While reviewing coverage on Comcast’s new usage meter, I ran across a disappointing quote from an article in The Hill newspaper from Gigi Sohn, president of public interest group Public Knowledge:
But as more consumers are downloading movies and streaming TV shows on their computers, bandwidth use is inching up. Imposing caps on consumers can become a form of discrimination, said Gigi Sohn, president of Public Knowledge, this morning at a panel I moderated about copyright and net neutrality.
“Public Knowledge doesn’t oppose usage-based pricing,” she said. “But if you set the cap low enough you discriminate against high-bandwidth applications. “If consumers have a finite amount of bandwidth each month, they could be forced to stay away from bit-hogging sites, like video high-quality video streaming services.
Sohn seems to grasp the very real risk of rationed broadband, but drops the ball completely in not opposing the scandal that “usage-based pricing” represents for broadband users. It was a real disappointment to see a group fail to understand the implications of these kinds of Internet Overcharging schemes. As the industry seeks to further monetize broadband usage, these pricing changes guarantee fatter profits and reduced costs for providers, and a higher bill for rationed broadband for consumers.
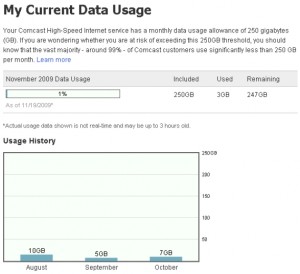
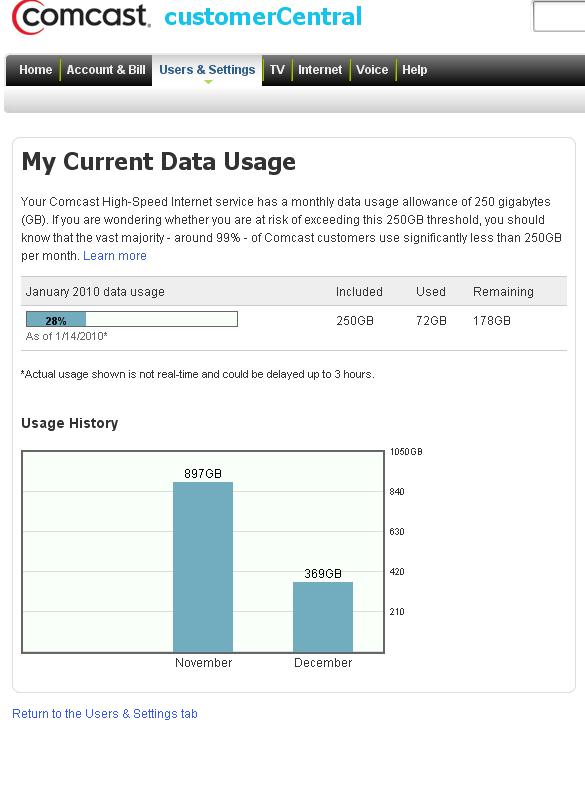
Comcast’s two year old 250GB usage cap seems generous by today’s standards, but note it has remained the same, despite growing overall broadband usage. What was generous two years ago is slightly less so today, and could be downright stingy a few years from now.
For customers stuck with providers with a different definition of “generous,” it is even more worrisome. Rochester, New York faced the prospect of a 5GB usage allowance from the local phone company’s DSL service, or a 40GB allowance from the local cable operator. The latter called their experiment fair, consumption-based pricing, but in reality it would have tripled the cost of broadband service for residents seeking to maintain the same level of service they enjoyed previously. There should be plenty to oppose in a $150 monthly broadband bill.
Internet Overcharging schemes involve all the ways a profitable broadband industry, enjoying record revenue and declining costs, could force consumers to pay more for the exact same service they receive today:
- The arbitrary usage cap, which ranges incredibly from 5GB-250GB per month, depending on the provider.
- The false “consumption/usage-based pricing” model which doesn’t actually charge consumers for what they use, but rather confines them into ranges of data allowance plans that carry stiff penalties for consumers who exceed their limit. Think cell phone plan for broadband, only markup the penalty fee by several thousand percent above cost.
- The overlimit penalty or fee, which seeks to punish and monetize usage at the same time. Customers, most of whom don’t have a clue about what a “gigabyte” is, will pay a stiff price for not intuitively knowing how much they’ll use month to month, and pay an overlimit penalty of $1-5 per gigabyte for excess usage. That’s far above the pennies per gigabyte large providers pay, but it’s a great way to make consumers think twice about daring to use high bandwidth services like online video.
- The overlimit insurance policy, which Bell Canada introduced to protect consumers from their own rapacious pricing. They pocket the proceeds from the “insurance” as well, picking customer pockets at every opportunity.
- The usage meter, not subject to independent scrutiny or verification. What they say you used, you used, even if you didn’t. Customers have learned these meters aren’t as accurate as providers suggest they are.
The fact is, customers pay for access based on speed, which has its own natural built-in usage limits. You can’t exceed certain consumption thresholds if your service doesn’t deliver the speed required to do so. Heavier users naturally gravitate towards faster speed, often premium-priced tiers. Lighter users often choose “lite” plans (when the provider makes them aware they exist) which deliver lower speed service perfectly adequate for web page browsing and e-mail. Current pricing models remain highly profitable for providers, even more so than some of the other components of their “triple play” packages. It’s the service consumers cancel last.
With a duopoly for wired broadband service in most American communities, tolerating “usage-based pricing” that isn’t (or will be overpriced even when offered) repeats the terrible mistake Canada made which today lives with the results — pricey, slow-speed broadband and a decline in broadband rankings. Canadians are livid about handing over considerably more of their money for throttled, usage-limited Internet access.
Public Knowledge advocates for Net Neutrality. In terms they might better understand, advocating for Net Neutrality while also not being opposed to the industry’s definition of “network management,” defined to create an exploitable loophole, makes Net Neutrality protection meaningless.
Without a ban on such pricing schemes, providers will keep their best possible tool to stop the threat of broadband video competing with their pay television offerings, and can favor certain content partners over others with exemptions from the dreaded cap ‘n tier system.
Matthew Henry, Internet Policy Counsel for Data Foundry, a database company, said on the panel that usage-based pricing presents serious “conflicts of interest” for cable companies that provide both cable TV and Internet services.
As people watch more cable content online, as both Comcast and Time Warner are pushing with their TV Everywhere services, more demands are placed on their broadband networks.
“Companies have a real incentive to force consumers to turn off the computer and pick up the remote,” he said.
Public Knowledge should carefully consider what happens in a Net Neutral world with onerous data caps and consumption pricing that exists for some, but not all online services. It’s an end run around the kind of open Internet we all support.
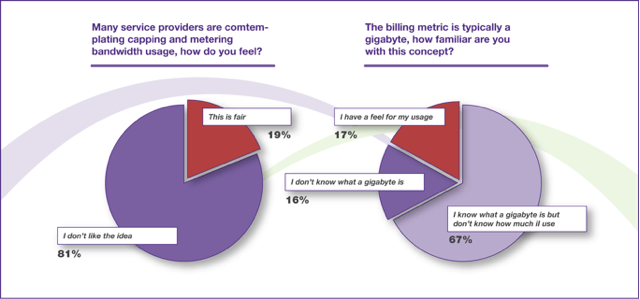
A survey conducted by International Data Corporation on behalf of Zeugma Systems, a company that makes an edge router for broadband networks, shows that consumers simply hate bandwidth caps and will likely switch to another carrier if they have the option
Over the last year, over 600 articles here have documented the abuse of consumers’ wallets from such schemes. We’ve also shown the real world consequences this pricing has in retarding development of new multimedia applications and higher bandwidth features. Innovative high bandwidth services seeking funding in a usage-capped world are deemed untenable if usage limits or overpriced broadband make customers think twice about using them. In the south Pacific, online video services have been literally shuttered simply because of data caps. Australian broadband, littered with caps and consumption billing, has become so bad the government is proposing its own National Broadband Plan to provide relief to those down under. Public Knowledge’s position would bring that broadband backwater to America if it became commonplace here.
Make no mistake — consumers are overwhelmingly opposed to such pricing, already pay higher-than-average costs for broadband, and are threatened with even higher bills if such schemes are imposed.
Public Knowledge needs to carefully reconsider its position and get on the side of consumers who recognize highly profitable broadband providers don’t need another major payday at their expense. Free Press understands the implications. We respect and appreciate Public Knowledge’s hard work for consumers on other issues. We invite them to join the consumer movement to retain fair broadband pricing.


 Subscribe
Subscribe