All Verizon Wireless customers, regardless of their data plan, will begin seeing throttled video on their phones, tablets, and tethered devices starting today, Aug. 23.
All Verizon Wireless customers, regardless of their data plan, will begin seeing throttled video on their phones, tablets, and tethered devices starting today, Aug. 23.
The change coincides with the introduction of two new “unlimited” data plans that come with an unprecedented number of tricks and traps in the fine print.
Existing customers can keep their current plan, but will still experience throttled online video speeds to at or below 10Mbps that will make it impossible to view 4K streamed video. On smartphones, the top permitted video resolution will be substantially lower than that.
Verizon claims the new throttled video plans will deliver better service for all of their wireless customers.
“We’re doing this to ensure all customers have a great experience on our network since there is no visible difference in quality on a smartphone or tablet when video is shown at higher resolutions,” a Verizon spokesperson claimed. That refers to video resolution above 720p for phones and 1080p on tablets and laptops.
More likely, Verizon engineers observed video traffic spiking as a result of its unlimited data plan reintroduced in February. Independent speed measurement services detected significant speed and performance hits on Verizon’s wireless network as customers got the most they could out of an unlimited plan that started at $80 a line. Even with Verizon’s soft cap of 22GB before customers were subject to throttled performance was not enough to manage traffic loads, so Verizon has decided to specifically target online video.
Although many streaming services offer customers an option to reduce video resolution to cut back on data usage, customers often ignore the option, particularly if enrolled in “unlimited” data plans. Starting today, Verizon’s network management speed throttle tells streaming services a customer’s connection is limited and cannot sustain the speeds needed for the highest resolution video. The video player reduces video playback resolution on its own as a result. In turn, this can dramatically lighten the traffic load on Verizon’s network.
Verizon’s new plans seem designed for the “light touch” era the current administration’s FCC advocates for telecom regulation, and the carrier’s new plans will give blatant priority for some customers over others, relegating lower paying users into the slow lane while premium plan customers can race on by.
Verizon’s new unlimited data plans for the Net Neutrality-free future are here, scoff critics.
“‘Unlimited’ = ‘Limited’ and ‘Beyond Unlimited’ = ‘Slightly less limited’,” wrote one customer on Verizon’s customer forum.
Verizon put its best face on its new unlimited plans.
“These plans give you the best unlimited choices, but you also get what only Verizon can give you: the best network, the best rewards program, the best way to manage your plan with the My Verizon app and the best selection of phones and devices,” the company said in a press release.
“If this isn’t a sign that Verizon’s network is crumbling from offering unlimited, I don’t know what is!” countered John Legere, CEO of T-Mobile USA.
Here are the new unlimited plans from Verizon Wireless, effective immediately:
 Go Unlimited – $75 (1 line), $65 per line (2 lines), $50 per line (3 lines), $40 per line (4+ lines) – Paperless billing and autopay required (or add $5 per month)
Go Unlimited – $75 (1 line), $65 per line (2 lines), $50 per line (3 lines), $40 per line (4+ lines) – Paperless billing and autopay required (or add $5 per month)
Verizon’s new base unlimited plan automatically throttles your speed when a cell site reports as congested. This plan puts your data usage at a lower priority over other customers and you can experience throttled speeds at any time, regardless of usage. Video streaming is limited to 480p on smartphones and 720p on all other devices. You also get unlimited mobile hotspot, but speeds are permanently locked at a maximum of 600kbps. Unlimited talk and text with no restrictions is included
Beyond Unlimited – $85 (1 line), $80 per line (2 lines), $60 per line (3 lines), $50 per line (4+ lines) – Paperless billing and autopay required (or add $5 per month)
This plan more closely resembles the current unlimited data plan, but costs considerably more. You get unlimited 4G LTE data, but are subject to a speed throttle in congested service areas once exceeding 22GB of usage per month. Video streaming is limited to 720p on smartphones and 1080p on all other devices. No 4K video on any device is allowed. Unlimited mobile hotspot data really means up to 15GB of usage at LTE speed before you are throttled. Unlimited talk/texting included in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
Customers on 2017 Unlimited and Legacy Unlimited Data Plans:
You will be able to keep your current unlimited plans. For those who enrolled in Verizon’s 2017 unlimited plan starting in February, video speed throttles now apply: 720p on smartphones, 1080p on all other devices. You will get a free upgrade to 15GB of mobile hotspot usage, up from 10GB.
For customers on Verizon’s original unlimited plan discontinued several years ago, nothing changes except the introduction of video speed throttles: 720p on smartphones, 1080p on all other devices.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Nearly every wireless provider in the United States is intentionally slowing down your data service, detrimentally affecting smartphone apps and video streaming.
Nearly every wireless provider in the United States is intentionally slowing down your data service, detrimentally affecting smartphone apps and video streaming.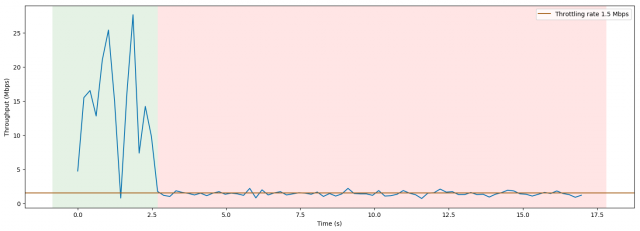



 Despite claims satellite broadband has improved, our readers respectfully disagree:
Despite claims satellite broadband has improved, our readers respectfully disagree: