The National Association of Broadcasters is warning a Congressional plan proposed on behalf of the wireless industry could force every broadcast station in Detroit off the air, and drive at least one network affiliate in many northern U.S. cities along the Canadian border to “go dark” if the plan is adopted.
The FCC’s National Broadband Plan contains provisions now on Capitol Hill to recapture spectrum currently used by free over-the-air television stations and provide it to wireless providers to bolster mobile broadband and cell phone networks. Lawmakers expect the wireless industry will pay up to $33 billion for the lucrative spectrum, to be shared with vacating broadcasters and the U.S. Treasury.
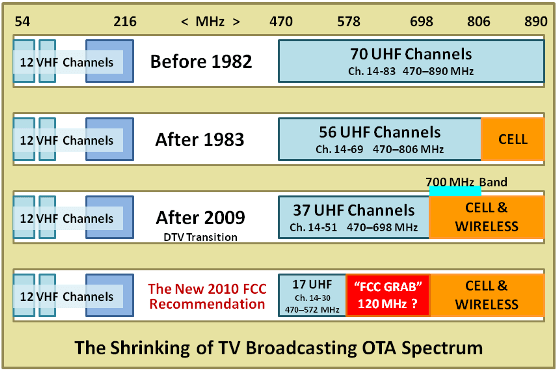
But the NAB says the FCC plan goes too far, forcing stations to vacate UHF channels 31-51 to crowd into the remaining channel space of 11 VHF channels (2-13) and 17 UHF channels (14-31). According to a study conducted by the broadcasting lobby, there is simply not enough remaining channel space to accommodate 1,735 U.S. stations, forcing at least 210 to sign off, permanently.
Because of agreements with the Canadian government to protect American and Canadian stations from mutual interference, the results could be devastating for northern cities along the U.S.-Canadian border. The worst impact would be in Detroit, Michigan where the NAB predicts every local station would have to leave the airwaves.
The cities of Buffalo, Seattle, Syracuse, Cleveland, Spokane, Rochester and Watertown, NY and Flint, Mich. would likely lose at least one major network affiliated-full power station each. At least 73 stations in the top-10 largest television markets would be forced off the air, unable to find appropriate channel space in the remaining available spectrum. Hundreds of stations would be forced to change channels and potentially reduce power and coverage areas to protect stations sharing the same channel number in adjacent cities.
“If the FCC’s National Broadband Plan to recapture 20 more TV channels is implemented, service disruption, confusion and inconvenience for local television viewers will make the 2009 DTV transition seem like child’s play,” said NAB President Gordon Smith. “NAB endorses truly voluntary spectrum auctions. Our concern is that the FCC plan will morph into involuntary, because it is impossible for the FCC to meet spectrum reclamation goals without this becoming a government mandate.”
Broadcasters are feeling a bit peeved at the federal government for repeatedly returning to sell off a dwindling number of channels for other uses. The original UHF dial included channels 14-83, but over the years the highest channel number has dropped to 51, mostly for the benefit of the cell phone industry. Now they’re back for more, seeking channels 31-51 for wireless broadband and mobile telephony.
The cell phone industry wants broadcasters to “voluntarily” give up their channel space and reduce transmitter power so more stations can share the same dial position in nearby cities. But that could leave fringe reception areas in rural communities between cities without over-the-air television reception, and make free television more difficult to watch without a rooftop antenna.
The NAB called on the FCC to immediately make public its analyses of the broadband plan’s potential negative impact on viewers of free and local television.
“We’ve waited patiently for over a year for FCC data on how the Broadband Plan impacts broadcasters, and more importantly, the tens of millions of viewers who rely every day on local TV for news, entertainment, sports and lifeline emergency weather information,” said the NAB’s Smith. “Even Congress can’t get information from the FCC. All we are seeking is more transparency. We have but one chance to get this right if we are to preserve future innovation for broadcasters and our viewers.”
[flv width=”512″ height=”308″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/NAB Free TV Spot.f4v[/flv]
The National Association of Broadcasters is distributing this ad to local broadcasters to air on their stations to inform viewers about the spectrum controversy. (1 minute)
The consumer wireless handset lobby does not deny the plan will leave Americans with fewer channel choices, but they believe that will come from corporate station owners voluntarily shutting down stations for profit.
“The study presumes an unrealistic scenario in which every single existing TV station continues to operate over-the-air. However in the event of incentive spectrum auctions, it is highly likely numerous stations will capitalize on their spectrum assets by exiting the business or sharing resources,” said Consumer Electronics Association senior vice president for government affairs Michael Petricone.
Petricone believes the number of Americans spending time with broadcast television is dwindling, and less important than the wireless industry’s spectrum woes.
“Our nation faces a crisis as demand for wireless spectrum will soon outstrip supply,” said Petricone. “Meanwhile, the number of Americans relying purely on over-the-air TV is less than 10 percent, according to both CEA and Nielsen market research. Incentive auctions would be a financial windfall for broadcasters, free up the spectrum necessary for the next generation of American innovation to move forward and bring in $33 billion to the U.S. Treasury.”
The cellular industry’s top lobbying group CTIA was more plain: it’s survival of the fittest.
“Since spectrum is a finite resource, it is vital that the U.S. government ensures the highest and best use of it,” said CTIA vice president Chris Guttman-McCabe.
[flv width=”512″ height=”308″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/NAB Explains Spectrum.flv[/flv]
The NAB explains the concept of “spectrum” — or ‘the airwaves’ to consumers and what a major reduction in UHF channel space would mean for “free television.” (3 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe