From writing friendly reports defending Internet Overcharging to the FCC’s new chief economist — D.C.’s revolving door keeps on spinning for Professor Steven Wildman.
The Federal Communications Commission has proved that Washington’s revolving door enjoys perpetual motion with the announcement it hired a new chief economist who just three weeks earlier was peddling his findings favoring usage caps and consumption billing before a National Cable & Telecommunications Association gathering that paid for his research.
Professor Steven Wildman’s move from the cable industry’s go-to-guy for defending Internet Overcharging to a cushy new position at the FCC just weeks after shilling for the country’s largest cable industry lobbying group is shocking even by Washington’s standards.
Remarkably, FCC Chairman Julius Genachowski praised this cheerleader of wallet-pilfering by saying “his deep economic expertise and problem solving abilities” are the perfect fit for an agency pressed with challenging initiatives – like charging you more for your broadband service and calling it “pro-consumer.”
There is no doubt Wildman has deep economic expertise — he has found success penning dubious research bought and paid for by an industry that expects his findings to echo their own talking points. His problem-solving abilities at fixing the facts around the cable industry’s agenda are also unquestioned.
But his research reports aren’t worth wasting your monthly usage allowance to download because they only tell part of the story.
At the December NCTA Connects event, Wildman was the darling of the cable industry echo chamber telling tall tales about the problems of broadband penetration in a country where providers enjoy up to 95 percent gross margins on broadband pricing:
“One of the key mechanisms through which positive welfare effects are realized is the crafting of lower-priced plans for users who otherwise might not take service, while users who have a more intensive demand for broadband are able to contract for more advanced services. We also showed that UBP has flexibility advantages for users whose data service needs vary over time. Because UBP creates an incentive to offer lower cost-lower usage plans to consumers who otherwise could not profitably be served at a unitary price, UBP can be an effective tool for promoting increased broadband penetration in the United States, a role that is enhanced by the fact that low price-low usage options reduce the financial risks to consumers thinking about trying broadband for the first time.”
“Tiered pricing also has benefits for the recovery of shared network costs and for network investment. Whereas investment decisions are also influenced by other factors, including the costs of extending networks, potential revenues, and overall economic conditions, we found that, other things equal, usage tiers will likely contribute to better cash flows and stronger incentives to invest in broadband plant, both to improve the quality of service for current customers and to extend networks into unserved and underserved territories.”
 Wildman does not mention his cable benefactors earn a higher percentage of profit on broadband than oil sheikhs in the Middle East rake in charging $90+ for a barrel of oil. So it is unsurprising his analysis lacks one simple solution providers could use to differentiate their services and enhance broadband penetration: lower the price to compete. He also ignores the fact that true usage pricing would offer consumers a chance to pay only for what they actually consumed during a month, but those plans are not on offer anywhere.
Wildman does not mention his cable benefactors earn a higher percentage of profit on broadband than oil sheikhs in the Middle East rake in charging $90+ for a barrel of oil. So it is unsurprising his analysis lacks one simple solution providers could use to differentiate their services and enhance broadband penetration: lower the price to compete. He also ignores the fact that true usage pricing would offer consumers a chance to pay only for what they actually consumed during a month, but those plans are not on offer anywhere.
Wildman ignores the real industry agenda: monetizing broadband usage to create even higher profits. The cable industry is well on its way, using the enormous market power enjoyed in the current monopoly/duopoly state of consumer broadband to preserve today’s near-extortionist pricing while trying to pick up customers currently unwilling to pay, charging for slightly discounted service that comes with a paltry usage allowance.
The meme that unlimited, flat rate broadband is somehow responsible for America’s broadband-unserved is a popular one at the FCC, where Chairman Genachowski has applauded usage based pricing as an “innovative” experiment that could change how broadband is marketed in the U.S. and promote its expansion.
While those in D.C. may live in a bubble populated by industry lobbyists, others do not.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/NCTA Connects The Pros and Cons of Broadband Peak Load Pricing Dec 2012.flv[/flv]
Message Confusion: While some in the cable industry still advocate usage pricing and caps as a matter of “fairness” and as a salve for peak time congestion, today’s advocates of usage-based billing appearing at a cable-industry event in December admit congestion is simply no longer a problem on wired networks. Sandvine’s Dave Caputo and Professor David M. Lyons of Boston College Law School dismiss the notion of congestion-based pricing only during peak usage, arguing congestion is no longer the real issue driving usage caps. That is why everyone must be subjected to higher priced, usage-capped broadband no matter what time of day they use the network. (3 minutes)
The inevitable outcome of “differentiated pricing” is charging consumers more to access popular websites, as is already the case in countries like Colombia.
Wildman argues that like car manufacturers that offer many different models ranging from basic to well-appointed with luxury extras, providers should be free to offer different types of plans to consumers.
Wildman’s auto analogy fails because consumers have more than a dozen different manufacturers to choose from, each making a range of different models. For broadband, the overwhelming majority of Americans have two choices: the cable and phone company. Unlike auto manufacturers that respond to consumer demand, broadband providers are hellbent on eliminating the overwhelmingly popular flat rate, unlimited option in favor of mandatory usage pricing and/or usage caps. It would be like telling auto-buyers that their Honda Accord, Toyota Camry, or Chevy Malibu no longer met the needs of manufacturers. Instead, you have one choice: the Toyota Yaris. But you can get it with heated leather seats, so what’s the problem?
Wildman also ignores the fact providers already sell different plans, based on different speeds. Customers with only light web use can select a cheaper, lower speed tier and never notice the difference. Heavier users buy up into premium speed tiers, paying higher prices to cover their additional usage and expectations of performance.
