 Should a deal to merge Time Warner Cable with Comcast be approved by regulators, Time Warner Cable customers can expect a number of changes to their cable, Internet, and phone service because of Comcast’s much more involved rate plans¹.
Should a deal to merge Time Warner Cable with Comcast be approved by regulators, Time Warner Cable customers can expect a number of changes to their cable, Internet, and phone service because of Comcast’s much more involved rate plans¹.
Customers should expect to pay significantly higher prices for a package comparable to what Time Warner Cable offers today, especially for cable television.
Broadband speeds will be faster with Comcast, but also likely usage-capped at 300GB a month, with overlimit fees applied to “heavy users.”
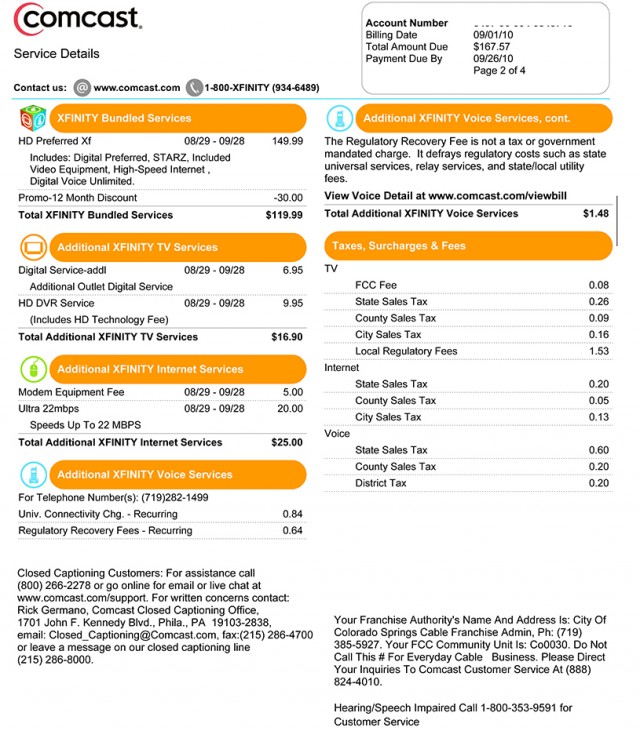
A sample Comcast bill
Customers may also be surprised to discover Comcast levies a number of ancillary fees that Time Warner does not, especially for various tasks completed by a Comcast customer service representative.
Comcast and Time Warner Cable have very different operating philosophies. Comcast is quickly moving customers to all-digital cable television service, so those Time Warner customers without set-top boxes or CableCARDs should be ready for a rapid transition to all-digital TV. Time Warner Cable, in comparison, has moved slowly towards digital service and uses a stop-gap technology that delivers some digital channels to neighborhoods only when being watched as a bandwidth conservation measure. Comcast will likely scrap that technology in favor of an all-out drive to switch to digital service.
Comcast’s television packages are very different from what TWC customers are used to buying. Time Warner customers can expect significant channel losses with Comcast’s nearest equivalent basic cable service. If you enjoy a lot of sports or old movies, Comcast will make you spend nearly $20 more on a higher-cost tier to get back the networks that Time Warner used to bundle as part of their basic cable service. But Comcast makes adding “whole home” DVR service look a lot more affordable than the $30+ unbundled fee Time Warner Cable has traditionally charged for the equipment and service.
In general Time Warner Cable customers should expect a higher bill for cable television, unless they want to downgrade service (for which Comcast also charges a service fee).
Broadband service from Comcast is also very different from what Time Warner Cable has offered. Most TWC customers now get 15/1Mbps service. Most Comcast customers get 25/5 or 50/15Mbps service. However, TWC doesn’t force usage caps on customers and Comcast is systematically reimposing them on theirs city by city, usually 300GB a month. The tradeoff with Comcast is faster advertised speed that comes usage-limited vs. slower speeds you can use as much as you want. Comcast also charges the highest modem rental fees in the country — now $8 a month in most places. Customers can and should buy their own modems. Those Time Warner Cable customers who already have better double-check to make certain Comcast will still support that equipment.
Phone service isn’t much different between the two companies, so we’re not covering it here.
Television Packages
Comcast offers a bigger variety of television packages than Time Warner Cable. Comcast likes to bundle premium channels into some of their higher end packages. Time Warner Cable’s prefers an a-la-carte approach with HBO and other similar networks.
 Comcast customers start with Limited Basic service, comparable to Time Warner Cable’s Broadcast Basic package. It primarily features over the air local television stations and often runs under $10 a month. Effective this year, there is also a $1.50/month Broadcast TV surcharge applicable to all cable TV customers.
Comcast customers start with Limited Basic service, comparable to Time Warner Cable’s Broadcast Basic package. It primarily features over the air local television stations and often runs under $10 a month. Effective this year, there is also a $1.50/month Broadcast TV surcharge applicable to all cable TV customers.
A new concept for Time Warner Cable customers is Comcast’s Digital Economy package that includes Limited Basic, Digital Economy channels, and a standard definition cable box and remote. Consider this barely promoted tier the economy bare bones basic cable package. In addition to local channels, Digital Economy offers a lineup of home shopping channels, CNN, HSN, Cartoon Network, Lifetime, History, A&E, E!, Comedy Central, Spike TV, USA Network, Fox News Channel, The Weather Channel, Food Network, Animal Planet, TLN, BET, TV Guide Network, Discovery Channel, Comcast Network, CSPAN, EWTN, Jewelry Television, and Music Choice. This package is $40 a month, although promotions may cut the cost. For some, this may be more than enough.
But most Comcast cable TV customers choose the Digital Starter package that also includes Limited Basic, Expanded Basic, MoviePlex, and Music Choice. The lineup includes just over 80 channels. This $69.95 package is still smaller than what Time Warner Cable offers its digital cable customers, leaving out networks including Cloo, CNBC World, Al Jazeera America, Discovery Fit & Health, Disney XD, DIY, a range of ESPN’s extra networks, EWTN, Fine Living, Fox Business News, Great American Country, IFC, Investigation Discovery, Lifetime Real Women, Military Channel, MLB, most of MTV’s extra networks, NBA, National Geographic Channel, NFL Network, NHL Network, most of Nickelodeon’s extra networks, OWN, Oxygen, Sundance, Turner Classic Movies, The Science Channel, and VH1’s extra networks. There are other channels left out of the lineup as well. But Digital Starter customers do get the full lineup of Encore movie channels, for which TWC charges extra. However, sports and old movie fans will be dismayed to find so many sports networks and Turner Classic Movies excluded. Comcast customers have to pay more to get them back in the lineup.
Those who can’t live without sports networks and TCM, among other networks noted above, will have to pay for Comcast’s 150+ channel Digital Preferred package. This tier brings back the cable channels you used to get with Time Warner Cable (plus Encore), but it costs an extra $17.95 a month. Check your current Time Warner Cable TV bill. Compare it against Comcast’s total combined charge of $87.89 a month for a comparable lineup. How much is your cable TV bill going to increase after Comcast takes over?
 For those who want even more, Comcast offers Digital Premier, with more than 190 channels. This package includes Digital Preferred, HBO, Showtime, Starz, Cinemax and Comcast’s Sports Entertainment Package. It adds an extra $57.45 a month on top of the $69.95 Digital Starter package. That is $127.40 a month just for television service.
For those who want even more, Comcast offers Digital Premier, with more than 190 channels. This package includes Digital Preferred, HBO, Showtime, Starz, Cinemax and Comcast’s Sports Entertainment Package. It adds an extra $57.45 a month on top of the $69.95 Digital Starter package. That is $127.40 a month just for television service.
Time Warner customers looking for a DVR will probably be mystified by the way Comcast charges for DVR service. Comcast markets “whole house” DVR service much more aggressively than TWC. This service, dubbed AnyRoom, lets customers watch recorded shows on any set-top box-equipped television in the home, along with managing recordings. DVR service with Comcast costs an extra $8-10 a month, but Comcast also charges an “HD Technology Fee” of $9.95 a month to enable “whole house” service. Many higher end bundled packages incorporate the DVR service into the package, along with the Technology Fee.
