
Sen. Lee
Several key Republicans are backing a corporate-friendly measure that would hurry the Federal Trade Commission, the Department of Justice, and the Federal Communications Commission through merger reviews, likely leading to less scrutiny of multi-billion dollar merger and acquisition deals that could ultimately cost consumers billions.
Retiring Sen. Orrin Hatch (R-Utah), Mike Lee (R-Utah), Thom Tillis (R-N.C.) and Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa) are the key backers of the “Standard Merger and Acquisition Reviews Through Equal Rules (SMARTER) Act,” a bill that would amend the Clayton Act and Federal Trade Commission Act to align the standards and processes for the Federal Trade Commission’s (FTC) and Department of Justice’s (DOJ) review of proposed mergers and acquisitions. The SMARTER Act claims it will eliminate bottlenecks that sometimes hold up merger reviews at the DOJ and FTC, and require agencies like the FCC to speed up merger reviews.

Sen. Hatch
Republicans claim corporations are being unfairly treated by excessive regulator scrutiny and delays of merger and acquisition transactions. Because different agencies have their own procedures about reviewing such deals, and federal agencies like the FCC are likely to put deals on hold when companies stonewall the Commission over document requests, Republicans are complaining about bureaucratic holdups. Supporters also claim that current delays associated with merger reviews “fuel politicization” of deals by politicians, consumer groups and media personalities, giving them time to organize public opposition and mount coordinated challenges.
Without a fully enforced shot clock, the FCC “creates uncertainty for transacting parties and effectively enables the FCC to evade judicial review,” bill supporters add.
The FCC already has a limit on open-ended merger reviews — its 180-day “shot clock” that requires mergers be approved or denied within six months. The FCC’s shot clock carried some built-in protection for its integrity, however, by including the power to pause the clock if companies attempted to “run out the clock” by slow-walking requested documents or stonewalling the Commission on other requests. The SMARTER Act would make it easier for companies facing a difficult review to wear down regulators by stripping away the agency’s power to put its shot clock on hold. Instead officials at the FCC would be required to make frequent trips to court to win permission from a judge to stop the clock while waiting for receipt of documents or reviewing merger objections. If the merger is ultimately turned down, the Republican bill also offers corporations the opportunity to streamline any court challenge by eliminating the step of first holding a FCC administrative law judge hearing.
Republicans have overwhelmingly favored The SMARTER Act, with Democrats almost universally opposed. In the previous Congress, House Republicans voted nearly unanimously for the bill. But the bill died after facing opposition in the then Democratic-held Senate. This term, Republicans control all branches of the federal government, giving the bill a better chance of becoming law.

Sen. Tillis
The SMARTER Act is heavily favored by the country’s top telecommunications companies, many that would directly benefit from its passage. No company would stand to benefit more than AT&T, which has seen several high-profile merger and acquisition cases fall apart before regulators. The bill strips away several layers of antitrust protection for consumers that were used to stop several multi-billion dollar telecom company mergers, and scared off others from trying.
The DOJ was instrumental in stopping AT&T’s acquisition of T-Mobile, and combined skepticism by the FCC and the DOJ forced Comcast to withdraw its proposed acquisition of Time Warner Cable. If the SMARTER Act becomes law, internal agency reviews of challenges to a merger will be eliminated. Merger opponents will have to file challenges to mergers in federal court instead. Such a law would have offered AT&T a dramatically better chance that its merger with Time Warner, Inc., would have been approved months ago without a court proceeding.
Two of the Republican FCC commissioners issued statements applauding the proposed legislation.
“Among other improvements, the bill includes two key reforms to the FCC’s merger review process that I have longed championed: setting a non-aspirational, 180-day shot clock for agency review of license transfers and addressing the abusive practice of designating an application for hearing to the Administrative Law Judge (ALJ), which effectively serves to kill a transaction,” wrote Commissioner Michael O’Rielly. “Applicants deserve a timely, complete, fact-based, and straightforward answer from the Commission – not one built on interminable delays or shady denials.”
“I applaud Senator Lee for working to ensure that good government is the law of the land,” said FCC Commissioner Brendan Carr. “With the SMARTER Act, Senator Lee would put the Federal Communications Commission on a shot clock and thus codify the agency’s commitment to open, transparent, and timely decision making.”
Although supporters of the measure claim it will eliminate disparate treatment of mergers and speed their review, critics contend the bill is a “solution in search of a problem.”
The American Antitrust Institute slammed the bill as lacking any foundation to prove its case. AAI conducted an exhaustive review of merger deals that came before the DOJ or FTC and found very few companies ever ran into opposition of their merger deals in the first place. From 2001-2014, businesses enjoyed a 97.5% chance their deals would be approved without challenge and a 96.7% chance their mergers or acquisitions would be approved without a second request.