Providers have spent the last few years trying to justify adding a usage component to the pricing equation and Wildman is perplexed by public policy and consumer groups overwhelmingly hostile to plans that would leave current pricing largely intact and add an artificial usage cap. Considering who pays for his research, this is not too surprising.
Wildman’s style of “innovation” already exists in countries like Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and in parts of Europe allowing everyone to witness what actually happens when these pricing schemes gain a foothold. Usage-based pricing has successfully boosted the profits of providers but has done nothing to expand rural broadband networks or offer customers big savings. When providers gorge on profits made possible in uncompetitive markets, the money goes straight into bank accounts or back to investors, not into capital spending to improve service or expand into areas deemed unprofitable to serve.
Customers despise usage caps so much that in Australia and New Zealand, the government has partially taken over rebuilding infrastructure with new fiber to the home networks and promoting international capacity expansion that will eventually banish usage pricing for good. In western Canada, Shaw Cable heard so much condemnation about usage caps during its listening tour, it greatly relaxed them. (The fact its biggest competitor Telus barely enforces their own caps didn’t hurt either.)
In the rest of Canada, independent ISPs have found a growing niche selling plans with considerably larger usage allowances or flat rate access. How did dominant providers like Bell (BCE) respond? They asked regulators to force the competition to stop selling flat rate service.
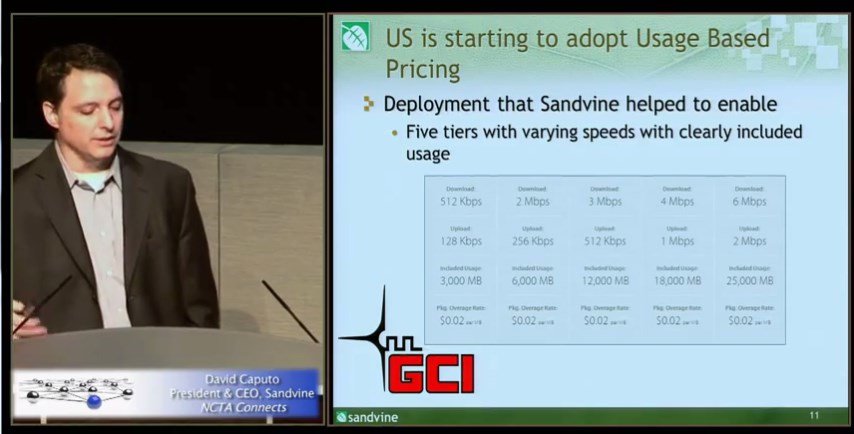
How Sandvine helps providers “innovate.” Alaska’s GCI implemented its draconian caps and overlimit fees using Sandvine’s Internet Overcharging technology.
Wildman’s report flies in the face of reality, and every so often the cable industry itself admits as much. Take the word of Suddenlink president and CEO Jerry Kent, who runs a largely rural cable company that launched its own Internet Overcharging scheme:
“I think one of the things people don’t realize [relates to] the question of capital intensity and having to keep spending to keep up with capacity,” Kent said. “Those days are basically over, and you are seeing significant free cash flow generated from the cable operators as our capital expenditures continue to come down.”
Unsurprisingly, that sentiment did not make it into Wildman’s analysis either.

Wildman
Financial reports from providers that have usage caps and those that don’t show the same remarkable trend: broadband expenses are way down, capital intensity is well within expected norms, and cable operators are not pouring their profligate earnings into expanding rural broadband.
That makes Wildman the consummate team player, and hardly the best choice for taxpayers who will cover his salary for a few years before he takes another trip through the revolving door back to his industry friends. When Americans wonder why Washington doesn’t seem to be living in the reality-based community, this is why. We can hardly expect Mr. Wildman to represent our interests when he has spent the last several years representing an extremely profitable industry reviled for its overcharging, poor service, and scheming, and will be more than welcomed back if he remembers his friends while working at the FCC.
This latest move represents another disappointment from Chairman Julius Genachowski, who increasingly appears to be warming up to a telecommunications industry he used to aggressively oversee at the start of his tenure.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/NCTA Connects The Evolving Internet – Patterns in Usage and Pricing Dec 2012.flv[/flv]
Three weeks ago, the Three Musketeers of Internet Overcharging appeared at a cable industry-sponsored event promoting usage caps and consumption billing. Sandvine CEO Dave Caputo makes his living scaring providers and consumers about Internet growth and (conveniently) selling the equipment that manages the traffic “tsunami” with speed throttles and usage limits. Professor David M. Lyons of Boston College Law School calls usage pricing “second degree price discrimination,” a term he hopes the industry will rebrand into something less ominous and obvious. He argues selling broadband at incremental costs will never recover “fixed costs” for networks the cable industry itself admits have already been largely paid off. Professor Steven Wildman, now on the way to the FCC as its new chief economist, peddles research bought and paid for by the cable industry. They got their money’s worth. (1 hour, 9 minutes)



 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Wildman does not mention his cable benefactors earn a higher percentage of profit on broadband than oil sheikhs in the Middle East rake in charging $90+ for a barrel of oil. So it is unsurprising his analysis lacks one simple solution providers could use to differentiate their services and enhance broadband penetration: lower the price to compete. He also ignores the fact that true usage pricing would offer consumers a chance to pay only for what they actually consumed during a month, but those plans are not on offer anywhere.
Wildman does not mention his cable benefactors earn a higher percentage of profit on broadband than oil sheikhs in the Middle East rake in charging $90+ for a barrel of oil. So it is unsurprising his analysis lacks one simple solution providers could use to differentiate their services and enhance broadband penetration: lower the price to compete. He also ignores the fact that true usage pricing would offer consumers a chance to pay only for what they actually consumed during a month, but those plans are not on offer anywhere.