At regular prices, a Comcast triple play customer should expect to pay $141.99 for the most bare bones TV, phone, and broadband package, $154.99 for the most popular package without premium channels, and $164.99 a month for a bundle that brings along a similar lineup to what TWC offers, along with Starz. Comcast’s nearest equivalent to Time Warner Cable’s $200 Signature Home service costs $239.99 a month and offers no better Internet speeds than what “regular” customers get.
Internet Plans
 Comcast does offer faster Internet service than what Time Warner Cable has sold for the last 3-4 years, but it will likely come with a usage cap of 300GB per month, with overlimit fees applied to those who exceed their allowance. Internet-only customers are going to find higher prices for broadband service than what Time Warner Cable charges. Comcast prefers bundled service customers, and deters cord-cutters with extremely high Internet-only pricing.
Comcast does offer faster Internet service than what Time Warner Cable has sold for the last 3-4 years, but it will likely come with a usage cap of 300GB per month, with overlimit fees applied to those who exceed their allowance. Internet-only customers are going to find higher prices for broadband service than what Time Warner Cable charges. Comcast prefers bundled service customers, and deters cord-cutters with extremely high Internet-only pricing.
Comcast’s Internet Tiers (The first price is for Internet-only service followed by the price, when different, for customers subscribing to more than broadband)
- Economy: 1.5Mbps/384kb (N/A)
- Economy Plus: 3Mbps/768kbps ($39.95 $29.95)
- Performance Starter: 6/1Mbps ($49.95)
- Performance: 25/5Mbps ($64.95 $51.95)
- Blast: 50/15Mbps ($74.95 $61.95)
- Extreme 105: 105/20Mbps ($114.95 $99.95)
Modem fees are extra unless you buy your own equipment.
Other Comcast Fees You Better Know About
 Comcast charges a number of extra fees and surcharges that raise customer bills without affecting Comcast’s advertised prices. The ones we have not already covered are included below. Among our favorites: Comcast charging $20 to hound you at your front door for a past due payment, charging shipping/handling and other fees for “self-install” kits that save Comcast money not having to dispatch a technician to your home, installation -and- activation fees for extra outlets, and that $249 “go away” service charge for their 105Mbps broadband tier. It is important to note not everyone will pay these fees and promotions often waive some of them. Customer service representatives will also drop some of them when asked, and may remove them from your bill if you complain loudly enough.
Comcast charges a number of extra fees and surcharges that raise customer bills without affecting Comcast’s advertised prices. The ones we have not already covered are included below. Among our favorites: Comcast charging $20 to hound you at your front door for a past due payment, charging shipping/handling and other fees for “self-install” kits that save Comcast money not having to dispatch a technician to your home, installation -and- activation fees for extra outlets, and that $249 “go away” service charge for their 105Mbps broadband tier. It is important to note not everyone will pay these fees and promotions often waive some of them. Customer service representatives will also drop some of them when asked, and may remove them from your bill if you complain loudly enough.
Ancillary Service Fees You May Encounter
- Reactivation fees: Shut off for non-payment or vacation? Comcast charges $5 to reactivate Internet service, $5 to reactivate a phone line, and $1.99 to turn back on your cable television;
- Field Collection Charge: If Comcast sends someone to your residence to collect a past due balance or pick up unreturned equipment, there is a $20 charge per visit;
- Returned Payment Fee: $20 per returned payment;
- Late Fee: 5% of your account balance;
- Name Change Fee: $1.99;
- Pay by Phone Convenience Fee: Making a payment by phone with a customer care representative will cost $5.99 per payment;
- Copy of Bill: For bill statement copy requested by phone or in person, there is a $5 charge per bill;
- Unreturned/Damaged Equipment: Charged at the suggested manufacturer’s replacement cost.