Sen. Grassley
“The enforcement data suggest many things, but one of them is definitely not what the SMARTER Act purports to cure: an ‘unfairness’ caused by differences in standards and procedures at the FTC and DOJ,” wrote Diana Moss, president of AAI. “On the contrary, the SMARTER Act would create uncertainty and new litigation to solve a problem that, empirically, does not exist.”
Critics of the measure suspect the Republicans have a larger agenda in mind – curtailing government and regulatory oversight of public interest antitrust enforcement. AAI summarized their concerns:
First, the FTC’s use of administrative powers should be carefully safeguarded, because it has contributed critically to the effective shaping of U.S. merger policy without detracting from the speed or effectiveness of merger review.
Second, any difference in the preliminary injunction standard is more theoretical than real, and if a uniform standard is to be adopted, it should be the FTC’s standard, which allows the agency to obtain a preliminary injunction “[u]pon a proper showing that, weighing the equities and considering the Commission’s likelihood of ultimate success, such action would be in the public interest.”
Third, any change in the law may have harmful unintended consequences, including unnecessarily burdening the federal judiciary with new litigation over the meaning and value of the body of legal precedent involving merger cases brought by the FTC in federal court under the existing standard.
SMARTER Act by Senator Mike Lee on Scribd


 Subscribe
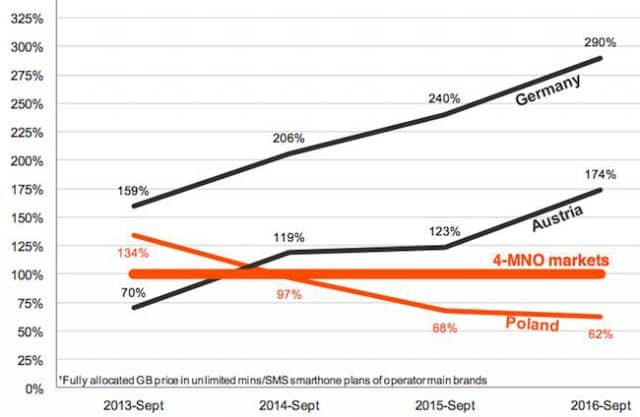
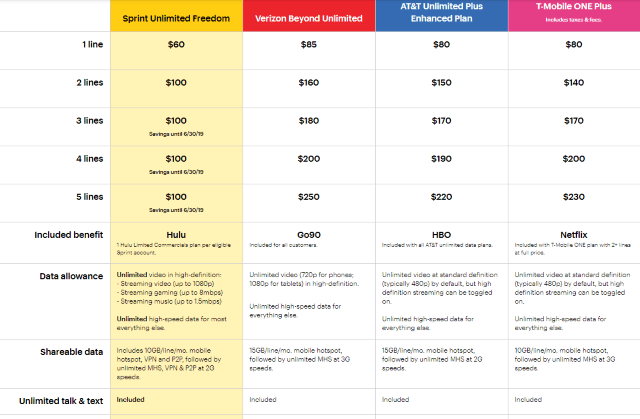
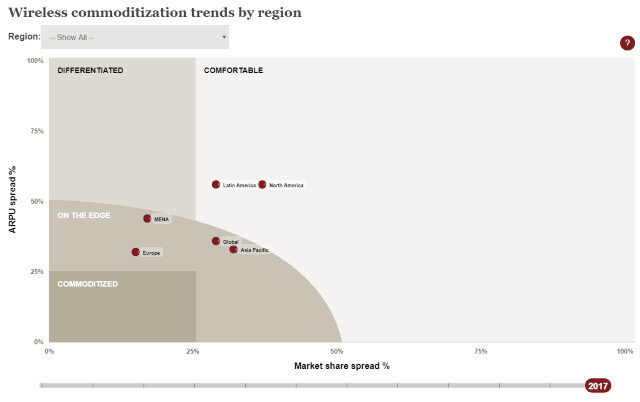
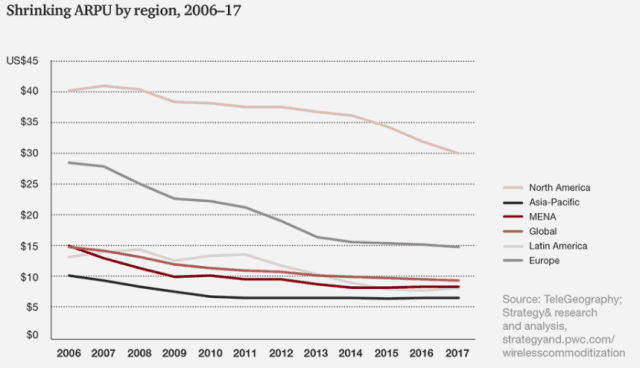
Subscribe Despite rosy predictions from Sprint and T-Mobile executives that the two companies joining forces will result in plentiful competition, lower prices, and more advanced service, the results of prior mergers in the wireless industry over the last 20 years delivered increasing prices, reduced innovation, and a lower customer service experience instead.
Despite rosy predictions from Sprint and T-Mobile executives that the two companies joining forces will result in plentiful competition, lower prices, and more advanced service, the results of prior mergers in the wireless industry over the last 20 years delivered increasing prices, reduced innovation, and a lower customer service experience instead. The two wireless industry giants initially ignored T-Mobile, suggesting CEO John Legere’s noisy and confrontational PR campaign had no material impact on AT&T and Verizon’s subscriber base and revenue. Ironically, Legere was named CEO one year after AT&T’s 2011 failed attempt to further consolidate the wireless industry with its acquisition of T-Mobile. A very generous deal breakup fee and accompanying wireless spectrum provided by AT&T after the deal collapsed gave T-Mobile some room to navigate and transform the company’s position — long the nation’s fourth largest national wireless carrier behind Sprint. It is now in third place, poaching customers from the other three, and has repeatedly forced other carriers to change their plans and pricing in response.
The two wireless industry giants initially ignored T-Mobile, suggesting CEO John Legere’s noisy and confrontational PR campaign had no material impact on AT&T and Verizon’s subscriber base and revenue. Ironically, Legere was named CEO one year after AT&T’s 2011 failed attempt to further consolidate the wireless industry with its acquisition of T-Mobile. A very generous deal breakup fee and accompanying wireless spectrum provided by AT&T after the deal collapsed gave T-Mobile some room to navigate and transform the company’s position — long the nation’s fourth largest national wireless carrier behind Sprint. It is now in third place, poaching customers from the other three, and has repeatedly forced other carriers to change their plans and pricing in response.

