Cadillac prices for some sports networks you pay for whether you watch or not. (Early Summer 2012 – Prices have since risen for some networks)
About 50 percent of your monthly cable television bill covers the cost of live sporting events and the networks that cover them, and the price is not going down anytime soon.
At least $21 of that bill is split between more than 50 national and regional channels covering every imaginable sport.
What customers may not know is that a handful of self-interested giant corporations and major sporting leagues have successfully bid up the price to carry those events using your money.
The Philadelphia Inquirer took a hard look at spiraling sports programming costs last weekend, discovering a lot of cable subscribers are paying for sports programming they will never watch.
“Here is a little old lady who wants to watch CNN,” Ralph Morrow, owner of Catalina Cable TV Co. in Avalon, Calif., a 1,200-subscriber system, told the newspaper. “But I can’t give it to her without $21 a month in sports.”
 In the last 20 months, some of the biggest names in sports programming including Comcast/NBC, Fox, ESPN, CBS, and Turner have agreed to collectively pay $72 billion in TV rights to air pro, college, and Olympic events over the next decade. Costs are anticipated to soar to $100 billion or more once those contracts come up for renewal.
In the last 20 months, some of the biggest names in sports programming including Comcast/NBC, Fox, ESPN, CBS, and Turner have agreed to collectively pay $72 billion in TV rights to air pro, college, and Olympic events over the next decade. Costs are anticipated to soar to $100 billion or more once those contracts come up for renewal.
To cover the growing expense, the pay television industry’s business model insists that every subscriber must pay for sports networks as part of the “basic package” whether they watch or not. Nothing fuels annual rate increases faster than sports programming, and there is no end in sight.
Many contracts specifically prohibit operators from selling their networks “a-la-carte” or in special “sports tiers” that carry extra monthly fees. Any additional costs are quickly passed onto subscribers in the form of regular rate hikes.
Charlie Ergen from Dish Networks suggests at the current pace of sports programming rate increases, it won’t be long before subscribers will face cable bills up to $2,000 a year, just to watch television.
 If you don’t believe him, consider estimates from NPD Group, which predicts the national average for cable TV bills could reach $200 a month as soon as 2020. That is up from the already-high $86 a month customers pay today, after all costs and surcharges are added up.
If you don’t believe him, consider estimates from NPD Group, which predicts the national average for cable TV bills could reach $200 a month as soon as 2020. That is up from the already-high $86 a month customers pay today, after all costs and surcharges are added up.
It was not always this way. As late as the 1980s, the overwhelming majority of marquee sporting events were televised on “free TV” networks like ABC, CBS, and NBC. For decades, major broadcast networks largely had only themselves and the economics of advertiser supported television to consider when submitting bids to win carriage rights.
With the advent of cable sports networks, supported by dual revenue streams from both advertising and subscriber fees, ESPN eventually amassed a back account large enough to outbid traditional broadband networks. If another network moves in on ESPN’s action, the cable network simply raises the subscription fee charged to every cable subscriber to up the ante.
Broadcasters have enviously watched this dual revenue stream in action for several years now, and have recently insisted they be treated equally. Today, cable operators face demands for similar monthly payments from television stations and their network owners. In effect, customers are paying both sides to outbid one another for sports programming.

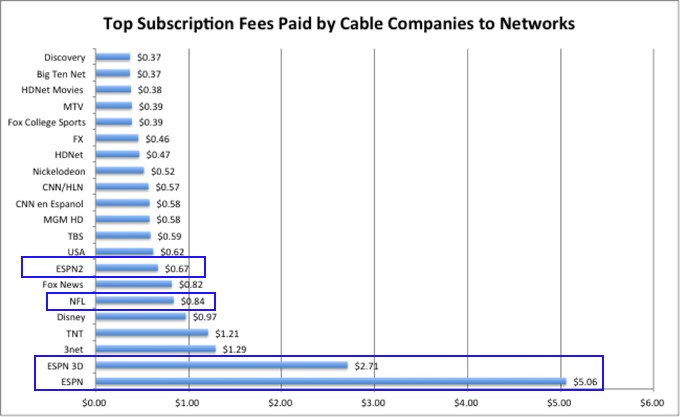
Consider ESPN as a case study in sports programming inflation. From 1989-2012, ESPN rates increased 440 percent. Today, every cable subscriber pays at least $5.13 for ESPN alone. In fact, the actual amount is considerably higher, because ESPN has successfully compelled most cable and satellite programmers to also carry (and pay for) several additional ESPN-branded networks also found on your lineup.
But why do cable companies agree to pay astronomical fees for sports networks, only to later alienate customers with annual rate hikes?
First, because customers watch sports. If a cable company does not carry the network showing a game or team a customer wants to see, that company will likely hear about it, either in a complaint call or cancellation.
Second, watching live sporting events is not easy for a cord-cutter. With fewer games appearing consistently on broadcast television, a cord cutting sports fan risks missing the action only available from a pay television provider.
 In a defensive move, many cable and satellite companies assume the more live sports a provider offers, the lower the chance a sports enthusiast will consider canceling service.
In a defensive move, many cable and satellite companies assume the more live sports a provider offers, the lower the chance a sports enthusiast will consider canceling service.
Cross-ownership also muddies the water for consumers. Comcast, the largest cable operator in the country, has an obvious self-interest loading its systems up with its own sports programming and compelling customers to pay for it.
Comcast owns about a dozen regional sports networks, NBC, NBC Sports Network and Golf.
Other large cable operators are concluding if you can’t beat ’em, join ’em. Time Warner Cable found one lucrative reason to own its own sports networks: its ability to charge competing cable and satellite providers sky high prices to carry that programming.
Time Warner is asking fellow cable, telco, and satellite providers to pay $3.95 a month for its SportsNet English and Spanish language networks, which feature the Los Angeles Lakers. For good measure, the same cable company that routinely complains about being forced to pass on mandatory sports programming costs from others insists companies place both of their sports channels on basic lineups, which guarantees every subscriber will also pay the price for two more sports channels, one in Spanish, they may have no interest in watching.


 Subscribe
Subscribe









