Several million Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers in New York, California, Texas and Florida will lose CBS programming this Wednesday at 5pm if the three companies do not iron out their differences in contract renewal negotiations.
Several million Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers in New York, California, Texas and Florida will lose CBS programming this Wednesday at 5pm if the three companies do not iron out their differences in contract renewal negotiations.
CBS and Time Warner Cable have taken their fight public over retransmission consent talks that have left the two sides far apart. The cable operators say CBS has gotten greedy asking for as much as 600 percent more than what the cable companies paid under the old agreement that expired in June. CBS says the fact its stations have never been thrown off cable systems before is proof that their terms are reasonable.
Cable analysts say CBS’ old agreement cost the two cable operators between 75 cents and one dollar a month per subscriber. Most believe CBS is now asking for between $1-2 a month per subscriber to renew the agreement.
 CBS wants to be paid at levels comparable to the most popular cable networks and believes the fact the network is now number one in the ratings delivers negotiating power. CBS has not made its aggressive position on carriage fees a secret. Executives have told investors it plans to quadruple cable and satellite fees over the next four years with a goal to raise an extra $1 billion. Wall Street analysts have recommended the stock to investors and its value has risen at least 65% in the past year.
CBS wants to be paid at levels comparable to the most popular cable networks and believes the fact the network is now number one in the ratings delivers negotiating power. CBS has not made its aggressive position on carriage fees a secret. Executives have told investors it plans to quadruple cable and satellite fees over the next four years with a goal to raise an extra $1 billion. Wall Street analysts have recommended the stock to investors and its value has risen at least 65% in the past year.
But Time Warner Cable spokeswoman Maureen Huff believes CBS is asking for too much.
“Broadcasters have already hit customers with 84 broadcaster blackouts in the past 18 months,” Huff said in a statement. “Les Moonves, president and CEO of CBS, has always been outspoken about the programming fees he believes he deserves. He has said ‘the sky is the limit’ when talking about the price he thinks he deserves for his CBS stations, and he clearly means it. He doesn’t seem to care about our customers’ budgets or the going rates for CBS programming.”
But critics contend Time Warner Cable does not come to the table with clean hands on the issue of expensive carriage fees. Time Warner Cable seemed less concerned about the skyrocketing costs of cable programming when it set high asking prices for TWC-owned regional sports networks SportsNet and TWC Deportes.
CBS says it deserves at least as much as what Time Warner Cable pays Time Warner Entertainment’s TNT, which reportedly charges at least $1 a subscriber.

[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBS Time Warner Cable Customers about to lose CBS 7-20-13.mp4[/flv]
CBS is now running this ad in New York City warning Time Warner Cable customers they are about to lose WCBS-TV, the local CBS affiliate. (1 minute)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Time Warner Cable CBS Outrageous Fees 7-20-13.mp4[/flv]
Not so fast, says Time Warner Cable. CBS wants 600% more for WCBS, driving up the price customers pay for cable television. (1 minute)
If no agreement is reached, CBS expects customers will lose access to its network-0wned affiliates starting at 5pm Wednesday afternoon. Although most media reports are focused on the fact CBS stations in New York, Los Angeles, and Dallas are affected, not all are CBS affiliates. In fact, customers in a few other cities will also find their CBS-owned stations dropped:
- New York: WCBS (TWC)
- Los Angeles: KCBS, KCAL (TWC)
- Dallas-Ft. Worth: KTVT, KTXA (TWC)
- St. Petersburg-Tampa: WTOG (Bright House)
- Riverhead (Long Island): WLNY (TWC)

Some Bright House customers are also affected by dispute.
The Wall Street Journal reported that Time Warner Cable and Bright House would also drop Showtime from lineups across the country in a retaliatory move, but this was not confirmed by either cable company.
Station owners are seeking higher retransmission consent payments from cable and satellite operators to establish additional sources of revenue. Pay television customers ultimately foot the bill with higher priced cable television service. As prices rise, pay television operators increasingly worry customers will either defect to a competitor or cut the cable television cord for good. Some operators are adopting a tougher stance, willing to drop stations from the lineup.
Most station owners believe the larger number of stations they own or control, the less likely a cable operator will actually throw a station off the lineup. This month, Wisconsin-based Journal Broadcast Group is threatened with the loss of nearly half of its 15 television stations on Time Warner Cable systems in Wisconsin, Nebraska, and California:
- WTMJ Milwaukee
- KMTV Omaha
- WGBA Green Bay/Appleton, Wisc.
- WACY Green Bay/Appleton, Wisc.
- KMIR Palm Springs, Calif.
- KPSE Palm Springs, Calif.

