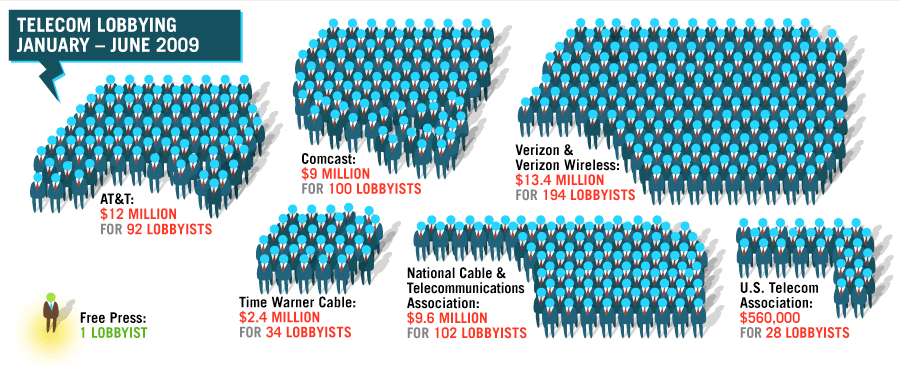
A Wall Street Journal article this morning calls the imminent introduction of Net Neutrality policy “a boon for consumers […] to use their computers or cellphones to enjoy videos, music and other legal services that hog bandwidth.”
A Wall Street Journal article this morning calls the imminent introduction of Net Neutrality policy “a boon for consumers […] to use their computers or cellphones to enjoy videos, music and other legal services that hog bandwidth.”
The article refers to the widely expected announcement today by FCC Chairman Julius Genachowski that Net Neutrality should be adopted as the fifth principle governing Internet service in the United States.
But Journal reporter Amy Schatz’s judgment about who wins and who loses in the Net Neutrality debate is framed by the flawed broadband provider arguments she adopts as reality:
The proposed rules could change how operators manage their networks and profit from them, and the everyday online experience of individual users. Treating Web traffic equally means carriers couldn’t block or slow access to legal services or sites that are a drain on their networks or offered by rivals.
The rules will escalate a fight over how much control the government should have over Internet commerce. The Obama administration is taking the side of Google, Amazon.com Inc. and an array of smaller businesses that want to profit from offering consumers streaming video, graphics-rich games, movie and music downloads and other services.
Setting aside the inappropriate use of the word “hog” to define broadband usage, which comes straight out of the broadband industry’s public relations strategy, Schatz ignores the fact some of the biggest drains on these networks will soon come from the industry’s own efforts to dominate online video — TV Everywhere.
In fact, the excuses for imposing Internet Overcharging schemes in 2009 do not reference much beyond online video growth as a justification to impose speed throttles and price increases on consumers.
Schatz adopts industry positions as fact in a number of places throughout her piece, which belongs on the Editorial page of the Journal:
If the FCC does force U.S. wireless carriers to open their networks to data-heavy applications like streaming video, it could push them beyond the limited capacity they have. Already, in areas like New York and San Francisco, a high concentration of iPhones has caused many AT&T customers to complain about degrading service.
In fact, many wireless carriers already provide their own wireless video to customers, and don’t seem to be engaging in a lot of hand-wringing over that. Should Net Neutrality force open the wireless platform, the quality of the service, not the provider’s self interest will govern the success and failure of individual applications. AT&T, which has earned massive revenue from its exclusive iPhone arrangement with Apple, can and should continue to invest some of that revenue into expanding their network to meet the demand. If they cannot, it is an open question why they would allow any online video or other data-heavy applications on their networks until those networks can handle the traffic.
In such a scenario, wireless carriers may have to rethink how much they charge for data plans or even cap how much bandwidth individuals get, said Julie Ask, a wireless analyst at Jupiter Research.
This ignores the fact providers have already rethought about how much they charge for data plans. Some providers are now compelling subscribers to choose data plans as part of their two year service agreements, while the industry is replete with 5GB usage caps on wireless data services today. Someone should ask Ask what she thinks is forthcoming that hasn’t already happened.
The FCC’s proposal will take into account the bandwidth limitations faced by wireless carriers, according to people familiar with the plan, and would ask how such rules should apply to current networks.
…which takes the wind out of the sails of the argument Net Neutrality would be ruinous to wireless providers.
The proposals come as the FCC faces a federal appeals court case over its authority to regulate Web traffic. Comcast is fighting an FCC decision last year to ding it for violating the agency’s “net neutrality” principles when it slowed traffic for some subscribers who were downloading big files. Comcast said it didn’t violate any rules because the FCC had never formally adopted any, but it did change how it manages its network.
In reality, Comcast’s speed throttle targeted files small and large, all because they were delivered over a specific network Comcast didn’t like: peer to peer. That’s a protocol that relies on a group of people obtaining files by sharing pieces already downloaded with one another until the file is complete for everyone. That involves uploading and downloading file pieces, often over a lengthy period. Comcast’s network was built with the assumption most customers would download far more than they upload, and peer-to-peer challenged that model with its file sharing methodology. The surge in upload traffic challenged their network at times, so Comcast decided to throttle the maximum speeds consumers could use while engaged in peer-to-peer file sharing.
Republicans are likely to oppose the FCC’s new proposal — both at the FCC and in Congress — arguing that the FCC is trying to fix problems that don’t exist and that the agency should take a more hands-off approach to the fast-changing industry.
“With only a few isolated instances of complaints alleging net neutrality-like abuses ever having been filed, it is a mistake,” said Randolph May, president of Free State Foundation, a free-market oriented think tank.
It’s difficult to fathom exactly how much more “hands-off” the agency can get with respect to broadband, an unregulated service in the United States. That “hands-off” policy was responsible for the establishment of de facto monopoly/duopoly broadband service in most American cities, wireless broadband that charges nearly the same price for the same usage capped service, and is tinkering with Internet Overcharging to leverage that market status into higher pricing for all consumers.
May’s argument is akin to calling the fire department only after a fire has consumed half of your home, not when the smoke detector first goes off.
As a result, both the cable companies and phone companies had incentives to create conditions on the Internet — either through pricing or slowing or speeding up certain sites — to favor their own content.
This sentence, buried towards the end of the piece, exemplifies exactly why Net Neutrality is so important. Let’s put this fire out before it burns out of control.


 Subscribe
Subscribe