Common Equipment Fees
- Signal Amplifier: $35/each
- Self-Install Kit Convenience Fee: $40
- Self-Install Kit Shipping & Handling: $9.95 (Standard Delivery)
- Self-Install Kit Shipping & Handling: $29.95 (Priority Mail)
- Remote Control Replacement by Mail (Separate Shipping): $5.95/each
 Voice/Data Modem (Used for customers with phone and Internet service): $8/mo²
Voice/Data Modem (Used for customers with phone and Internet service): $8/mo²- Wireless Gateway (Provides Wi-Fi service): $8/mo²
- Cienna 3931 Modem & Netgear Wireless Router: $19.95/mo
- Wireless Adapter (each, one-time charge): $30.00
- Limited Basic Only Service Converter: $1/mo
- Digital Converter: $2.50/mo
- Remote Control: $0.18/mo
- HD Digital Converter (Limited Basic Only): $2.20/mo
- Digital Adapter (Limited Basic Only): $0.50/mo each
- CableCARD: 1st card is free, each additional is $1/mo
- Customer-Owned Video Equipment Credit: $2.50/mo
Installation and Service Calls (May vary with promotions)
- Installation fee for one product: $32
- Installation fee for two products: $80
- Installation fee for three products: $90
- In-Home Service Call: $32.10
- Service Charge for Custom Installation Work: $33.20/hr
- Installation fee for additional outlets: $13.35/ea at time of new customer visit, $32.15/ea for existing customers
- Activation fee for additional outlets: $5.60/ea for new customers, $22.05/ea for existing customers
- Relocation fee for additional outlets: $13.60/ea for new customers, $28.55/ea for existing customers
- VCR/DVD Connection Charge: $7.90 for new customers, $16.35 for existing customers
- Upgrade/Downgrade Service Fee (no in-home visit required): $1.99 per instance
- Upgrade/Downgrade Service Fee (in-home visit required): $26.30 per instance of an upgrade, $12.05 per instance of a downgrade
 Upgrade Standard Definition DVR or HD DVR Service: $26.30
Upgrade Standard Definition DVR or HD DVR Service: $26.30
Broadband-Specific Installation/Service Charges
- Additional IP Address (first): $4.95/mo
- Additional IP Addresses (second and/or third) $9.00/mo each
- Professional Internet Installation: $99.95
- Wireless Networking On-Site Professional Set-up (up to 4 devices per trip): $49.95
- Wireless Networking On-Site Professional Set-Up (extra trips): $99.95/ea
- Wireless Networking On-Site Professional Set-Up (each additional device over 4): $29.95/ea
- Broadband-related In-Home Service Visit: $40/per trip
- Extreme 105Mbps Broadband Professional Installation/Activation Surcharge: $249.00
¹The rates and services quoted in this piece were taken from Comcast’s current rate card for Cambridge, Mass. Rates and services may vary slightly in other markets. The rate card was effective June 2013.
²Comcast charges $7 a month for their modem rental in certain other markets.







 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Gizmodo
Gizmodo 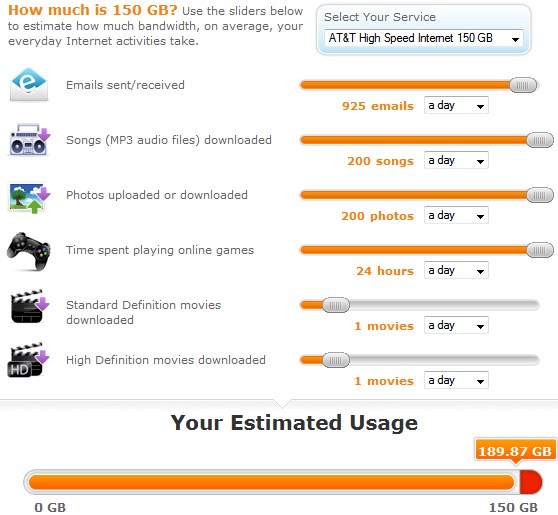
 Few were surprised more by the sudden announcement that Comcast was seeking to acquire Time Warner Cable all by itself than the negotiating team from Charter Communications.
Few were surprised more by the sudden announcement that Comcast was seeking to acquire Time Warner Cable all by itself than the negotiating team from Charter Communications. According to Bloomberg News, the
According to Bloomberg News, the 

 Malone called today’s divided industry “Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs” and insisted on a new major consolidation wave to enhance “value creation” and deliver some major blows to satellite and telephone company competitors.
Malone called today’s divided industry “Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs” and insisted on a new major consolidation wave to enhance “value creation” and deliver some major blows to satellite and telephone company competitors.
