobile phone company last week introduced Sprint Any Mobile, Anytime. It allows you to call and receive calls from any cell phone on any network in the USA unlimited for free. You’re not limited to just one network or one calling circle. The feature is now automatically added to the Sprint Everything Data plans starting at either the $69.99. The plan also comes with unlimited text messaging and data. The new Any Mobile, Anytime will be especially popular with younger people who have already abandoned traditional landline telephone service and rely exclusively on mobile phones. You literally cannot exhaust your minute allowance calling these people. In fact, the only way to burn your minutes under this plan is to roam outside of Sprint’s network or call people on traditional wired phone lines.
Sprint Nextel: Already offering unlimited calling to other Sprint mobile customers, the third largest national mobile phone company last week introduced Sprint Any Mobile, Anytime. It allows you to call and receive calls from any cell phone on any network in the USA unlimited for free. You’re not limited to just one network or one calling circle. The feature is now automatically added to the Sprint Everything Data plans starting at either the $69.99. The plan also comes with unlimited text messaging and data. The new Any Mobile, Anytime will be especially popular with younger people who have already abandoned traditional landline telephone service and rely exclusively on mobile phones. You literally cannot exhaust your minute allowance calling these people. In fact, the only way to burn your minutes under this plan is to roam outside of Sprint’s network or call people on traditional wired phone lines.
![]() T-Mobile: T-Mobile offers the myFaves Minutes plan, which gives customers unlimited minutes to any five numbers of your choice on any network, mobile or landline (excludes toll-free/900 numbers). It’s easy to use T-Mobile as an unlimited wireless phone provider assuming the majority of your minutes are spent talking to up to five numbers every month.
T-Mobile: T-Mobile offers the myFaves Minutes plan, which gives customers unlimited minutes to any five numbers of your choice on any network, mobile or landline (excludes toll-free/900 numbers). It’s easy to use T-Mobile as an unlimited wireless phone provider assuming the majority of your minutes are spent talking to up to five numbers every month.
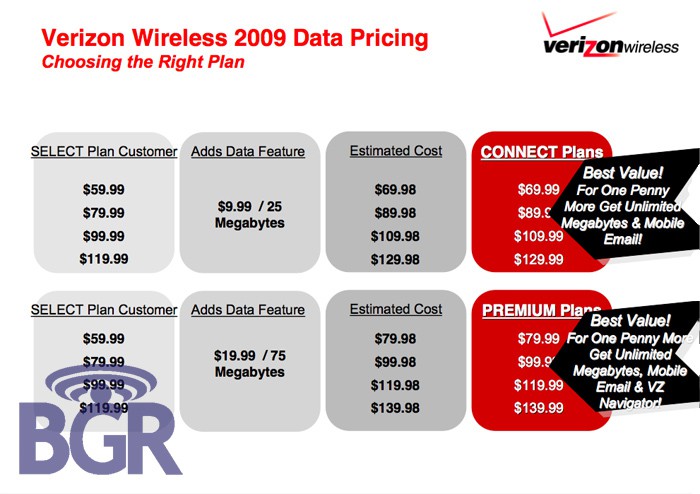
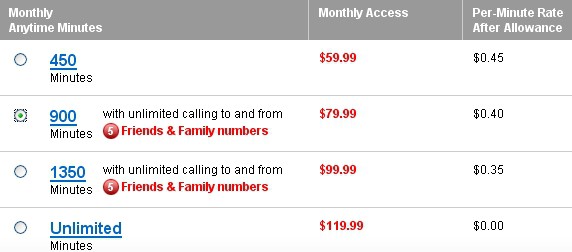
![]() Verizon Wireless: Already offering unlimited free calling to other Verizon Wireless customers (there are a ton of those), the company also introduced Friends & Family in February. With an eligible plan, customers have unlimited calling to a select group of numbers outside their standard mobile-to-mobile calling group, including landlines. This gives single line accounts up to 5 numbers to choose from on plans with 900 or more minutes, and family plan accounts up to 10 numbers to choose from on plans with 1,400 or more minutes.
Verizon Wireless: Already offering unlimited free calling to other Verizon Wireless customers (there are a ton of those), the company also introduced Friends & Family in February. With an eligible plan, customers have unlimited calling to a select group of numbers outside their standard mobile-to-mobile calling group, including landlines. This gives single line accounts up to 5 numbers to choose from on plans with 900 or more minutes, and family plan accounts up to 10 numbers to choose from on plans with 1,400 or more minutes.
 Virgin Mobile: Virgin Mobile relies on Sprint’s network, and with Sprint Nextel’s planned purchase of Virgin Mobile, which the company hopes to complete this November, it may soon become Sprint Nextel’s in-house prepaid service. Virgin Mobile introduced its Totally Unlimited calling plan on April 15. For $50 a month, customers get unlimited calling. For an additional fee, unlimited texting is added, along with mobile data options.
Virgin Mobile: Virgin Mobile relies on Sprint’s network, and with Sprint Nextel’s planned purchase of Virgin Mobile, which the company hopes to complete this November, it may soon become Sprint Nextel’s in-house prepaid service. Virgin Mobile introduced its Totally Unlimited calling plan on April 15. For $50 a month, customers get unlimited calling. For an additional fee, unlimited texting is added, along with mobile data options.
It’s difficult, at best, to make the kind of analogy the broadband industry wants to regarding “paying for what you use” when one of their closest cousins is competing hard to give you “all that you want for one price.”
Update: 9/15 — Jayne Wallace, a representative for Sprint Nextel, wrote to clarify “Sprint Nextel has not yet purchased Virgin Mobile…we do expect the deal to close in November. As of now, we are publicly held. Also since you mention broadband, we’ve also applied the pay as you go pricing here with Broadband2Go, the only nationwide prepaid broadband product available.” The article text under Virgin Mobile has been adjusted to reflect the planned purchase.


 Subscribe
Subscribe