Sony’s bid to enter the “over-the-top” online video business has gotten a shot in the arm with news it has reached a preliminary agreement with Viacom, Inc., to carry its popular cable networks on the Japanese electronics giant’s planned online subscription TV service.
Sony’s bid to enter the “over-the-top” online video business has gotten a shot in the arm with news it has reached a preliminary agreement with Viacom, Inc., to carry its popular cable networks on the Japanese electronics giant’s planned online subscription TV service.
Sony wants to build its own virtual cable television service, offering live and on-demand programming delivered over broadband lines in direct competition with cable and phone companies Comcast, Time Warner Cable, AT&T and Verizon.
Getting agreements with traditional must-have cable networks like Comedy Central, ESPN, and USA have been difficult because the networks fear alienating their traditional customers — large cable, telco and satellite TV companies.
 The Wall Street Journal reports Viacom’s agreement remains preliminary at the moment and the final details have yet to be worked out. If a final agreement is reached, it will be a breakthrough for so-called online cable systems which have gotten nowhere with other cable network owners, including Comcast-NBC, Walt Disney, Time Warner, and CBS.
The Wall Street Journal reports Viacom’s agreement remains preliminary at the moment and the final details have yet to be worked out. If a final agreement is reached, it will be a breakthrough for so-called online cable systems which have gotten nowhere with other cable network owners, including Comcast-NBC, Walt Disney, Time Warner, and CBS.
Cable executives have repeatedly warned that a wider distribution of cable network programming would make them more reluctant to pay higher prices for the cable networks because of the loss of relative exclusivity. Many cable programming contracts restrict the ability of network owners to sell to would-be online competitors.
Viacom has had contentious relationships with cable and satellite companies in the past, so observers suggest it is no surprise Viacom would be among the first to break with tradition. Viacom’s CEO, Sumner Redstone, also controls CBS which is currently off Time Warner Cable systems in three major cities and has had its pay movie channels Showtime and The Movie Channel blacked out on Time Warner systems nationwide. If Sony’s service gets off the ground, CBS could ask Time Warner customers to sign up with Sony instead to get those networks back.
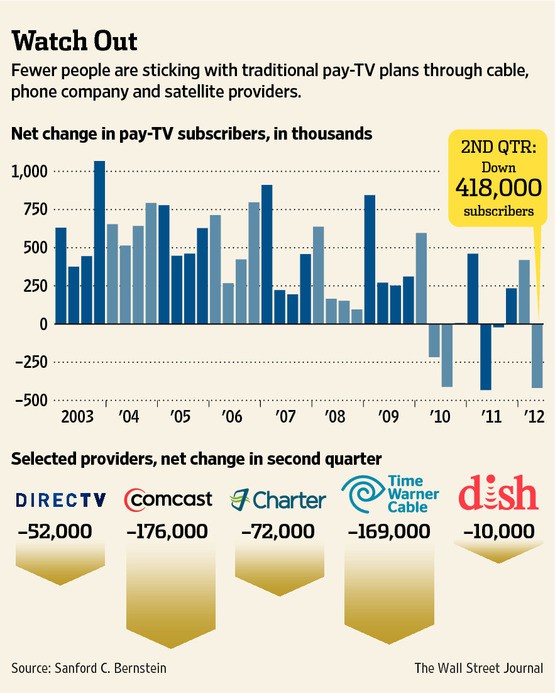
Cord Cutting is Real (Graphics: The Wall Street Journal)
Competing online video services from Intel and Google have largely gone nowhere because of stalled programming negotiations. How Sony managed a breakthrough remains a mystery. To secure rights, Sony may have been asked to sign a lengthy contract with favorable financial terms for Viacom, or Sony might have agreed to carry the full roster of Viacom-owned cable networks, which include:

The next generation of the Sony PlayStation may be your next cable box.
- BET
- CMT
- Comedy Central
- Logo
- MTV
- MTV2
- Nick at Nite
- Nick Jr.
- Nickelodeon
- Nicktoons
- Palladia
- Spike
- TeenNick
- Tr3s
- TV Land
- VH1
A source told the Journal Sony hopes to launch its new venture by the end of the year, perhaps on the next generation of Sony’s PlayStation gaming console due soon. Sony also could offer the service on its line of Bravia high-definition televisions, as well as tablets and smartphones.
The Journal:
People who have seen demonstrations of Sony’s system say it has some features that are appealing in comparison to traditional pay TV distributors, including one that recommends shows for users based on what they’ve previously watched. Content providers are allowed to supply some of those recommendations, so they can steer users to other episodes on their channels, according to the people familiar with the matter. Sony provides other content suggestions for viewers based on an algorithm.
The development of online cable television in direct competition with large cable and phone companies could spark a new wave of broadband usage restrictions including usage caps and metered billing. The same telecom companies that earn a substantial part of their revenue selling cable television service are likely to find it unsettling to discover Sony undercutting them on price and using “their” broadband lines to do it. Placing restrictions on the amount of broadband traffic a customer can use each month would deliver a significant deterrent to would-be cord cutters.


 Subscribe
Subscribe TracFone customers signed up for NET10 Wireless prepaid service are getting word in e-mail the 1.5GB monthly data cap on AT&T-based SIM cards introduced in March has been removed and unlimited data has returned.
TracFone customers signed up for NET10 Wireless prepaid service are getting word in e-mail the 1.5GB monthly data cap on AT&T-based SIM cards introduced in March has been removed and unlimited data has returned.




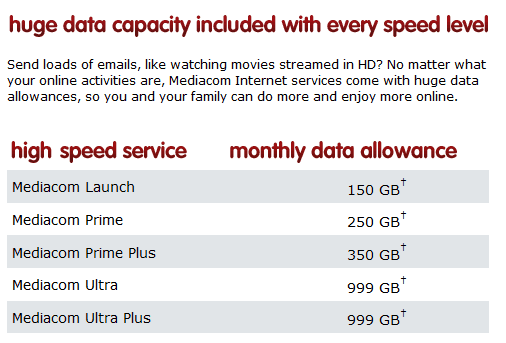 Actually, Mediacom will benefit from lower usage and higher revenue it will collect from the $10 overlimit fee for each additional 50GB of usage. Neighborhood congestion issues are largely a thing of the past because of upgrades to DOCSIS 3 technology.
Actually, Mediacom will benefit from lower usage and higher revenue it will collect from the $10 overlimit fee for each additional 50GB of usage. Neighborhood congestion issues are largely a thing of the past because of upgrades to DOCSIS 3 technology. If Time Warner Cable is concerned about the rising cost of cable television, it sure didn’t show it after sources revealed the cable company quickly accepted CBS’ demands for more compensation but is refusing to budge until it wins rights to show CBS programming on mobile platforms.
If Time Warner Cable is concerned about the rising cost of cable television, it sure didn’t show it after sources revealed the cable company quickly accepted CBS’ demands for more compensation but is refusing to budge until it wins rights to show CBS programming on mobile platforms.