Bigger is better
Some stations have been off the lineup since July 10 in some markets, with digital sub-channels first removed by Time Warner Cable in a warning shot in others.
Larger station owners like Sinclair Broadcast Group have felt less threatened. The more stations under negotiation, the more leverage station owners have in contract renewal talks.
Sinclair is further boosting its position in the local TV station business, spending almost $2 billion in the last 18 months buying 81 more television stations.
Sinclair owns and operates, programs or provides advertising sales services to 140 television stations in 72 markets nationwide. They are a force to be reckoned with. Despite angry words over the station owner’s asking price, both Dish Networks and DirecTV renewed their carriage agreements with Sinclair without disrupting viewing.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WSJ Retransmission Dispute TWC CBS 7-20-13.flv[/flv]
The Wall Street Journal’s “Moneybeat” looks into the retransmission dispute between CBS and Time Warner Cable and what impact it may have on viewers. (5 minutes)
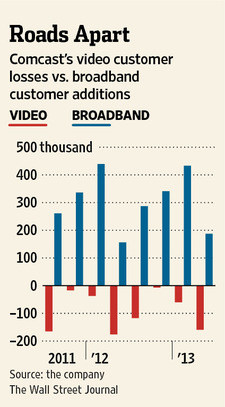
 Time Warner Cable has added two new lobbying firms, despite running up nearly $4 million in lobbying expenses during the first half of 2013, to advocate a hands-off policy on broadband and changes in how television stations get compensated from cable providers after a month-long dispute with CBS helped fuel subscriber losses.
Time Warner Cable has added two new lobbying firms, despite running up nearly $4 million in lobbying expenses during the first half of 2013, to advocate a hands-off policy on broadband and changes in how television stations get compensated from cable providers after a month-long dispute with CBS helped fuel subscriber losses.



 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Several million Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers in New York, California, Texas and Florida will lose CBS programming this Wednesday at 5pm if the three companies do not iron out their differences in contract renewal negotiations.
Several million Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers in New York, California, Texas and Florida will lose CBS programming this Wednesday at 5pm if the three companies do not iron out their differences in contract renewal negotiations. CBS wants to be paid at levels comparable to the most popular cable networks and believes the fact the network is now number one in the ratings delivers negotiating power. CBS has not made its aggressive position on carriage fees a secret. Executives have told investors it plans to quadruple cable and satellite fees over the next four years with a goal to raise an extra $1 billion. Wall Street analysts have recommended the stock to investors and its value has risen at least 65% in the past year.
CBS wants to be paid at levels comparable to the most popular cable networks and believes the fact the network is now number one in the ratings delivers negotiating power. CBS has not made its aggressive position on carriage fees a secret. Executives have told investors it plans to quadruple cable and satellite fees over the next four years with a goal to raise an extra $1 billion. Wall Street analysts have recommended the stock to investors and its value has risen at least 65% in the past year.


 Free TV? Not quite.
Free TV? Not quite. Would you be surprised to learn a company with just a basic, outdated website replete with spelling and grammar errors holds at least 760 television station construction permits and licenses and just wrote a check for $46.5 million to buy 52 more stations from nine different owners, with plans to shut every last one of them down in the future?
Would you be surprised to learn a company with just a basic, outdated website replete with spelling and grammar errors holds at least 760 television station construction permits and licenses and just wrote a check for $46.5 million to buy 52 more stations from nine different owners, with plans to shut every last one of them down in the future? CTB Spectrum Services
CTB Spectrum Services