
Does Canada’s Food TV need special protection when it made 53% gross profits on the backs of cable subscribers that pay for the network whether they watch it or not?
“If you cut your cable, then your Internet is going to go up,” predicts Gary Pelletier, president of the Canadian chapter of the Cable & Telecommunications Association for Marketing.
That is just one of several predictions many Canadian cable and phone companies are claiming will come from the “disastrous decision” to allow consumers the freedom to pick and pay for only the cable channels they want to watch. Amidst claims that over 10,000 jobs will be lost, chaos and bankruptcy will stalk minority and niche cable networks, consumers will pay much higher bills, and American programming will boycott Canada fearing a-la-carte could make its way into the United States, Canada is at least having an adult discussion about the future of television and where it fits in the country’s identity.
Big changes are coming as a result of the latest great soul-searching made by our good neighbors to the north, always concerned about the potential of the Canadian Experience being overrun, if not decimated by the United States’ entertainment hegemony. In a moment of clarity, regulators have just realized what the rest of English-speaking Canada already knew: protectionist content regulations don’t work on the Internet. Canadians routinely bypass geographical restrictions and Canadian content laws with virtual private networks that relocate them, online at least, to a home address in the U.S. so they can binge-watch the unrestricted American versions of Netflix, Hulu and other online video services.
Regulators have now adopted the attitude – “if you can’t beat ’em, join ’em,” encouraging Canadian entertainment producers to create fewer, but better shows that will not only attract Canadian audiences, but those abroad.
Only the exchange is supposed to be mutual. High quality Canadian television productions like Orphan Black, Schitt’s Creek, X Company, The Book of Negroes, This Life, 19-2, Vikings, Killjoys, Rookie Blue, and Murdoch Mysteries are all among Canadian critics’ top favorites. But relatively few Americans know these shows exist or assume they are co-productions owned by some American entertainment conglomerate. Only a brief glimpse of a Canadian flag during the warp speed end credits might clue viewers this isn’t the case.
Despite protectionist media policies that have endured since 1970, the Canadians are now boldly going where Americans have so far feared to tread. They are having the conversation about the future of television and online entertainment in all forms while American media barons remain in denial.
For average consumers, the biggest change will begin next spring when the era of Canadian a-la-carte cable television arrives, allowing consumers to take an ax to the expensive 120-300 channel television package once and for all. Starting March 1, all Canadian providers will be required to offer consumers a basic cable package priced at no more than $25 a month, containing Canadian and U.S. over the air stations and networks, educational, and public channels. If you want more, you can have it by buying channels or mini-packages of networks individually to create a personalized cable TV lineup of networks you actually care to watch.
Programmers across Canada, particularly those catering to sports fans, foreign audiences, religious viewers, and minorities are horrified by the idea. So are media critics that fear the change could help bring an end to Canada’s unique multilingual and multicultural identity.
 Customers like James Rehor of Hamilton explains why.
Customers like James Rehor of Hamilton explains why.
“Why would I pay for it? Why do I get it? Why does it come on my TV?” asks the 60-year-old construction worker. He’s ready on day one to purge the large number of French and other non-English channels from his Cogeco Cable lineup. Rehor offers comfort to sports programmers, however. He’s a big fan of the Toronto Maple Leafs, so Leafs TV, Sportnet, and TSN will stay.
Non-sports fans are another matter. They can’t wait to ditch the sports networks that are always the most expensive channels in a Canadian cable package.
“Clearly the most expensive (channels) will always be sports,” Pelletier tells the Canadian Press. “At the end of the day, for sports watchers, their cable bill will probably stay the same or increase, maybe … In the case of someone who doesn’t watch any sports at all, their bill will probably decrease.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CRTC Supporting the creation of content made by Canadians for Canadians and global audiences 3-2015.mp4[/flv]
An Age of Abundance: Canadian telecom regulators are transforming media regulations in Canada, recognizing the way Canadians watch television has changed. Quality, not quantity, is now most important. CRTC chairman Jean-Pierre Blais discusses the new reality. (6:08)
Pelletier and his industry friends are on a mission to convince Canadians to leave well enough alone and not drop the current all-for-one price cable television package for a-la-carte — not realizing the potential consequences.
 Some in the cable industry have tried other scare tactics to no avail.
Some in the cable industry have tried other scare tactics to no avail.
