Consumers across 13 states impacted by the proposed Verizon sale to Frontier Communications, as well as existing Frontier customers, should tell regulators to reject the deal.
Those of us living and working in Rochester, New York are extremely familiar with Frontier Communications. For more than 100 years, Rochester Telephone Corporation provided excellent, independent telephone service to Rochester and a significant part of the Genesee Valley. The company had a reputation for excellent reliability and charged rates considerably lower than New York Telephone, a Bell subsidiary, in other upstate cities like Buffalo and Syracuse. In 1995, Rochester Telephone was renamed Frontier Communications, because the company wanted to position itself as something more than just a phone company.
Frontier was acquired in 2001 by Citizens Communications of Stamford, Connecticut, who has provided service ever since. Ironically, that company thought Frontier was a better name than the one they had used for decades, and Citizens renamed themselves Frontier Communications in 2008.
Today, Frontier Communications serves just under three million customers, primarily in suburban and rural communities in 24 states.
Since Citizens acquired Frontier, and its largest operating service area in metropolitan Rochester, the company has made some changes to the local telephone network. Fiber optic connections are now common between their central offices and smaller “satellite” central offices. A local wi-fi network was installed in association with Monroe County, in part as a political maneuver to stop municipally owned and operated affordable wi-fi networks from getting off the ground. As a concession to the county, a much smaller “free” wi-fi network was also included. (See below the jump for video news coverage of Frontier’s promises vs. reality)
The company’s broadband service relies on ADSL technology delivered by traditional copper telephone wiring, providing service in Rochester at speeds up to a theoretical 10Mbps. Actual speeds vary tremendously depending on the distance between your home or business and the telephone company central office serving it. In most smaller communities, speeds are far lower. In Cowen, West Virginia, Frontier markets broadband service at just 3Mbps, a typical speed for Frontier’s smaller service areas.
Unfortunately, Frontier has shown no initiative to move beyond offering traditional DSL service to its customers, including those in western New York. Across other New York State cities, Verizon is taking a far different approach. In larger communities, it is aggressively installing fiber optic wiring to both homes and businesses. Verizon FiOS positions the company to effectively compete against their traditionally closest competitor – cable television. For several years, cable operators have offered a better deal for its “digital phone” service, which works with existing home phones but delivered over cable TV lines, often charging less than a traditional phone line, and cable throws in free long distance on many of its plans.
The ubiquitous cell phone has not helped. Many younger Americans can’t understand why they would want to bother getting a traditional phone line, when the mobile phone in their pocket works just fine, and they can take it with them wherever they go. The result has been a steady erosion of traditional “wireline” phone lines, and a corresponding decline in the revenue earned from the service in many areas.

The Communications Workers of America contract Verizon promises with reality for consumers impacted by earlier deals. (click to enlarge)
In September Verizon CEO Ivan Seidenberg told a Goldman Sachs investor conference that the wired phone line business was effectively dead. Seidenberg recognized that trying to guess when the company would stop losing “landline” customers was like guessing when a dog will stop chasing a bus. In other words, the future of Ma Bell is not delivering phone service — it’s deploying advanced networks that are capable of providing customers with video, broadband, and phone service across one wire, preferably a fiber optic one. Those that can manage the transition will succeed, those who cannot or won’t will face a steady decline to obsolescence.
There is only one major problem — it costs a lot of money to rewire entire communities, much less states, with fiber optic wiring. It’s like building a phone network from scratch. A company contemplating such a challenging undertaking starts by asking how much it is going to cost and when will it profit from its investment. Many on Wall Street don’t like either question because of the up front cost, and are even less happy with the prospect of taking the long view waiting for those costs to be recouped from customers.
To date, Verizon is the most aggressive major phone company in the nation building a pure fiber optic system in its larger service areas. AT&T, which provides phone service in many states, has taken a more cautious approach using a hybrid fiber-copper wire design they market as U-verse. A handful of independent phone companies and municipally owned providers have undertaken to wire fiber optics to the home as well, so they can sell video, telephone and broadband service to their customers.