 In 2017, negotiations between the city of McAllen, Tex. and wireless companies over the cost of placing new wireless infrastructure neared agreement at $1,500 per network node, an amount not out of line with the kind of infrastructure fees being charged in other cities where utilities want to place their equipment in the public rights-of-way. But just before contracts were ready to sign,
In 2017, negotiations between the city of McAllen, Tex. and wireless companies over the cost of placing new wireless infrastructure neared agreement at $1,500 per network node, an amount not out of line with the kind of infrastructure fees being charged in other cities where utilities want to place their equipment in the public rights-of-way. But just before contracts were ready to sign, 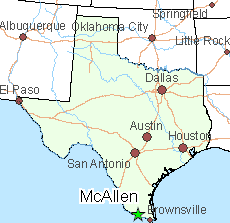 Bennett Sandlin, executive director of the Texas Municipal League, called that an “unconstitutionally low amount of money.”
Bennett Sandlin, executive director of the Texas Municipal League, called that an “unconstitutionally low amount of money.”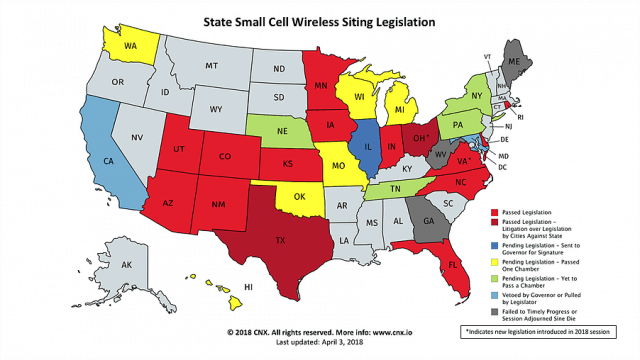

 He is the second major public official to call it quits on FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s Broadband Deployment Advisory Committee. In January, San Jose Mayor Sam Liccardo
He is the second major public official to call it quits on FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s Broadband Deployment Advisory Committee. In January, San Jose Mayor Sam Liccardo 
 “I shouldn’t have been surprised to learn industry completely re-wrote proposed broadband legislation to their favor as a ‘substitute bill’ in legislative committee today,” Orr wrote on her Facebook page on Feb. 19. “The substitute bill is substantially different than the original bill. And it wasn’t posted online or anywhere for anyone except insiders to have access to. CenturyLink and Spectrum are bullies. It’s wrong, and they are hurting Cheyenne and other Wyoming communities from gaining affordable access.”
“I shouldn’t have been surprised to learn industry completely re-wrote proposed broadband legislation to their favor as a ‘substitute bill’ in legislative committee today,” Orr wrote on her Facebook page on Feb. 19. “The substitute bill is substantially different than the original bill. And it wasn’t posted online or anywhere for anyone except insiders to have access to. CenturyLink and Spectrum are bullies. It’s wrong, and they are hurting Cheyenne and other Wyoming communities from gaining affordable access.”