[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNN Netflix Slowdown Who is to Blame 6-6-14.flv[/flv]
CNN explores who is responsible for Netflix’s streaming problems on Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse. While one industry analyst seems keen to blame Netflix, his other articles on the subject show an increasing bias towards big ISPs like Verizon and AT&T. (2:54)
Netflix’s May speed rankings confirm Verizon FiOS customers are likely to find a degraded video streaming experience while using the otherwise speedy fiber to the home service. Netflix performance on Verizon FiOS dropped considerably last month — so much so that Frontier and Windstream DSL customers now get better Netflix performance than any Verizon customer receives. AT&T U-verse customers fared even worse with streaming performance below that offered by Mediacom — America’s bottom-rated cable company and CenturyLink DSL. In fact AT&T U-verse customers receive only marginally better service than Hughes satellite and Clearwire wireless customers. Verizon’s DSL came in dead last.
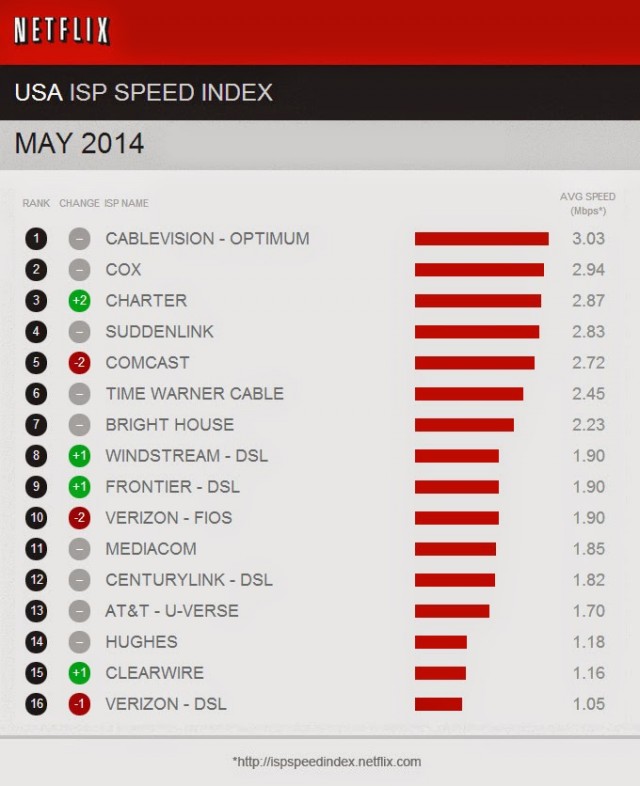
Coincidentally, both Verizon and AT&T, following Comcast’s lead, have been in negotiations with Netflix to receive payment from the streaming video provider to better handle its traffic. Verizon CEO Lowell McAdam said he’s confident about getting payments from Netflix, and he turned out to be correct — Verizon and Netflix reached an agreement in late April that is still being implemented. AT&T also says it is negotiating with Netflix. Verizon’s streaming video partnership with Redbox has not been affected by the sudden deterioration in online video streaming on Verizon’s network.

The problems with Netflix on some ISP’s have gone all the way to the top.
“My wife and I like to lay in bed and watch Netflix,” Tom Wheeler, chairman of the US Federal Communications Commission, said in January. The two companies serving Wheeler’s neighborhood are Comcast and Verizon. When enough customers launch streams on Netflix, saturating the inbound connection to either ISP, the video stops. When it does, Wheeler’s wife joins the parade of irritated customers.
“You’re chairman of the FCC,” she says to him. “Why is this happening?”
Last week, Netflix decided to answer that question with a more informative error message appearing when available bandwidth is insufficient to support a high quality stream.

“The Verizon network is crowded right now,” the message says. Netflix then attempts to restore the stream by serving up a degraded, lower quality/bit rate version to the paying customer.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg Netflix-Verizon War of Words 6-6-14.flv[/flv]
Bloomberg interviews Todd O’Boyle from Common Cause. He places the blame for this debacle solely on the shoulders of Verizon and other ISPs. (5:39)
The inability to successfully maintain a stable stream of Netflix content that ranges from 256kbps to 5.8Mbps seems odd on ISPs that offer customers connections far faster than that. The average Netflix stream is 2Mbps, slow enough to be comfortably supported on even a 3Mbps DSL connection. Netflix’s problems with Comcast evaporated after agreeing to pay the cable company to maintain a better connection between its customers and Netflix’s content delivery network. The same cannot be said for perfomance on AT&T’s U-verse platform. Although Verizon signed an agreement with Netflix, it has clearly not been implemented as of yet.
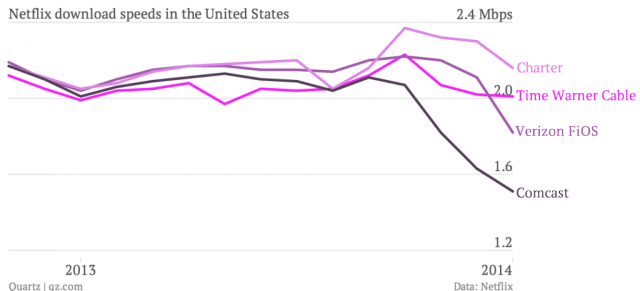
“We started a small-scale test in early May that lets consumers know, while they’re watching Netflix, that their experience is degraded due to a lack of capacity into their broadband provider’s network,” said Netflix’s Joris Evers. “We are testing this across the U.S. wherever there is significant and persistent network congestion.”
 The companies with the biggest drops in Netflix performance are the same ones strongly advocating special paid “fast lanes” on the Internet for preferred traffic to resolve exactly these kinds of performance problems.
The companies with the biggest drops in Netflix performance are the same ones strongly advocating special paid “fast lanes” on the Internet for preferred traffic to resolve exactly these kinds of performance problems.
“Some large US ISPs are erecting toll booths, providing sufficient capacity for services requested by their subscribers to flow through only when those services pay the toll,” said Evers. “In this way, ISPs are double-dipping by getting both their subscribers and Internet content providers to pay for access to each other. We believe these ISP tolls are wrong because they raise costs, stifle innovation and harm consumers. ISPs should provide sufficient capacity into their network to provide consumers the broadband experience for which they pay.”
The error message fingering Verizon as the culprit for a poorer Netflix experience brought an angry response from Verizon on its blog:
Reports from this morning have suggested that Netflix is engaging in a PR stunt in an attempt to shift blame to ISPs for the buffering that some of its customers may be experiencing. According to one journalist’s tweet from last night, Netflix is displaying a message on the screen for users who experience buffering which says: “The Verizon network is crowded right now.”
This claim is not only inaccurate, it is deliberately misleading.
The source of the problem is almost certainly NOT congestion in Verizon’s network. Instead, the problem is most likely congestion on the connection that Netflix has chosen to use to reach Verizon’s network. Of course, Netflix is solely responsible for choosing how their traffic is routed into any ISP’s network.
[…] It is sad that Netflix is willing to deliberately mislead its customers so they can be used as pawns in business negotiations and regulatory proceedings.
It would be more accurate for Netflix’s message screen to say: “The path that we have chosen to reach Verizon’s network is crowded right now.”
However, that would highlight their responsibility for the problem.

Milch
That was quickly followed by a cease and desist letter from Verizon demanding Netflix remove error messages that blame Verizon for the problem. It also demanded a list of Verizon customers that received the Netflix notification.
“Failure to provide this information may lead us to pursue legal remedies,” wrote Verizon general counsel Randal Milch in a letter to Netflix general counsel David Hyman.
“This is about consumers not getting what they paid for from their broadband provider,” Netflix spokesman Jonathan Friedland said. “We are trying to provide more transparency, just like we do with the ISP Speed Index, and Verizon is trying to shut down that discussion.”
“Verizon’s unwillingness to augment its access ports to major Internet backbone providers is squarely Verizon’s fault,” Netflix general counsel David Hyman wrote.
“Netflix does not purposely select congested routes,” added Evers. “We pay some of the world’s largest transit networks to deliver Netflix video right to the front door of an ISP. Where the problem occurs is at that door — the interconnection point — when the broadband provider hasn’t provided enough capacity to accommodate the traffic their customer requested.”
Despite all that, Netflix also admitted it plans to drop the error messages after the “small-scale test” ends on June 16.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNBC Buffering Blame Game 6-6-14.flv[/flv]
CNBC explains how Netflix content gets to end viewers over a complicated series of Internet connections between Netflix and your ISP. (1:31)


 Subscribe
Subscribe Effective June 1st, all Sprint contract and prepaid customers, as well as those using Virgin Mobile USA and Boost will find their wireless data speeds throttled if Sprint finds they are among the top 5% of users on a congested cell site.
Effective June 1st, all Sprint contract and prepaid customers, as well as those using Virgin Mobile USA and Boost will find their wireless data speeds throttled if Sprint finds they are among the top 5% of users on a congested cell site. Sprint says the throttle will only be activated on “congested cell sites” and will impact WiMAX, 3G and LTE 4G networks owned by the company. Anyone who has used Sprint’s 3G network will discover most urban and suburban Sprint cell towers are frequently congested, judging by the low speeds many customers endure. Rural customers or those served on the edge of a suburban area may never find themselves throttled and Sprint promises once traffic clears, the throttle is shut off.
Sprint says the throttle will only be activated on “congested cell sites” and will impact WiMAX, 3G and LTE 4G networks owned by the company. Anyone who has used Sprint’s 3G network will discover most urban and suburban Sprint cell towers are frequently congested, judging by the low speeds many customers endure. Rural customers or those served on the edge of a suburban area may never find themselves throttled and Sprint promises once traffic clears, the throttle is shut off. Wireless operators are playing up fears that without comprehensive reassignment of wireless spectrum to their businesses, a massive data crunch will slow wireless networks to a crawl.
Wireless operators are playing up fears that without comprehensive reassignment of wireless spectrum to their businesses, a massive data crunch will slow wireless networks to a crawl.

 “We don’t have data caps — and haven’t for about two years,” said Sena Fitzmaurice, Comcast’s vice president of government communications. “We have tested data thresholds where very heavy customers can buy more if they want more — but that only affects a very small percentage of our customers in a few markets.”
“We don’t have data caps — and haven’t for about two years,” said Sena Fitzmaurice, Comcast’s vice president of government communications. “We have tested data thresholds where very heavy customers can buy more if they want more — but that only affects a very small percentage of our customers in a few markets.” Customers who exceed this allowance won’t have their broadband service suspended, they will just get a higher bill, as Comcast charges $10 for each additional 50GB of usage.
Customers who exceed this allowance won’t have their broadband service suspended, they will just get a higher bill, as Comcast charges $10 for each additional 50GB of usage.
 Media ownership laws were relaxed,
Media ownership laws were relaxed, 