A major challenge confronts phone companies servicing more distant suburban and rural phone customers, often living far apart from one another in sparsely populated regions. It costs more to service these customers, and the potential revenue gained is often not as great as what can be earned from their urban cousins. Verizon doesn’t see many rural customers as part of their future business plans and have begun to systematically sell some areas off to other phone companies, usually in tax-free transactions. One company that sees an ambitious future in serving rural America is Frontier Communications. For them, finding a niche among the big boys gives them safety and security, particularly in areas that don’t have a cable competitor (or any competitor at all).
Frontier’s acquisition strategy is to sell regulators and the public on the idea that allowing Frontier in guarantees a much better chance for broadband service to reach the communities Verizon skipped over. Their argument for success in a business seeing steady declines in customers is that broadband service will stem the tide, and help them remain profitable. More than doubling their size with the acquisition of Verizon’s latest castoffs means more opportunity to market broadband service to those underserved communities. Frontier argues it can be a more nimble player than Verizon because it has marketing and service experience in rural communities previously ignored by Verizon.
Frontier’s ability to provide broadband service is not the most important question. More important is how Frontier will define broadband and at what speed. Also critically important is how Frontier will be prepared to deliver the next generation broadband platform that other communities will see with speeds up to 100Mbps, often on fiber optic networks.
Frontier’s reliance on ADSL technology, which worked fine for 1990s Internet connectivity, is increasingly falling behind in the speed race, and for much of the next generation of online content, speed will matter very much.
Unfortunately, the track record for the success of these spinoffs has been universally lousy for consumers and for many employees who live and work in the impacted communities. Promises made quickly become promises delayed, and later broken as companies like Hawaii Telecom and FairPoint tried to integrate former Verizon operations into their own. Service outages, billing errors, confusion, and finally a mass exodus by customers looking for better alternatives has been the repeated result. The faster customers depart, combined with the enormous debt these transactions create for the buyer, the faster the journey ends in Bankruptcy Court. There is nothing about the Frontier deal proposal that suggests their experience will be any different.
Shouldn’t Three Strikes Mean You Are Out?
Consumers should tell state regulators they should pay careful attention to the failures Verizon has left in its wake from previous deals:
- FairPoint Communications, which assumed control of phone service in Maine, New Hampshire and Vermont just last year declared bankruptcy this morning, even now still plaguing customers with billing and service problems. The company choked on the debt it incurred from financing the deal. Before this morning’s bankruptcy, their stock price had lost 95% of its value, and customers were leaving in droves, only accelerating the company’s demise. FairPoint thought it could integrate Verizon’s byzantine billing system into its own. Thinking and doing turned out to be two entirely different things. Frontier has experience integrating other small independent phone companies into its billing system, but now faces the same prospect of dealing with Verizon’s own way of doing everything, and for twice the number of customers Frontier serves today.
- Hawaii Telecom and its 715,000 customers were dumped by Verizon in 2005. Once again, transition issues plagued the post-sale experience for those customers, and almost a quarter fled the company over three years. Last December, Hawaii Telecom declared bankruptcy.
- Verizon’s yellow pages unit was also thrown overboard by the company to Idearc in November 2006. Saddled with $9.5 billion in debt and interest payments representing almost one quarter of the entire company’s revenues, Idearc finally had enough in March 2009 when it also declared bankruptcy.
The deal between Verizon and Frontier could easily follow the same path, as Frontier gets loaded down with massive debt financing the purchase, and has to immediately provide better service than Verizon did, or face a stampede of customers heading for the exit. The impact of a debt-laden Frontier could be felt by more than just the newcomers. Existing Frontier customers could also be impacted as the company turns its attention to a potentially lengthy integration process.
The Promise of Anemic Broadband, The Fiber Myth & The 5GB Acceptable Use Policy
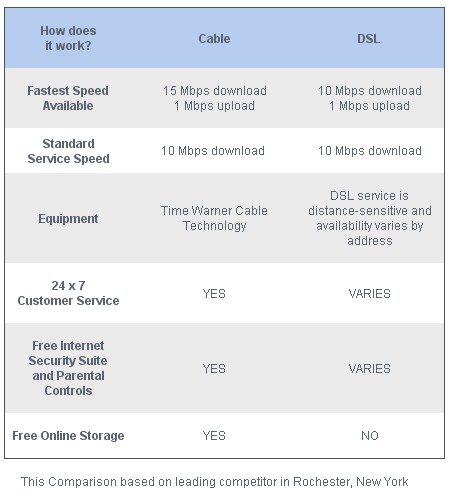
Time Warner Cable competes effectively against Frontier DSL in the phone company's largest service area
Frontier’s plan to bring broadband to a larger number of customers is a noble gesture, particularly for households that currently do not receive any broadband service. Unfortunately, a short term gain of what will likely be 1-3Mbps DSL service will leave these communities behind in the next few years as broadband speeds accelerate far faster than what Frontier is prepared to provide.
Some press accounts in West Virginia have left residents with the impression fiber optic service will reach their individual homes should Frontier be successful in purchasing Verizon’s assets. There is no evidence to suggest this is true.
In earlier deals, these kinds of rumors started when companies advocating the sale staged press-friendly events announcing a fiber connection between hospitals, schools, or community centers, allowing the media to give the impression there would be fiber upgrades for all… if the deal gets approved. In the case of Frontier, they have suggested they will continue work on Verizon’s FiOS system in the communities where construction was already underway. That’s an important distinction for the millions of customers who don’t live in those communities. Verizon’s FiOS network that is part of this transaction serves less than 70,000 residents.
Residents should consider what possibility their community has of obtaining this type of advanced service when Frontier refuses to provide anything comparable in their largest service area – Rochester, New York.
If they are not doing it in Rochester, do you really believe they will do it in your community?
The company certainly has a competitive need to provide such service in our city where Time Warner Cable has accelerated speeds beyond what Frontier is capable of providing. Indeed, Time Warner Cable officials tout their largest number of new Road Runner broadband sign-ups comes from departing DSL customers who are fed up with the anemic, inconsistent speeds offered by this aging technology.
In the town of Brighton, I gave Frontier DSL service a try this past spring. The company promises up to 10Mbps of service to my area, which is less than 1/2 mile from the city of Rochester, and literally just a few blocks from the town’s business center. After installation, the company was only able to provide me with service at 3.1Mbps, just less than one-third of the speed marketed to local residents. Even more surprising was the fact they charged a higher price for that service (including taxes, fees, and modem rental charge) than their competitor, Time Warner Cable.
This website was founded after Frontier inserted language into its Acceptable Use Policy defining “reasonable” broadband usage at just five gigabytes per month. That’s right, the same limit your mobile phone provider applies to their wireless broadband service. Viewing one HD movie over Frontier’s DSL service would put you perilously close to unreasonable use.
Are consumers willing to give up unlimited Verizon DSL service for a company that refuses to drop a 5GB acceptable usage definition from their terms and conditions?
America is on the threshold of 50-100Mbps broadband service, with some communities already enjoying those speeds. If your community isn’t served by a competing provider, do you want to limit your future to yesterday’s DSL technology, and then told it is inappropriate for you to actually use it beyond five gigabytes per month?
The Billing and Customer Service Nightmare
The days of local customer service are over with Frontier. Back during the days of Rochester Telephone, there were several occasions when a local customer service representative would recognize me by name. Those days are long gone. Now, a good deal of Frontier’s customer service is handled by a call center in DeLand, Florida. While the representatives mean well, experiences with them suggest many are not well equipped to understand and consistently market Frontier’s products to existing customers. Pile on more than double the number of new customers, and the problems are likely to become much worse.
Frontier has personally plagued me with billing errors this past year, gave inconsistent and inaccurate answers to pricing and service inquiries, and created major runaround hassles to correct them. From the DSL self-install kit that never arrived (requiring me to visit a local office to pick one up myself), to the impenetrable and inaccurate bills that resulted, the company could not correct the problems without consulting someone with supervisor status. I canceled service within the month.
Customers signing up for service have been pressured into “peace of mind” agreements that lock customers into long term contracts that automatically renew unless the customer actively cancels them (and is certain the request to cancel was processed correctly.) Frontier has been fined twice by the New York State Attorney General for “misleading advertising and marketing tactics,” once in 2006 and again just a few weeks ago. Some customers are now waiting for substantial refunds ranging from $50-400 dollars for “early termination fees” charged when they tried to cancel service.
