Phillip "Of course you know this means war" Dampier
Sizing up the big winners from FCC Chairman Julius Genachowski’s latest Net Neutrality proposals is as simple as putting those praising Genachowski in column “A” and those outraged by downsized consumer protections into column “B.” It comes as no surprise Big Telecom, the employees whose jobs depend on those companies, their trade associations and lobbyists are all living it up on the “A” side while consumers and public interest groups sit in the dark in column “B.”
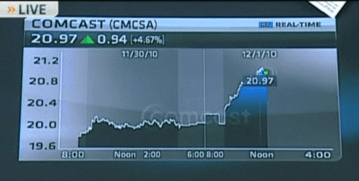
Among the high-five club is Kyle McSlarrow, the outgoing head of the National Cable and Telecommunications Association, the cable industry’s top lobbying enterprise.
On the NCTA’s blog, an indication of your broadband future has been placed front and center — a meter. Perhaps putting a coin slot on your cable modem or a credit card reader on the side of your monitor would be a bit too brazen, even for this industry.
McSlarrow, among others, heaped bountiful praise on the FCC chairman for his ‘enlightened’ views on Net Neutrality. That hardly a surprise considering Genachowski has opened his phone line, and apparently his heart, to industry propaganda and arguments.
Genachowski’s remarks about usage-based pricing, in particular, were a breath of fresh air to Wall Street and providers clamoring to dispense with unlimited broadband service for consumers to increase profits:
Our work has also demonstrated the importance of business innovation to promote network investment and efficient use of networks, including measures to match price to cost such as usage-based pricing.
“This approach reflects a responsible and considered view of a fast-moving and highly dynamic marketplace but it doesn’t assume that there is any one ‘correct’ answer,” McSlarrow wrote.
It’s also a view consumers strongly disagree with, but those opinions are off the FCC’s radar. Consumers don’t have the chairman’s direct phone number. If they did, they could argue the fact “matching price to cost” would mean a dramatic reduction in pricing for today’s unlimited broadband account. Instead, we have a lobbying effort to end “unlimited” entirely, backed by manufactured studies funded by providers expecting pre-determined conclusions. Too bad the FCC doesn’t read provider financial reports.
Writes McSlarrow:
Some consumers don’t see the need to go online. Others are constrained by cost. Still others want to use the service they have in cutting-edge ways. And the ability to pigeonhole companies and their business plans as being one thing or another is breaking down, particularly in an environment where Internet applications, content, and services change the way we behave as consumers, provide new opportunities for providers and consumers and alter how we all interact with both traditional and new devices and features.
The key point is that that we need to focus on what best serves consumers. With all this change, it is necessary to have the flexibility to test new business models – and perhaps new pricing plans – in order to see if they make sense.
A usage-based pricing model, for instance, might help spur adoption by price-sensitive consumers at the lower end of the socioeconomic ladder. As Sanford Bernstein analyst Craig Moffett noted in a report issued yesterday, “{u}sage-based pricing for broadband would have profound implications. At the low end, it would allow cable operators to introduce lower priced tiers that could boost penetration and help in efforts to serve lower income consumers.”