 Should a deal to merge Time Warner Cable with Comcast be approved by regulators, Time Warner Cable customers can expect a number of changes to their cable, Internet, and phone service because of Comcast’s much more involved rate plans¹.
Should a deal to merge Time Warner Cable with Comcast be approved by regulators, Time Warner Cable customers can expect a number of changes to their cable, Internet, and phone service because of Comcast’s much more involved rate plans¹.
 Comcast customers start with Limited Basic service, comparable to Time Warner Cable’s Broadcast Basic package. It primarily features over the air local television stations and often runs under $10 a month. Effective this year, there is also a $1.50/month Broadcast TV surcharge applicable to all cable TV customers.
Comcast customers start with Limited Basic service, comparable to Time Warner Cable’s Broadcast Basic package. It primarily features over the air local television stations and often runs under $10 a month. Effective this year, there is also a $1.50/month Broadcast TV surcharge applicable to all cable TV customers. For those who want even more, Comcast offers Digital Premier, with more than 190 channels. This package includes Digital Preferred, HBO, Showtime, Starz, Cinemax and Comcast’s Sports Entertainment Package. It adds an extra $57.45 a month on top of the $69.95 Digital Starter package. That is $127.40 a month just for television service.
For those who want even more, Comcast offers Digital Premier, with more than 190 channels. This package includes Digital Preferred, HBO, Showtime, Starz, Cinemax and Comcast’s Sports Entertainment Package. It adds an extra $57.45 a month on top of the $69.95 Digital Starter package. That is $127.40 a month just for television service. Comcast does offer faster Internet service than what Time Warner Cable has sold for the last 3-4 years, but it will likely come with a usage cap of 300GB per month, with overlimit fees applied to those who exceed their allowance. Internet-only customers are going to find higher prices for broadband service than what Time Warner Cable charges. Comcast prefers bundled service customers, and deters cord-cutters with extremely high Internet-only pricing.
Comcast does offer faster Internet service than what Time Warner Cable has sold for the last 3-4 years, but it will likely come with a usage cap of 300GB per month, with overlimit fees applied to those who exceed their allowance. Internet-only customers are going to find higher prices for broadband service than what Time Warner Cable charges. Comcast prefers bundled service customers, and deters cord-cutters with extremely high Internet-only pricing. Comcast charges a number of extra fees and surcharges that raise customer bills without affecting Comcast’s advertised prices. The ones we have not already covered are included below. Among our favorites: Comcast charging $20 to hound you at your front door for a past due payment, charging shipping/handling and other fees for “self-install” kits that save Comcast money not having to dispatch a technician to your home, installation -and- activation fees for extra outlets, and that $249 “go away” service charge for their 105Mbps broadband tier. It is important to note not everyone will pay these fees and promotions often waive some of them. Customer service representatives will also drop some of them when asked, and may remove them from your bill if you complain loudly enough.
Comcast charges a number of extra fees and surcharges that raise customer bills without affecting Comcast’s advertised prices. The ones we have not already covered are included below. Among our favorites: Comcast charging $20 to hound you at your front door for a past due payment, charging shipping/handling and other fees for “self-install” kits that save Comcast money not having to dispatch a technician to your home, installation -and- activation fees for extra outlets, and that $249 “go away” service charge for their 105Mbps broadband tier. It is important to note not everyone will pay these fees and promotions often waive some of them. Customer service representatives will also drop some of them when asked, and may remove them from your bill if you complain loudly enough. Voice/Data Modem (Used for customers with phone and Internet service): $8/mo²
Voice/Data Modem (Used for customers with phone and Internet service): $8/mo² Upgrade Standard Definition DVR or HD DVR Service: $26.30
Upgrade Standard Definition DVR or HD DVR Service: $26.30 AT&T wants customers to pay attention to their broadband account’s monthly usage limits: 150GB for DSL or 250GB for U-verse. Customers who exceed their allowance are more likely than ever to get a warning letter from AT&T threatening overlimit fees if they continue to ‘use too much’ Internet.
AT&T wants customers to pay attention to their broadband account’s monthly usage limits: 150GB for DSL or 250GB for U-verse. Customers who exceed their allowance are more likely than ever to get a warning letter from AT&T threatening overlimit fees if they continue to ‘use too much’ Internet.