Are you comfortable knowing some customers have been inappropriately placed on a one to three year contract without their full informed consent, and billed hundreds of dollars when they tried to cancel?
The Art of the Deal
By no means will a Verizon-Frontier transaction be the last. As the industry continues to consolidate around a dwindling number of wired phone line customers, it’s a safe bet there will be more phone customers thrown away by the bigger players. Nothing guarantees Frontier itself will be freestanding when the consolidation wave ends. While these deals may make sense for some shareholders and company executives, they often don’t for local experienced employees who know the network and how to provide quality service. They never have for consumers who will always have to foot the bill to pay off these transactions and have to live with the company trying to integrate Verizon’s bureaucracy with their own.
What is the ultimate price to pay? For employees — their jobs, and as FairPoint employees are discovering today, those workers are being asked to pay the price for management mistakes. In West Virginia, some of the most experienced Verizon employees are getting out with their pensions intact, not willing to take a chance on Frontier. For customers living with FairPoint, horror stories of weeks without service, $400 phone bills for service long since canceled, company technicians that cannot find the customer even when they are located right next door to the phone company, and broken promise after broken promise continue.
Some consumer groups and local workers correctly predicted, in each instance, the horrific outcome of these kinds of deals. Their uncanny knack to correctly predict disaster contrasts with company marketing, lobbying, and astroturf efforts that promise the sky and tell each successive news reporter covering the latest atrocity that “things are getting better” and “will be fixed soon.” Unfortunately for too many customers, the fix has to come from a judge in Bankruptcy Court.
The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers who repeatedly warned about the perils of FairPoint, now warns state regulators about Frontier, and direct attention to the numbers:
If the transaction is approved, Frontier management will have to deal with a 300% increase in access lines (from 2.2 million access lines now to 7 million after the sale) and a 200% increase in employees (from 5,700 employees now to 16,700 after the sale).
Frontier’s debt will increase from $4.55 billion to $8 billion—an increase of over $3.4 billion. Servicing this debt will mean less money for infrastructure, service quality, and high-speed internet build out.
While Frontier argues that somehow this deal will make it stronger, the issue for the states being sold is how much weaker it will make the operations in those states.
The leverage ratio is one way to measure the financial health of a company. The leverage ratio is calculated by taking net debt and dividing it by earnings (before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization). The leverage ratio for the states being sold will increase from 1.7 immediately before the transaction closes to 2.6 after the sale. The entire deal revolves around Frontier’s ability to cut its operational expenses by $500 million or 21%.
This is significantly greater than the 8-10% cut that FairPoint hoped to achieve—and much of these savings were to be generated from replacing Verizon’s network and back-office systems. Yet, Frontier states that all of the operations except for West Virginia will continue on Verizon’s existing systems—for which Frontier will pay a fee.
Where will Frontier generate the savings—from reduced service quality, workforce, or maintenance of the communications infrastructure? In spite of brave talk from Verizon and Frontier, as recent events have demonstrated, obtaining financing for a transaction this size can be difficult. Frontier does not currently have financing for the additional debt it will take on for this transaction.
As an existing Frontier customer, I’d like an answer myself.
<
p style=”text-align: center;”>
Watch these two Wall Street guys talk about the previous Verizon deals that threw customers under the bus. Plenty of praise for the skilled deal maker Verizon CEO Ivan Seidenberg, and no concern for you, the consumer and telephone customer impacted by a deal that got a few people very rich and left you with a bankrupt phone company. (3 minutes)
It’s Not Worth the Risk
Unfortunately, for too many rural Americans impacted by this deal, there is only one phone company. Cable television is not in their future, and in mountainous regions like West Virginia, wireless phones may not be suitable as a phone line replacement. Risking 100 years of solvent phone service on a deal that could ultimately follow earlier deals into bankruptcy is not worth the risk. The nightmares of converting operations from one provider to another is a hassle consumers should not have to face.
For decades, you faithfully paid your Verizon telephone bill and made the company the telecommunications powerhouse it is today. Now they want to abandon you because, frankly, you just aren’t important enough to them anymore. It doesn’t have to be this way. State regulators can tell Verizon they need to make different plans — by forgetting about trying to cash in on a deal that is good for them and bad for you, and by staying put and providing consumers with the same kinds of network upgrades they are building in communities across the country.
