 While the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities was able to quickly settle its differences with Verizon by granting the phone company’s wish to walk away from its commitment to offer 45Mbps broadband across the state, New Jersey ratepayers are out $15 billion in excess phone charges levied since 1993 for promised upgrades many will never get.
While the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities was able to quickly settle its differences with Verizon by granting the phone company’s wish to walk away from its commitment to offer 45Mbps broadband across the state, New Jersey ratepayers are out $15 billion in excess phone charges levied since 1993 for promised upgrades many will never get.
The Opportunity New Jersey plan the state government signed with Verizon was supposed to expand advanced broadband across the state in return for “a modest amount of pricing flexibility” in the fees Verizon charged customers in New Jersey. But Verizon is not a modest company and a new report shows the phone company used the agreement to boost rates as much as 440% — primarily through ancillary surcharges including inside wire maintenance, wire investment, an investment recovery fee, a local number portability surcharge, merged local calling area charge, and various other charges for phone features including Caller ID, Call Waiting, etc.
Tom Allibone, the president of LTC Consulting joined forces with New Networks’ Bruce Kushnick to analyze more than 30 years of Verizon New Jersey phone bills and discovered when it comes to tallying up rate increases, Verizon’s addition skills are akin to taking out a bag of M&M’s and only counting the yellow ones.
“This Verizon New Jersey bill from April 2002 […] has an “FCC Subscriber Line Charge”, which was $6.21 cents per line. Verizon’s quote doesn’t include this charge in their analysis of no increases between 1985 to 2008,” Kushnick writes. “The FCC Line Charge (it has many names), is on every local phone bill and the charge started in 1985. You can’t get service without paying this charge and the money does NOT go to fund the FCC but is direct revenue to Verizon New Jersey.”
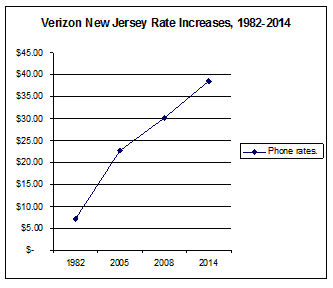 After adding up various other surcharges, Kushnick’s bill increased a lot.
After adding up various other surcharges, Kushnick’s bill increased a lot.
“Add up the ‘Total Monthly Charges’ for 2 phone lines— It’s ugly,” Kushnick said. “While the cost of the ‘monthly charges’ was $25.62, there’s an extra $17.70 cents — 70%. I thought that Verizon said there were no ‘increases.’”
“Anyone who has ever bought a bundled package of services from Verizon (or the other phone or cable companies) knows that they all play this shell game; the price of service you have to pay is always 10-40% more than the advertised price. That’s because the companies leave out the cost of these ancillary charges and taxes in their sale pitch,” he added.
Verizon raised local residential service rates 79% in 2008, according to Kushnick. Business customers paid 70 percent more. Caller ID rates increased 38% — remarkable for a service that has a profit margin of 5,695%. But Verizon did even better boosting the charge for a non-published number by 38% — a service that has a 36,900% profit margin as of 1999 — the services are even cheaper to offer now.
Telephone service is one of those products that should have declined in price, especially after phone companies fully depreciated their copper wire networks — long ago paid off. Companies like Verizon have cut the budgets for outdoor wire maintenance and the number of employees tasked with keeping service up and running has been reduced by over 70 percent since 1985, dramatically reducing Verizon’s costs. But Verizon customers paid more for phone service, not less.
The cost of service might not have been as much of an issue had Verizon taken the excess funds and invested them in promised upgrades, but that has not happened for a significant percentage of the state and likely never will. Instead, they just increased company profits. More recently, Verizon has directed much of its investments into its more profitable wireless division.
Even though Verizon achieved total victory with the Christie Administration-dominated BPU, the company is still making threats about any future plans for investment.
“It’s important that regulators and legislators support public policies that encourage broadband growth in New Jersey rather than ones that could jeopardize the state’s highly competitive communications industry, or risk future investments by providers like Verizon,” wrote Sam Delgado, vice president of external affairs.


 Subscribe
Subscribe


 Netflix has reached an agreement with Verizon Communications for a paid-peering interconnection between the two that will help assure Verizon’s broadband customers can watch Netflix content without repeated buffering slowdowns.
Netflix has reached an agreement with Verizon Communications for a paid-peering interconnection between the two that will help assure Verizon’s broadband customers can watch Netflix content without repeated buffering slowdowns. AT&T and Verizon Wireless are thrilled customers are moving away from subsidized smartphones, because both are raking in extra revenue they are not returning to customers with lower plan prices.
AT&T and Verizon Wireless are thrilled customers are moving away from subsidized smartphones, because both are raking in extra revenue they are not returning to customers with lower plan prices. Verizon Wireless is a bigger taker.
Verizon Wireless is a bigger taker.