One industry-backed study predicted pick-and-pay could cost the economy 10,000 jobs. Consumers could care less. Unifor, a union that represents many in the television sector, seemed to agree Canada’s cultural heritage will be at risk with lowest common denominator programming dominating from St. John’s to Vancouver, much of it shoveled from the United States. But Canadians still want their House of Cards and Homeland.
Howard Law, a media spokesman for Unifor, predicts less profitable Canadian channels will fold under a pick-and-pay pricing model.
“The introduction of pick and pay will, in itself, lead to a major loss of revenues to Canadian broadcasting system, which ultimately plays out in less Canadian content and less Canadian jobs and less Canadian broadcasting,” he said in an interview on CBC’s The Exchange with Amanda Lang.
Minority interest and religious channels are also worried about their future. Most of those networks are classified as “specialty channels” by the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC). Legacy networks that have been around since at least the 1990s have been sitting pretty, protected by their designation as a “Category A” specialty station. Unlike in the United States, Canadian cable networks are licensed to operate by the CRTC, and at least 60 of those Category A networks also enjoy “genre protection,” a CRTC policy that guarantees their channel carriage on Canadian cable, satellite, and telco TV systems and protection from other cable networks that want to run the same kind of programming.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC How New CRTC Rules Will Change Canadian TV 3-2015.mp4[/flv]
For decades, protectionist Canadian content regulations made certain Canadian television reflected its audience. But online video and the Internet has allowed Canadians to bypass traditional cable television to watch they want, not what the government hopes they will. New CRTC rules reflect that reality as Canadian TV rethinks how to get the viewer’s attention. From CBC-TV’s The National (4:16)
CRTC policies have allowed Canadian specialty channels to flourish despite operating in a smaller marketplace with fewer viewers than their American counterparts. That means networks like FoodTV and HGTV in Canada have profit margins ranging from 53-58 percent. Fashion Television and BookTV made an improbable $2.7 million in pre-tax profit, not so much from viewers but from the licensing fees every Canadian cable customer pays for the four networks whether they watch them or not.

From its start, Canadian TV has always faced a looming shadow from the south. Protecting Canada’s identity has been a priority for decades.
“If you’re a specialty channel that’s lived within the protective cocoon of bundling for years, you’ve gotten used to having a full-time job with benefits,” independent technology analyst Carmi Levy told CBC News. “Contrast that with living outside the protective cocoon, you’re essentially a freelancer, you fight for every contract, you have no benefits, there are no guarantees that money will be coming tomorrow or next week.”
It probably won’t be coming from subscribers like Mr. Rehor, who won’t hesitate to drop channels if they go unwatched.
The CRTC is also doing some dropping of its own, starting with genre protection, which could lead many specialty networks to follow American cable networks that today depend on chasing ratings to justify their licensing fees. The unintended result in the United States has been questionable lineup changes like the appearance of Law & Order rerun marathons on WEtv, a network supposedly dedicated to women’s entertainment. Ovation, a fine arts independent cable network that is about a niche as a network can be, depended on weekend binges of PBS’ Antiques Roadshow reruns in 2012 just to attract enough viewers to show up in the ratings.
Lesser known networks like OutTV, Canada’s only network dedicated to lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender viewers, may face an uncertain future if it can’t charge a premium price to make up for expected subscriber losses from pick and pay. Other niche channels may have to merge with other networks or more likely relaunch with an online platform and deliver a reduced menu of content to audiences.
 Large Canadian mainstream networks and programmers don’t expect too much change from pick and pay, as most Canadians will likely still demand a package with their programming included. But distributors – cable, satellite, and telco TV platforms, do expect some major changes. The average Canadian now pays around $50 a month for basic cable, a price that will be cut in half next spring.
Large Canadian mainstream networks and programmers don’t expect too much change from pick and pay, as most Canadians will likely still demand a package with their programming included. But distributors – cable, satellite, and telco TV platforms, do expect some major changes. The average Canadian now pays around $50 a month for basic cable, a price that will be cut in half next spring.
Rogers Cable already knows what is coming. It ran a trial in 2011 in London, Ont., with 1,000 customers who were given the choice of picking and paying for the channels they wanted. It didn’t take long for the cable company to discover customers loved it and TV stations and cable programmers hated it.
“We found that customers like bundles, but want to build their own. They want a basic package and an extra package they create,” Rogers spokesman Kevin Spafford told the Toronto Sun. “We did get push back from TV stations. There was concern about offering this service. They did not want us to proceed with that model.”
After the trial ended, Rogers allowed the pilot project participants to keep their pick and pay packages, something they’ve held tightly for over four years.
Rogers’ pilot offered something like what the CRTC is demanding be available to all Canadians:
 ROGERS PICK AND PLAY PILOT
ROGERS PICK AND PLAY PILOT
- $20 a month for “skinny basic” TV package of Canadian stations. (The CRTC plan mandates no more than $25.)
- 15-channel package for $27 a month. Other packages of 20 and 25 stations also offered, for more money. (The CRTC wants networks to offer channels individually or in mini-bundles.)
- U.S. major networks offered for $3 a month. (Under the CRTC policy, these stations may appear under the basic or a-la-carte tiers.)
REGULAR ROGERS
- Basic: $40 a month, 190 channels
- Digital Plus: $63, 220 channels
- Sports packages: $77, 230 channels
- VIP TV: $77, 270 channels
- VIP Ultimate: $119, 320 channels
The upcoming changes are probably the biggest in Canadian cable television history, but they still may not be enough to attract cord-nevers — those who have never subscribed to cable TV. Most are under 30 and already watch all their favorite shows online. Some budget-minded Canadians who want to cut their cable bill may consider joining them by cutting the cord altogether or slimming down their cable packages, but Pelletier warns that cable operators will not leave their money on the table.
 Supplementing a slimmer cable package with a streaming service or two could increase data charges, Pelletier warns. Plus, you may have to surrender any discounts you get from bundling cable with home phone, Internet and/or wireless service.
Supplementing a slimmer cable package with a streaming service or two could increase data charges, Pelletier warns. Plus, you may have to surrender any discounts you get from bundling cable with home phone, Internet and/or wireless service.
Usage capped Internet is also still an effective deterrent for cord-cutting and whether your television entertainment comes over the cable or online, providers will still make a run for your wallet. Some observers predict providers will dramatically increase the retail prices of a-la-carte networks to limit potential savings while also continuing to raise broadband prices.
A 2014 national PIAC poll found 90 per cent of 1,000 consumers polled were willing to pay an additional $1 a month per channel, while 54 per cent would be willing to go $3 a month, and 21 per cent would be willing to pay $5 a month for an extra channel of their choosing. Many don’t realize under the current system the wholesale rate for many channels is under 50 cents a month. Considering what Canadians are willing to pay, it is likely cable companies will price channels according to what the marketplace will tolerate, which could be around $3 for each channel a month.
Suspicion about any cable company offering a New Deal is something Americans and Canadians have in common. Mr. Rehor is already keeping a wary eye.
“I think it’s a good idea, I just don’t know how they’re going to really work it,” he says, fearing it could ultimately end up costing the same amount he pays now.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC Pick and Pay TV 3-2015.flv[/flv]
CBC News offers this extended discussion about the implications of “pick and pay” cable television. (10:11)


 Subscribe
Subscribe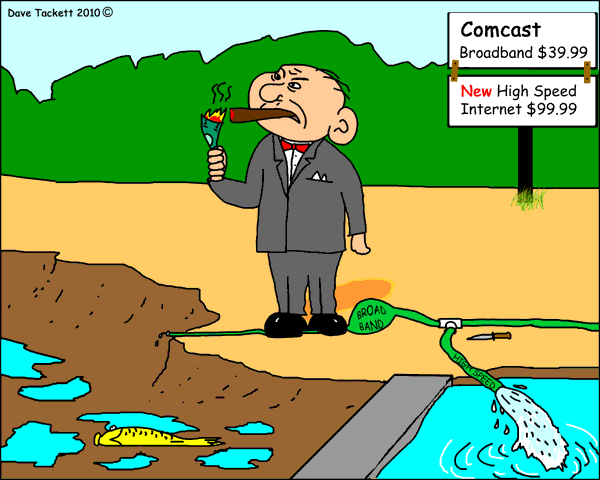 Stop the Cap! has received a growing number of complaints from Comcast customers in Georgia who are paying the cable company an extra $35 a month to get back unlimited Internet access that is performing worse than ever before for online video streaming.
Stop the Cap! has received a growing number of complaints from Comcast customers in Georgia who are paying the cable company an extra $35 a month to get back unlimited Internet access that is performing worse than ever before for online video streaming.
 Jeff Wemberly reports his Comcast usage meter is recording unprecedented levels of usage he has never seen on his broadband account before the caps.
Jeff Wemberly reports his Comcast usage meter is recording unprecedented levels of usage he has never seen on his broadband account before the caps.