Unfortunately, Frontier before this deal was ill-equipped to embark on the kind of investment necessary to provide fiber optic broadband connectivity to its customers. Now pile on billions of additional debt and the challenge of trying to more than double their size and integrate diverse phone networks in 13 different states and ponder what the chances will be for fiber service after the deal is done. Far more likely for residents is a company that will rely on slow speed DSL service, providing “good enough for them” broadband for the indefinite future.
Take Action!
As has been the case with Hawaii Telecom and FairPoint, naive regulators believed the false promises and approved earlier deals, and are frankly responsible for part of the blame. Face-saving telecommunications regulators in New England initially even tried to cheerlead for FairPoint as they stumbled through one customer service nightmare after another. Too late, they realized the grim reality that their approval saddled their states with a phone company totally unequipped to do the job.
Consumers who do not want a repeat performance can contact their state representatives and tell them to put pressure on each state’s public utility commission to reject the deal. You should also contact your state’s public utility commission yourself.
No amount of concessions and written agreements will make a difference if that phone company ends up in financial distress and takes a walk to Bankruptcy Court. Regulators should not even bother trying, after witnessing the debacle with FairPoint.
In your polite, persuasive and persistent communication with state officials, let them know:
- We’ve been down this road with Verizon before, with FairPoint Communications and Hawaii Telecom, leaving a litany of broken service promises, unfulfilled broadband commitments, unacceptable billing mistakes, and poor quality customer service. In both instances, customers fled and the companies ended up in bankruptcy;
- Frontier has been unable or unwilling to wire its largest service area, Rochester, New York, with the advanced fiber connectivity that Verizon is wiring throughout the rest of upstate New York. If the company cannot meet the needs of customers in their largest service area, what in the world makes you think they’ll do it for us?
- The company has been fined twice by the New York State Attorney General for dubious business practices, costing consumers hundreds of dollars the company has now agreed to return to those customers;
- A broadband service for our community’s future should not come with a 5 gigabyte monthly limit attached in the fine print. How can our community compete in the digital economy if you have to ration your broadband usage to an unprecedented level in wired broadband?
- The devil is always in the details. Verizon has an aggressive plan to stay relevant in a digital future, with video, telephone, and Internet service running across advanced fiber optic lines. Frontier has a plan to serve rural communities with yesterday’s technology. Frontier’s vision for video is to “get a satellite dish” and rely on the existing aging copper wiring to do everything else.
- What kind of service and growth can we expect from a company mired in debt? As seasoned Verizon employees in our community start retiring, understanding the writing on the wall, what do they know that you and I don’t?
- Phone companies are a regulated utility, essential to the public interest. Why permit a risky deal that could ultimately lead to a taxpayer bailout to keep operations running if Frontier follows its predecessors into bankruptcy, all while Verizon walks away with billions in proceeds?
You can locate the names and contact information for your state representative(s) on Congress.org simply by entering your zip code. When calling or writing, always be courteous, and request that your representative respond in writing to your concerns, and share with Stop the Cap! any correspondence you receive in reply. As always, we’ll be holding elected officials accountable.
Your next contact must be with your state public utility commission. If a hearing is planned in your community, share your views in person and feel free to point them here if they want to watch how bad telecommunications deals have unfolded in the past. We have countless hours of news reports archived for their viewing pleasure. Each state has a different procedure for contacting them. In West Virginia, for example, consumers can call the Commission at 1-800-642-8544. Ohio residents can fill out an online form.
Perhaps Frontier can one day take on a transaction like this, but only after it can demonstrate it has the resources and willingness to provide customers with better options for service. Had they done that in our community, local residents would not have taken to signing a petition for Verizon to overbuild, or buyout Frontier’s Rochester operation. Local residents want the advantage fiber optic service can bring our community and its local economy, some even expressing a willingness to send $10 and $20 checks to Verizon for an acquisition fund to get the sale done. When consumers give money to the phone company when they don’t owe anything, that should be a clear signal consumers are dissatisfied and want a change Frontier, thus far, has not provided.
There are more videos below the jump….


 Subscribe
Subscribe