McSlarrow
Evidently, to chase the small percentage of Americans who either don’t have an interest in going online, or think it costs too much, the NCTA wants those already online to face Internet Overcharging schemes ranging from usage caps to metered billing. Is it flexible for consumers who face the end of broadband pricing as they’ve lived with for more than a decade or is it flexible for providers who can run to the bank with the higher profits rationed broadband delivers?
McSlarrow quotes Moffett’s quest for higher profits for his clients — Wall Street investment banks, but ignores the implications Moffett himself admits — consumer rebellions, self-rationing of usage, a stifling of online innovation from independent companies not connected with providers, and higher prices.
American providers look north for an example of Big Telecom’s pot ‘o gold — Canadian ISPs that have managed to wreak havoc on the country’s broadband rankings, forcing consumers to live with higher prices and, in some cases, declining usage allowances. Canada’s broadband innovation graveyard is an object lesson for Americans: usage-based pricing doesn’t deliver savings to anyone except the most casual users living under constrained speeds and paltry allowances as low a 1GB per month. For everyone else, broadband prices are higher, speeds are slower, and usage allowances deliver stinging penalties for those who dare to exceed them. What do Canadian providers do with all of the money they earn? A good sum of it goes towards acquiring their competitors, further reducing an already-poor competitive marketplace.
As one Ontario reader of Broadband Reports noted, “our largest cable company has the money to buy three professional sports teams but not enough to roll out DOCSIS 3 [to all of its customers.] Our largest phone company, Bell, has the money to buy half the news stations in Canada, but cannot seem to get users off of 3Mbps DSL service. The whole system is a scam.”
While the rest of the world is decidedly moving away from limited-use broadband, American providers have sold Genachowski that rationing the Internet is “innovation.”
Of course, you and I know real innovation means investing some of the enormous profits providers earn back into their networks to keep up with growing demand. Providers can innovate all they like to attract price sensitive customers, so long as current unlimited plans remain available and affordable. But as AT&T illustrated earlier this year, the first thing off the menu is “unlimited,” replaced with overpriced and inadequate wireless data plans that only further alienate their customers.
AT&T should take a lesson… from AT&T. While it gouges its customers on the wireless side, the company has managed to solve the affordability question all by itself, without resorting to wallet-biting. It dramatically reduced prices on its DSL services — now just $14.95 a month for its customers, which includes a free gateway and modem. That sure sounds like a solution for budget-conscious customers and delivered all without antagonizing those who want to keep their current unlimited service plans.

AT&T seems to have managed to solve the affordability question without overcharging their customers.
Cable companies deliver their own budget broadband plans, but it comes as no surprise they barely market them, fearing their premium-paying customers could downgrade their service.
In short, Internet Overcharging is a solution chasing a problem that simply does not exist in a responsible broadband marketplace.
McSlarrow says he’s not arguing for or against any particular model. All he is really confident about is that the marketplace is changing and that “companies will have to adapt to that change.”
But as is too often the case, McSlarrow, his industry friends and colleagues, and Chairman Genachowski have forgotten it’s ultimately consumers who have to adapt to change, and we promise it means all-out war if providers tamper with unlimited broadband service.
 While some American broadband providers continue to dream of Internet Overcharging schemes for American customers, one of the world’s most usage-capped countries continues its march forward to abolish them. Australia’s Optus, a major broadband provider, today announced it was dramatically increasing usage allowances on customers, effective immediately.
While some American broadband providers continue to dream of Internet Overcharging schemes for American customers, one of the world’s most usage-capped countries continues its march forward to abolish them. Australia’s Optus, a major broadband provider, today announced it was dramatically increasing usage allowances on customers, effective immediately.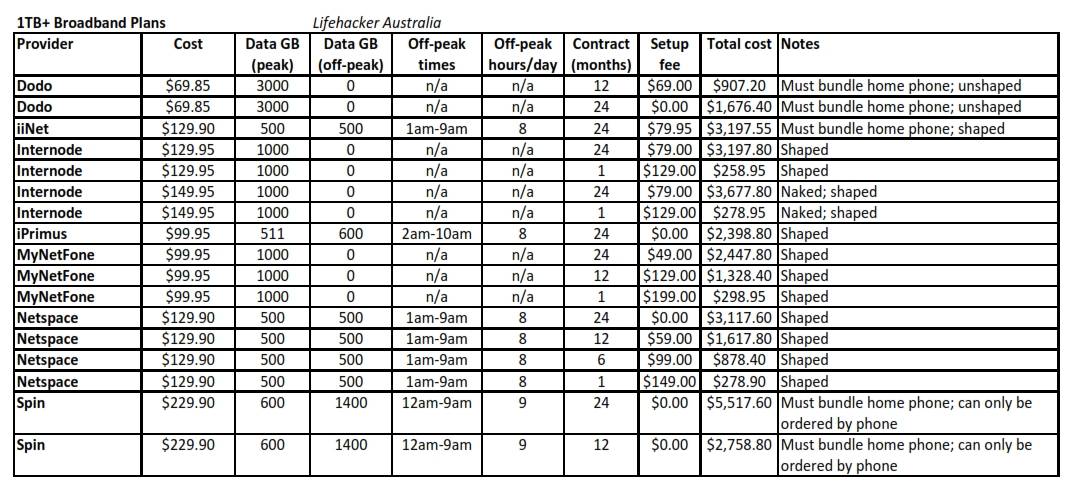


 Subscribe
Subscribe