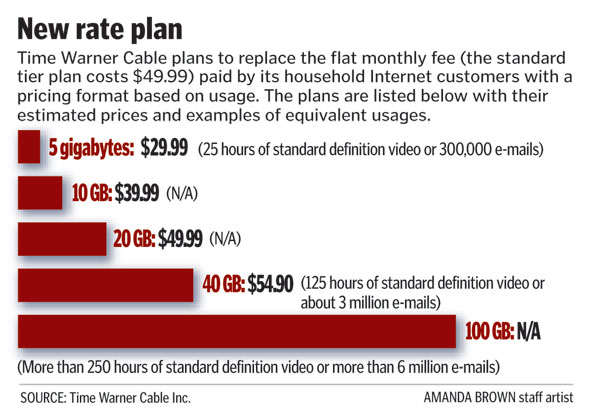
 If you are living with a Comcast data cap and want to see it gone, you can do something about it. Consider organizing your own local movement by tapping fellow angry customers and recruiting local activist groups to the cause. In Rochester, there was no shortage of angry college students and groups ready to protest. Google local progressive political groups, technology clubs, and technology-dependent organizations in your immediate area. Some are likely to be a good resource for building effective public protests, sign-making, and other TV-friendly protest techniques. Contact town governments, the mayor’s office of your city, technology-oriented newspaper columnists, radio talk show/computer support show hosts, etc., to build a mailing list for coordinated announcements about your efforts. Many local officials also oppose data caps.
If you are living with a Comcast data cap and want to see it gone, you can do something about it. Consider organizing your own local movement by tapping fellow angry customers and recruiting local activist groups to the cause. In Rochester, there was no shortage of angry college students and groups ready to protest. Google local progressive political groups, technology clubs, and technology-dependent organizations in your immediate area. Some are likely to be a good resource for building effective public protests, sign-making, and other TV-friendly protest techniques. Contact town governments, the mayor’s office of your city, technology-oriented newspaper columnists, radio talk show/computer support show hosts, etc., to build a mailing list for coordinated announcements about your efforts. Many local officials also oppose data caps. The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission is asking some hard questions of Quebec-based mobile provider Vidéotron, which began zero-rating preferred partner music streaming services last summer that allow customers to stream all the music they want without it counting against their data cap.
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission is asking some hard questions of Quebec-based mobile provider Vidéotron, which began zero-rating preferred partner music streaming services last summer that allow customers to stream all the music they want without it counting against their data cap. Observers say zero-rating enhances a customer’s perception that data has a measurable financial value, often arbitrarily assigned by competitors in a marketplace. If providers charge an average of $10 per gigabyte, customers will gradually accept that as the base value for wireless data, despite the fact many providers used to sell unlimited data plans for around $30. Zero rating content can be used in marketing campaigns to suggest customers are getting added value when a provider turns off the usage meter while using those services. Stream 3GB of music and a provider can claim that has a value of $30, but provided to you at “no charge.”
Observers say zero-rating enhances a customer’s perception that data has a measurable financial value, often arbitrarily assigned by competitors in a marketplace. If providers charge an average of $10 per gigabyte, customers will gradually accept that as the base value for wireless data, despite the fact many providers used to sell unlimited data plans for around $30. Zero rating content can be used in marketing campaigns to suggest customers are getting added value when a provider turns off the usage meter while using those services. Stream 3GB of music and a provider can claim that has a value of $30, but provided to you at “no charge.” Comcast is inviting controversy launching a new live streaming TV service targeting cord-cutters while exempting it from its own data caps.
Comcast is inviting controversy launching a new live streaming TV service targeting cord-cutters while exempting it from its own data caps.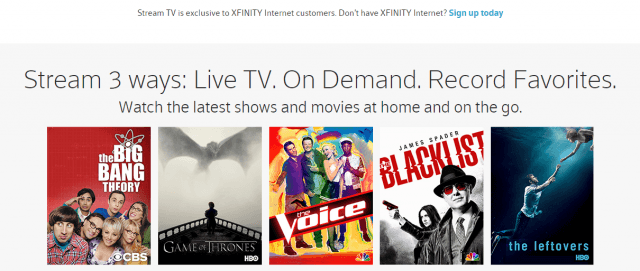
 Comcast claims it is reasonable to exempt Stream TV from its 300GB data cap being tested in a growing number of markets.
Comcast claims it is reasonable to exempt Stream TV from its 300GB data cap being tested in a growing number of markets.
