The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission late Tuesday ruled against a revised proposal from Bell that could have effectively ended flat rate Internet service across the country, but also allows the phone company to raise wholesale prices for independent Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission late Tuesday ruled against a revised proposal from Bell that could have effectively ended flat rate Internet service across the country, but also allows the phone company to raise wholesale prices for independent Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
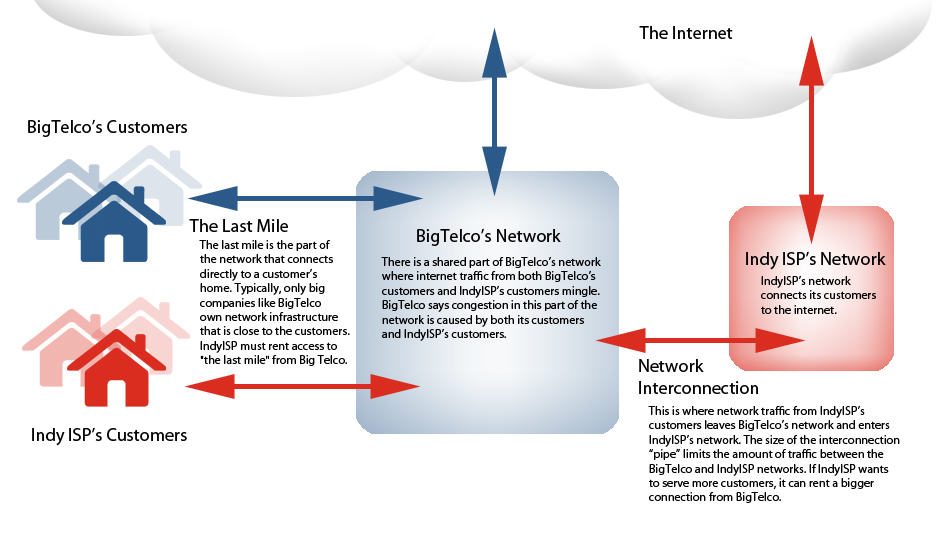
The Commission ruled Bell and cable companies like Rogers must sell access to third party providers at a flat rate or priced on speed and the number of users sharing the connection. The CRTC rejected a Bell-proposed usage-based pricing scheme that would have charged independent ISPs $0.178/GB.
Ultimately, the CRTC came down closest to adopting a proposal from Manitoba-based MTS Allstream, which suggested a variant on speed-based pricing, steering clear of charging based on usage. Under the CRTC ruling, independent ISPs can purchase unlimited wholesale access based on different speed tiers. The new pricing formula requires independent providers to carefully gauge their usage when choosing an appropriate amount of bandwidth. If an independent ISP misjudges how much usage their collective customer base consumes during the month, they could overpay for unused capacity or underestimate usage, leaving customers with congested-related slowdowns. ISPs will be able to purchase regular capacity upgrades in 100Mbps increments to keep up with demand. They can also implement network management techniques which may discourage heavy use during peak usage.
The CRTC decision underscores that Internet pricing should be based on speed, not on the volume of data consumed by customers. That’s a model Stop the Cap! strongly approves because it does not allow providers to monetize broadband usage.
But that is where the good news ends. Nothing in the CRTC ruling changes the Internet Overcharging regime already in place at the country’s leading service providers. Companies like Bell and Rogers are free to continue setting arbitrary limits on usage and charging overlimit fees for those who exceed them.
Konrad von Finckenstein, chair of the CRTC, says the regulator made a mistake in deciding last year to allow Bell to raise its prices for independent service providers.
“Our original decision was clearly not the best one. It was wrong and it was pointed out by a lot of people, including Minister Clement. He was right. We have today fixed it, we have made this new decision,” von Finckenstein said. “The bottom line is that you as a consumer will not face a cap or limitation of use because of anything mandated by the CRTC. Any kind of cap or limit, payment per use, that you will have to pay is because your ISP decides to charge you, not because we mandate it.”
But many independent providers are unhappy with the CRTC ruling because it also allows wholesale providers like Bell to raise prices, sometimes substantially, on the bandwidth they sell.
One independent ISP — TekSavvy, said it faced increased connectivity costs in eastern Canada.
“The CRTC decision is a step back for consumers. The rates approved by the Commission today will make it much harder for independent ISPs to compete”, said TekSavvy CEO Marc Gaudrault. “This is an unfortunate development for telecommunications competition in Canada,” he added.
“Rates are going up,” added Bill Sandiford, president of Telnet Communications and of the Canadian Network Operators Consortium, an independent ISP association.
![]() In addition to whatever rate increases eventually make their way to consumers, some independent providers may end up adopting network management and usage cap policies that attempt to slow down the rate at which they are forced to commit to bandwidth upgrades. That’s because providers purchase capacity based on what they believe their peak usage rate is likely to be. Providers will be free to upgrade service in 100Mbps increments. But with the new, higher prices, providers could overspend on capacity that goes unused or find themselves underestimating usage, creating congestion-related slowdowns for all of their customers.
In addition to whatever rate increases eventually make their way to consumers, some independent providers may end up adopting network management and usage cap policies that attempt to slow down the rate at which they are forced to commit to bandwidth upgrades. That’s because providers purchase capacity based on what they believe their peak usage rate is likely to be. Providers will be free to upgrade service in 100Mbps increments. But with the new, higher prices, providers could overspend on capacity that goes unused or find themselves underestimating usage, creating congestion-related slowdowns for all of their customers.
Some network management techniques that could reduce peak usage — and the need for upgrades — include speed throttles for heavy users during peak usage times or usage caps that fall away during off-peak hours when network traffic is lower.
Yesterday’s decision will provide some small relief to wholesale buyers of bandwidth in Quebec, where’s Videotron’s sky-high wholesale prices are set to be reduced. But the unusual divide in Internet pricing between eastern and western Canada will remain. Western Canadians will continue to enjoy much larger usage allowances, and lower wholesale pricing, than their eastern neighbors in Ontario and Quebec.
The CRTC’s ruling did not go far enough for NDP Digital Issues critic Charlie Angus. Angus notes only 6 percent of Canadians purchase Internet service from independent providers. The rest will still be stuck with what he calls “unfair billing practices and bandwidth caps.”
Angus is convinced the CRTC just gave the green light to force rate hikes for the minority of consumers who found a way around companies like Bell, Shaw, Videotron, and Rogers.
“Allowing big telecom companies to reach into the pockets of struggling families and ask for even more money is just plain wrong,” Angus said.
Bell’s senior vice-president for regulatory and government affairs, Mirko Bibic, still believes the company’s proposal to charge just under 20c per gigabyte to wholesale users was appropriate, but the CRTC’s permission to allow Bell to increase wholesale rates was a nice consolation prize. Bibic tried to frame the decision as forcing ‘independent ISPs to pay their fair share.’
Independent ISPs “are going to have to lease more traffic lanes,” he told CTV News. “I think the philosophy is [to] put the independent ISP in a position of responsibility. If usage goes up, you’re going to have to buy more lanes – it’s the same decision that we have to make.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe